Mayo Clinic faced a challenge that would make any healthcare executive lose sleep. In January 2025, they expanded their AI documentation partnership with Abridge to serve 2,000 clinicians treating around a million patients. But here’s what makes this remarkable: they’re doing it while maintaining some of the strictest data governance standards in healthcare.
Mayo Clinic has built internal accountability systems for safe, effective, and ethical implementation of artificial intelligence in medical practice. Their approach demonstrates how robust governance frameworks enable innovation rather than blocking it. When data governance works properly, organizations can pursue cutting-edge technologies without compromising patient safety or regulatory compliance.
This transformation didn’t happen overnight. Mayo Clinic’s Center for Individualized Medicine underwent digital transformation to equip clinicians with tools to analyze data and unlock critical insights for patient care. The result? Enhanced diagnoses, improved treatments, and better patient outcomes across their entire health system.
Healthcare organizations today manage exponentially more data than ever before. Healthcare data alone is projected to reach 10,000 exabytes by 2025. Without proper governance, this massive volume becomes a liability rather than an asset.
Ready to transform your healthcare organization’s data strategy like Mayo Clinic?
Schedule a consultation to explore governance solutions tailored to your specific needs.
The Real Cost of Poor Healthcare Data Governance
VillageCareMAX discovered this truth the hard way. Before implementing proper governance, their healthcare plan struggled with data integrity issues that undermined decision-making confidence. Duplicate patient records created billing confusion. Incomplete medical histories frustrated physicians. Outdated information led to inappropriate care recommendations.
The numbers tell a sobering story about industry-wide governance failures. Provider directories are inaccurate 49 percent of the time according to Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services data. When patients get referred to out-of-network specialists unnecessarily, everyone loses. Patients face higher costs and delayed care. Healthcare systems lose revenue and patient trust.
But the real cost isn’t financial. It’s human.
Consider what happens when a patient arrives at an emergency department with chest pain. Without proper data governance, the attending physician might not have access to the patient’s complete cardiac history. Previous EKGs remain trapped in a cardiology system. Medication lists sit incomplete in a primary care database. Lab results from last month never integrated properly.
The physician makes treatment decisions based on incomplete information. That’s not clinical incompetence—that’s governance failure.
How Effective Governance Transforms Patient Care
Organizations that implement comprehensive governance frameworks don’t just avoid problems—they create competitive advantages that directly benefit patients.
Clinical Decision Support Revolution
Strong governance enables physicians to make better decisions faster. When patient data flows smoothly between systems, clinical decision support tools can provide real-time alerts about drug interactions, allergy conflicts, and evidence-based treatment recommendations.
Michelle Hoiseth, Chief Data Officer of Parexel, explained how proper governance helps leverage data from electronic medical record systems, claim systems, and pharmacy claims systems to see the impact of new treatments. This comprehensive view transforms research capabilities and patient care quality simultaneously.
“…as we move into leveraging new sources of data, it’s on us to be able to look any patient in the eye and say, ‘We’ve done the best job we can here. We stand behind this result and the analysis, and that’s us all coming to the table together.’”
- Michelle Hoiseth, Chief Data Officer of Parexel
Consider a diabetic patient visiting multiple specialists. With proper governance, the endocrinologist sees recent lab values from primary care. The cardiologist accesses blood pressure trends from home monitoring devices. The ophthalmologist reviews previous retinal screening results. Each specialist makes informed decisions based on complete information rather than isolated snapshots.
Population Health Management Excellence
Governance frameworks enable population health initiatives that identify at-risk patients before they require expensive interventions. Organizations can analyze patterns across large patient populations to predict which individuals need preventive care, medication adjustments, or lifestyle interventions.
These capabilities proved invaluable during COVID-19. The World Economic Forum highlighted that accurate and trustworthy data helped with disease control tasks, including predicting illness spread, identifying infection clusters, and tracking carrier contacts. Organizations with strong governance responded more effectively to the pandemic while maintaining routine care quality.
Operational Efficiency Gains
Healthcare margins remain tight, making efficiency improvements essential for sustainability. A hospital that centralizes its data management can reduce costs associated with managing multiple fragmented systems, freeing up resources for patient care.
The math works beautifully. Through referential and probabilistic modeling methods, a repository with data from 7 million patients could be trimmed to 1 million patient records. Organizations reduce storage costs, improve system performance, and eliminate the administrative overhead of managing duplicate information.
