Data governance in banking is a fundamental aspect of effective data management in the financial industry. With data’s ever-increasing volume and complexity, banks must establish robust strategies and frameworks to ensure regulatory compliance, mitigate risks, and deliver exceptional customer service. This article will delve into the critical components of data governance in banking and explore its role in driving business outcomes. Moreover, we will discuss common challenges faced in implementing data governance strategies in the banking sector and provide best practices to overcome them.
Key Learnings
- Strong data governance is essential for modern banking, especially with rising data volumes, digital services, and real-time decision needs.
- Regulatory compliance drives governance maturity, with frameworks like BCBS 239, GDPR, PCI-DSS, and RBI/FDIC rules shaping how banks manage, protect, and report data.
- Modern governance requires the right architecture, including metadata management, lineage tracking, data quality controls, access control, and cloud-ready frameworks.
- Real-world case studies show tangible benefits, such as improved risk reporting (HSBC), stronger compliance (ING), and automated governance through cloud-native AI (Capital One).
- Future trends are moving toward AI-driven governance, real-time monitoring, automated policy enforcement, and cross-cloud interoperability for global banking operations.
Harness the Power of Data Governance for Security and Compliance
Partner with Kanerika Today.
What is Data Governance in Banking?
Data governance in banking is a critical process that involves managing, controlling, and accessing financial data within the banking industry. Additionally, it encompasses establishing policies, processes, and controls to ensure banking data’s accuracy, integrity, and security. The main objective of data governance in banking is to support the availability, accuracy, cleanliness, and high quality of data, enabling banks to offer their customers clear and easily understandable products and services.
Institutions must establish a comprehensive data governance framework to achieve effective data governance in banking. This framework outlines the guidelines and procedures for managing data, including data governance policies, data management processes, and data quality standards. By implementing a robust data governance framework, banks can ensure that data is consistently managed and utilized to align with regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
In the context of data governance in banking, data governance policies play a crucial role in defining the rules and procedures for data management. These policies serve as a roadmap for implementing data governance, covering various aspects such as data classification, access controls, data retention, data sharing, and data privacy. By adhering to these policies, banks can establish a strong foundation for data governance and ensure that data is handled securely and complies with applicable regulations.
How Data Governance Supports Business Outcomes in the Banking Industry
Data governance in the banking industry plays a vital role in supporting various business outcomes. From regulatory compliance to revenue growth, effective data governance strategies contribute to the overall success of banks. Here, we explore the key ways data governance supports important business objectives in the banking industry.
1. Regulatory Compliance
One of the primary benefits of data governance in banking is ensuring regulatory compliance. Banks operate in a highly regulated industry, and strict adherence to regulations is crucial for avoiding penalties and maintaining customer trust. Moreover, data governance provides a framework for effectively managing and protecting sensitive customer information. Ensuring compliance with privacy laws and facilitating transparency in reporting is crucial.
2. Risk Management
Data governance also plays a critical role in risk management within the banking industry. By establishing robust data governance practices, banks can identify and mitigate potential risks associated with data breaches, fraud, and cyber threats. Additionally, banks can enhance risk assessment capabilities and make well-informed decisions based on reliable data.
3. Operational Efficiency
Efficiency is key for banks to stay competitive and deliver exceptional customer service. Data governance enables operational efficiency by eliminating data redundancies, reducing errors, ensuring data consistency, and enabling efficient data processing. With a well-established data governance framework, banks can streamline data workflows and improve internal processes, leading to faster and more accurate decision-making.
4. Customer Experience and Innovation
Data governance in banking has a direct impact on customer experience and innovation. By maintaining high data quality standards, banks can provide personalized services, tailor marketing campaigns based on customer preferences, and offer seamless digital experiences.
5. Revenue Growth
Additionally, with access to clean and reliable data, banks can leverage advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to drive innovation, identify new growth opportunities, and deliver innovative products and services that meet customers’ evolving needs.
Regulatory Landscape for Banking Data Governance (300 words)
Banking operates in one of the most heavily regulated environments, and therefore, data governance must align with a wide range of global and local compliance rules. Below are the major regulatory frameworks and how they influence data governance practices.
Key Regulations Banks Must Follow
- BCBS 239 – Risk Data Aggregation & Reporting
This standard requires banks to maintain accurate, consistent, and timely risk data. Moreover, it emphasizes strong governance, lineage tracking, and auditability across all risk systems.
- GDPR – Data Privacy & Customer Rights
GDPR mandates strict controls on personal data, including consent, right to access, erasure, and data minimization. Consequently, banks must implement masking, encryption, and access control.
- PCI-DSS – Payment Card Security
This framework governs how cardholder data must be stored, transmitted, and processed. As a result, governance policies must include tokenization, restricted access, and secure logging.
- RBI Guidelines / FDIC / OCC / CFPB
These regional regulators require accurate reporting, strong operational resilience, fraud monitoring, and strict customer data protection. Therefore, banks must maintain full lineage, retention policies, and breach response processes.
- SOX – Financial Transparency & Auditability
SOX emphasizes accurate financial reporting and internal controls. Hence, banks must maintain traceable data, verified reports, and automated audit trails.
- AML/KYC Regulations – Anti-Money Laundering & Customer Screening
These rules require real-time monitoring of transactions, suspicious activity detection, and accurate customer identity verification. Thus, data must be complete, standardized, and continuously validated.
How Data Governance Enables Compliance
- Ensures audit readiness through lineage, logs, and evidence trails.
- Supports accurate regulatory reporting with validated, high-quality data.
- Enables automation of compliance checks and policy enforcement.
- Reduces penalties and operational risk by ensuring consistent data across all systems.
Data governance, therefore, acts as the foundation for meeting every major banking regulation effectively and efficiently.
Microsoft Fabric Vs Tableau: Choosing the Best Data Analytics Tool
A detailed comparison of Microsoft Fabric and Tableau, highlighting their unique features and benefits to help enterprises determine the best data analytics tool for their needs.
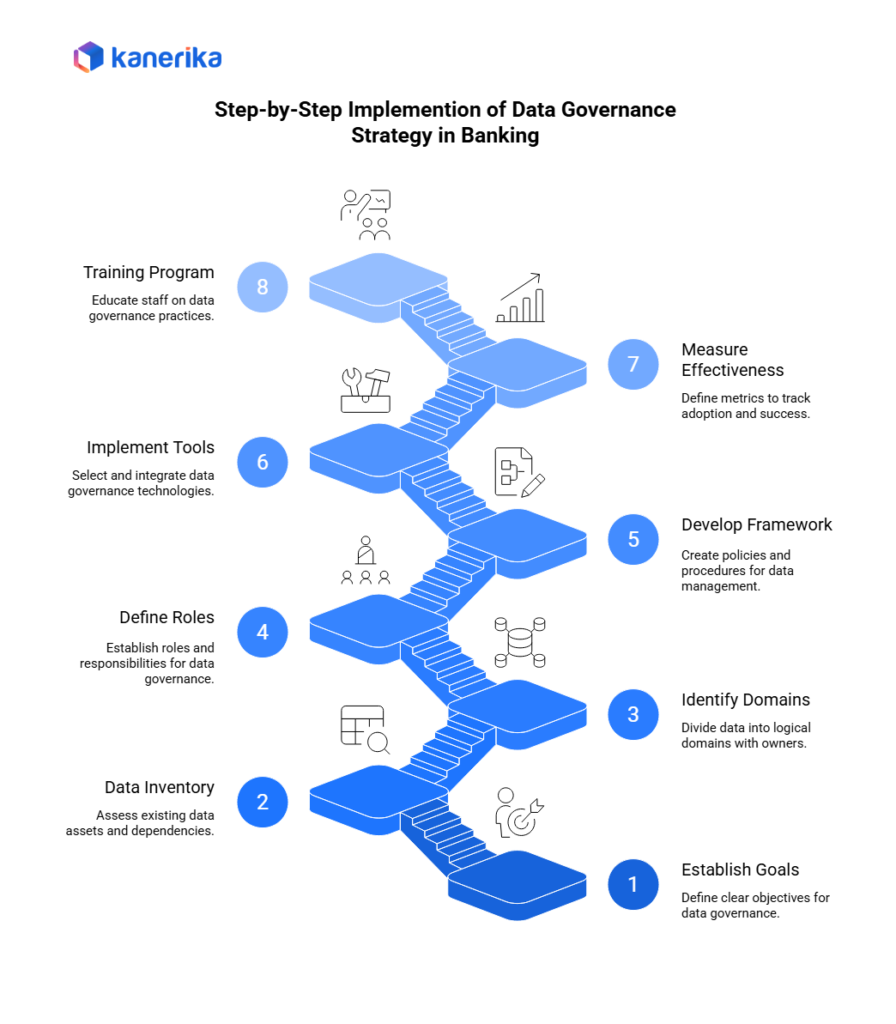
Implementing a Data Governance Strategy in Banking: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing a data governance strategy in the banking industry requires careful planning and execution. Here is a guide to help you navigate the process:
Step 1: Establish Clear Goals and Objectives
Start by defining the goals and objectives of your data governance strategy. Identify the specific outcomes you want to achieve, such as improved data quality, enhanced regulatory compliance, or increased operational efficiency. These goals will serve as the foundation for your entire data governance implementation.