Staff productivity improvements provide measurable benefits. When nurses can quickly access complete medication histories, they spend more time with patients and less time searching through multiple systems. When physicians receive automated alerts about critical lab values, they respond faster to urgent situations.
Ready to transform your healthcare organization’s data strategy?
Schedule a consultation to explore governance solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Navigating the 2025 Regulatory Environment
Healthcare data governance operates within an increasingly complex regulatory framework. Recent changes require immediate attention from compliance teams and technology leaders alike.
HIPAA Security Rule Revolution
The HHS Office for Civil Rights proposed the first major update to the HIPAA Security Rule in 20 years on January 6, 2025. This update specifically addresses AI integration challenges that didn’t exist when the original rule was written.
The new requirements focus on several critical areas that organizations must address immediately:
Organizations using AI systems that process protected health information must implement documented security and privacy controls. Regular AI audit procedures become mandatory for healthcare providers. Algorithmic bias testing and mitigation protocols must be established before AI deployment.
Enhanced third-party vendor oversight requirements apply to all AI systems accessing patient data. Organizations can no longer treat AI vendors differently from traditional business associates.
These changes reflect regulatory recognition that AI represents both tremendous opportunity and significant risk in healthcare settings. Organizations that proactively address these requirements will have competitive advantages over those scrambling to achieve compliance.
State-Level AI Regulation Complexity
2025 brings new state laws on AI regulation with varying privacy protections across different healthcare contexts. Organizations operating across multiple states face complex compliance matrices that require sophisticated governance approaches.
Some states focus on algorithmic transparency requirements. Others emphasize bias testing and patient notification obligations. Still others mandate specific security controls for AI systems processing health information. The patchwork creates challenges that centralized governance frameworks must address systematically.
Multi-state healthcare systems need governance policies that meet the most stringent requirements across all jurisdictions while maintaining operational efficiency. This often means implementing controls that exceed minimum requirements in some states to ensure consistent compliance everywhere.
International Compliance Considerations
The General Data Protection Regulation affects healthcare organizations serving EU citizens, regardless of where the organization is located. French authorities fined Dedalus Biologie, a medical software company, 1.5 million euros in 2021 for GDPR non-compliance due to inadequate security measures.
Healthcare organizations with international patients or research collaborations must integrate GDPR requirements into their governance frameworks. This includes explicit consent mechanisms, data portability rights, and strict breach notification procedures that don’t interfere with clinical workflows.
Microsoft Fabric Adoption: A Practical Guide for Enterprises
Cut through the noise—learn how to adopt Microsoft Fabric with practical steps that actually work for enterprises.
Essential Technical Capabilities to Ensure Data Governance in Healthcare
Building effective governance requires specific technical and operational capabilities. Organizations need more than good intentions and policy documents to manage healthcare data effectively.
Intelligent Data Discovery and Cataloging
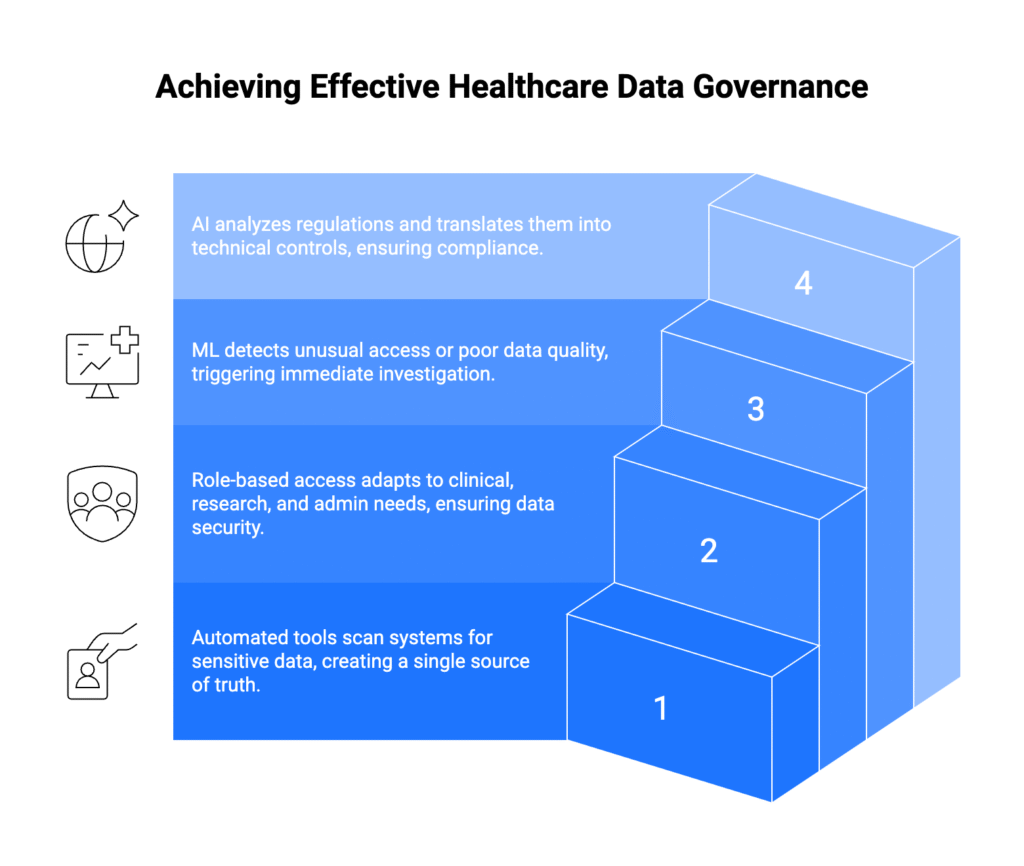
Modern healthcare organizations generate data faster than humans can catalog it manually. Automated discovery tools identify sensitive information across all organizational systems, creating comprehensive inventories that support both compliance and clinical operations.
An enterprise data catalog acts as the central nervous system for healthcare data governance. When a physician searches for a patient’s cardiac history, the catalog instantly surfaces relevant records from cardiology visits, emergency department encounters, and routine primary care appointments.
Automated metadata harvesting ensures catalogs remain current as systems change and data grows. Machine learning algorithms classify new data types and suggest appropriate governance controls based on sensitivity levels and usage patterns.
Advanced Access Control Systems
Healthcare requires more sophisticated access controls than traditional business environments. Emergency situations demand immediate data access for patient safety. Research applications need de-identified datasets. Billing departments require financial information without clinical details.
Role-based access control systems adapt to these complex requirements. Emergency department physicians can access complete patient records during critical situations. Research staff receive only de-identified data sets appropriate for their studies. Administrative staff see billing information without accessing clinical notes.
Automated access reviews prevent former employees from retaining system permissions. Time-based access controls ensure temporary staff receive appropriate permissions that expire automatically. Audit logs track every data interaction for compliance documentation.
Real-Time Monitoring and Incident Response
2024 saw a spike of interest in third-party risk management as security events dominated headlines. Healthcare organizations need governance frameworks that detect and respond to threats immediately rather than discovering problems during annual audits.
Modern monitoring systems use machine learning to identify unusual access patterns, potential data quality issues, and security threats. When a staff member attempts to access an unusually large number of patient records, the system flags the activity for review. When data quality metrics fall below established thresholds, relevant teams receive immediate notifications.
Real-time incident response capabilities prevent small issues from becoming major compliance violations or security breaches. Automated escalation procedures ensure appropriate stakeholders receive notifications based on incident severity and organizational protocols.
AI-Powered Policy Management
Artificial intelligence streamlines governance policy creation by analyzing existing organizational data, suggesting appropriate controls, and automating policy updates as regulations change. These capabilities become increasingly valuable as organizations manage larger datasets and more complex compliance requirements.
Natural language processing helps organizations parse regulatory documents and translate legal requirements into actionable technical controls. Machine learning algorithms automatically classify new data types and recommend governance policies based on similar existing datasets.
However, AI governance tools must themselves comply with healthcare regulations. Organizations need verification that AI systems processing patient data meet updated HIPAA requirements and undergo regular bias testing to prevent discriminatory outcomes.
Implementation Strategies That Deliver Results
Healthcare organizations typically fall into three categories when approaching governance implementation. Understanding which category applies helps determine the most effective implementation strategy.
The Foundation Builders
Some organizations start from scratch and need comprehensive frameworks. These organizations benefit from proven implementation methodologies that establish governance incrementally rather than attempting massive transformation overnight.
Shannon refers to a “one-time cleanup” as a common starting point for organizations improving their data repositories. This strategic preparation addresses decades of accumulated data inconsistencies before implementing new governance controls.
Through systematic cleanup processes, organizations often reduce their data footprint dramatically while improving quality. Duplicate records disappear. Incomplete information gets completed or removed. Outdated records from deceased patients are archived appropriately.
The Silo Breakers
Other organizations have basic governance structures but struggle with data silos across on-premises and cloud environments. These organizations need integration strategies that unite disparate systems without disrupting ongoing operations.
The challenge intensifies when clinical systems, administrative platforms, and research databases operate independently. Patient information exists in multiple places with different formats, quality standards, and access controls.
Successful silo integration requires careful planning and phased execution. Organizations must maintain system functionality while gradually implementing unified governance policies. Change management becomes critical as staff adapt to new workflows and data access procedures.
The Innovation Enablers
Advanced organizations want to scale existing governance for new applications like AI analytics and population health management. These organizations seek to become “enterprise-ready and future-proof” their governance investments.
Innovation enablers focus on emerging technologies that require high-quality, well-governed data. AI-powered clinical decision support, predictive analytics, and personalized medicine initiatives depend on comprehensive governance frameworks that ensure data reliability and regulatory compliance.
How to Choose the Right Technology for Healthcare Data Governance
Selecting the right technology for healthcare data governance is not just about features; it’s about finding a solution that ensures compliance, protects patient data, and supports everyday operations.
- Regulatory compliance – Ensure the technology supports HIPAA, GDPR, or other local healthcare regulations.
- Data security – Look for encryption, role-based access controls, and audit trails.
- Interoperability – The system should integrate with EHRs and other healthcare platforms.
- Scalability – Choose tools that can handle growing volumes of patient data.
- Ease of use – Staff adoption depends on intuitive design and simple workflows.
- Vendor support – Check for regular updates, responsive support, and training.
- Reporting and monitoring – Strong analytics and oversight features improve data governance.
Kanerika is a recognized leader in data governance solutions, enabling healthcare organizations to unlock better patient care through secure, accurate, and accessible data management systems. By partnering with Kanerika, hospitals and healthtech providers benefit from tailored frameworks, proven technologies, and real-world impact across operational, clinical, and compliance needs.
Kanerika’s Approach in Healthcare
Kanerika’s methodology centers on unifying fragmented records, establishing centralized data catalogs, and implementing cloud-based platforms for robust governance. Their layered approach spans data quality, security, interoperability, and compliance to meet HIPAA, GDPR, and local regulations. Leveraging tools such as Microsoft Purview, PowerBI, and automation frameworks, Kanerika empowers organizations with actionable insights, ensuring every patient’s information is managed with integrity and confidentiality.
Case Studies: Kanerika in Action
A global healthcare provider struggling with siloed systems partnered with Kanerika to revamp their architecture. By implementing cloud technologies and advanced governance, they streamlined data processing, improved patient self-care tools, and increased operational agility. The outcome included substantial reductions in response times and errors, with enhanced scalability for evolving medical needs.
A healthtech leader dealing with fragmented device tracking and operational inefficiencies adopted Kanerika’s Power BI-powered solution. The result was sharper insights, lower costs, and elevated patient safety through real-time analytics and seamless data integration.
In another case, Kanerika addressed poor data quality and inconsistent classification at a hospital by introducing a centralized data catalog. This not only cut report generation time by 45% but also boosted decision-making and data accessibility by over 90% and 70%, respectively.
Measurable Patient Care Benefits
Kanerika’s data governance solutions deliver:
- A unified patient record that provides clinicians a holistic view for informed treatments.
- Error reduction by ensuring data consistency and reliability across systems.
- Streamlined communication and collaboration for patients needing coordinated care between specialties.
- Real-time dashboarding and predictive analytics for proactive, personalized patient interventions.
Why Kanerika?
Partnering with Kanerika means leveraging deep expertise in data management, analytics, and automation. Their tailored governance frameworks help healthcare institutions strengthen compliance, maximize care quality, and foster innovation in an era of accelerating digital transformation. Kanerika’s commitment to ongoing support, staff training, and technology adoption ensures a sustainable, future-ready patient data ecosystem.
AI in Robotics: Pushing Boundaries and Creating New Possibilities
Explore how AI in robotics is creating new possibilities, enhancing efficiency, and driving innovation across sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 4 pillars of data governance?
Data governance rests on four key pillars: accountability (clear ownership and responsibility for data), compliance (adhering to regulations and policies), data quality (ensuring accuracy and reliability), and technology (leveraging tools to manage the data lifecycle). These pillars interlock; strong accountability enables effective compliance, leading to higher data quality and efficient technology usage. Ignoring any weakens the whole structure.
Why is data governance important in hospitals?
Data governance in hospitals is crucial for patient safety and operational efficiency. It ensures accurate, reliable patient information is readily available for better care, minimizing errors and improving outcomes. Strong data governance also aids in regulatory compliance and helps hospitals manage the ever-increasing volume of healthcare data effectively. Ultimately, it leads to improved decision-making and cost savings.
What are the 3 key roles of data governance?
Data governance ensures data quality, meaning accuracy and reliability are prioritized. It establishes clear accountability for data management, assigning responsibility and preventing data silos. Finally, it fosters compliance with regulations and internal policies, protecting sensitive information and avoiding legal issues.
What is data governance with example?
Data governance is like setting the rules and responsibilities for how an organization handles its data. It ensures data quality, security, and compliance. For example, a hospital might have data governance policies defining who can access patient records, how those records are stored, and how long they’re kept, all to protect privacy and ensure accurate medical information. This structured approach ensures data is used ethically and effectively.
What are the 3 key elements of good data governance?
Good data governance hinges on three crucial elements: accountability (clearly defining who’s responsible for data quality and compliance), transparency (ensuring data lineage and usage are readily understood), and consistency (applying standardized processes and policies across all data handling). These elements together foster trust and reliable insights from data.
What is the McKinsey data governance framework?
The McKinsey Data Governance Framework isn’t a single, rigid structure, but rather a flexible approach. It emphasizes aligning data strategy with business goals, ensuring data quality and accessibility across the organization. Essentially, it’s a roadmap for building trust and value from data by prioritizing ownership, processes, and technology in a holistic way. This differs from other frameworks by placing strong emphasis on achieving specific, measurable business outcomes through better data.
What are the four pillars of GDPR?
GDPR isn’t built on “four pillars” in a literal sense, but its core principles act like foundational supports. These include: lawfulness, fairness, and transparency; purpose limitation; data minimization; and accuracy. Essentially, it’s about processing data legitimately, responsibly, and only for specified, limited purposes, while keeping it accurate and minimizing what’s collected. These principles guide compliant data handling.
What is the PWC data governance framework?
PwC’s data governance framework isn’t a single, rigid structure, but rather a flexible approach tailored to client needs. It centers on establishing clear accountability, defining data quality standards, and implementing robust processes for data management throughout its lifecycle. Ultimately, it aims to ensure data is trustworthy, accessible, and used effectively to drive strategic decision-making. This involves a mix of technology, policies, and people.
What are the 4 pillars of big data?
Big data isn’t just about sheer volume; it’s defined by four key characteristics. These “pillars” are Volume (massive amounts of data), Velocity (speed of data influx), Variety (different data types), and Veracity (data accuracy and trustworthiness). Understanding these pillars is crucial for effectively managing and analyzing big data. Essentially, it’s about handling diverse, fast-flowing, massive, and reliable information.
What are the first four phases of data governance?
Data governance starts with defining the “why” – establishing clear objectives and accountability. Next, it’s about inventorying and understanding your existing data assets. Then, a crucial phase involves establishing policies and standards for data quality, security, and access. Finally, the initial implementation and enforcement of those policies lay the groundwork for ongoing governance.
What are the four key functional areas of data governance?
Data governance isn’t just about rules; it’s about *actionable strategy*. The four key areas are: defining data’s purpose and value (strategy), ensuring its quality and integrity (compliance), securing access and usage (security), and constantly improving processes (optimization). These areas intertwine to create a robust, trustworthy data ecosystem.
What are the 4 pillars of data analysis?
Data analysis rests on four key pillars: Data acquisition (getting the right information), data cleaning (handling messy realities), data exploration (uncovering patterns and insights), and data interpretation (drawing meaningful conclusions and communicating them effectively). These stages are iterative and interconnected, working together to transform raw data into actionable knowledge. Ignoring any weakens the entire process.
Why is data governance important in healthcare?
Data governance helps ensure that patient data is accurate, secure, and used responsibly. It reduces errors in medical records, supports compliance with laws like HIPAA/GDPR, and builds trust between patients and providers.
How does data governance improve patient care?
By setting clear rules for data quality and access, doctors and nurses can rely on consistent information. This means fewer duplicate tests, faster decisions, and better coordination across departments or hospitals.