Step 2: Conduct a Data Inventory Assessment
Perform a comprehensive assessment of your existing data assets. Identify the types of data you collect, store, and process. Moreover, determine the data sources, data flows, and data dependencies within your organization. This assessment will help you understand the scope and complexity of your data governance initiative.
Step 3: Identify Data Domains, Domain Owners, and Consumers
Divide your data into logical domains based on business functions or data categories. And assign domain owners responsible for overseeing the data governance within their respective domains. Identify the consumers of each domain, including teams or individuals who rely on the data for their work. This step ensures that data governance responsibilities are clearly defined and distributed across the organization.
Step 4: Define Data Governance Roles and Responsibilities
Establish a clear organizational structure for data governance. Define roles and responsibilities for data stewards, custodians, and other key stakeholders involved in the data governance process. Additionally, describe their responsibilities, decision-making authority, and accountability. This step helps ensure that everyone understands their roles and can effectively contribute to the data governance efforts.
Step 5: Develop a Data Governance Framework
Create a comprehensive data governance framework that outlines your organization’s policies, standards, and procedures for managing data. Define data governance processes like data quality management, metadata management, and access controls. Additionally, incorporate industry best practices and regulatory requirements into your framework to ensure compliance and consistency.
Step 6: Implement Data Governance Tools and Technologies
Select and implement data governance tools and technologies that align with your data governance framework. These tools can help automate data governance processes, facilitate data lineage tracking, and provide visibility into data quality and compliance. Moreover, choose tools that integrate well with your existing data management systems and support your data governance objectives.
Step 7: Define Metrics to Measure Adoption and Effectiveness
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to measure the adoption and effectiveness of your data governance strategy. Monitor data governance activities, such as quality improvements, compliance rates, and stakeholder engagement. Furthermore, regularly review these metrics to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and demonstrate the value of your data governance efforts.
Step 8: Develop a Training and Continuous Education Program
Invest in training programs and continuous education to build data governance awareness and enhance the data management skills of your workforce. Provide training on data governance policies, best practices, and tools. Foster a culture of data-driven decision-making and encourage employees to participate in ongoing learning and development opportunities.
Common Challenges in Implementing Data Governance in the Banking Industry
Data governance in the banking industry presents several challenges that organizations must overcome. These challenges include:
1. Insufficient high-level support: Lack of support from top management can hinder the establishment of a data governance framework and impede allocating necessary resources.
2. Internal resistance to cultural shifts: Implementing data governance requires a cultural shift, and employee resistance can hinder progress and adoption.
3. Segmented data and disparate systems: Banks often have fragmented data stored in disparate systems, making it challenging to establish centralized control and ensure data consistency.
4. Data quality issues: Inaccurate, incomplete, or inconsistent data can undermine the effectiveness of data governance efforts and impact decision-making processes.
5. Lack of data governance awareness: Many organizations have limited understanding and awareness of data governance concepts, which can hinder successful implementation.
6. Resource constraints: Limited budget, staffing, and technology resources can challenge establishing and maintaining a comprehensive data governance program.
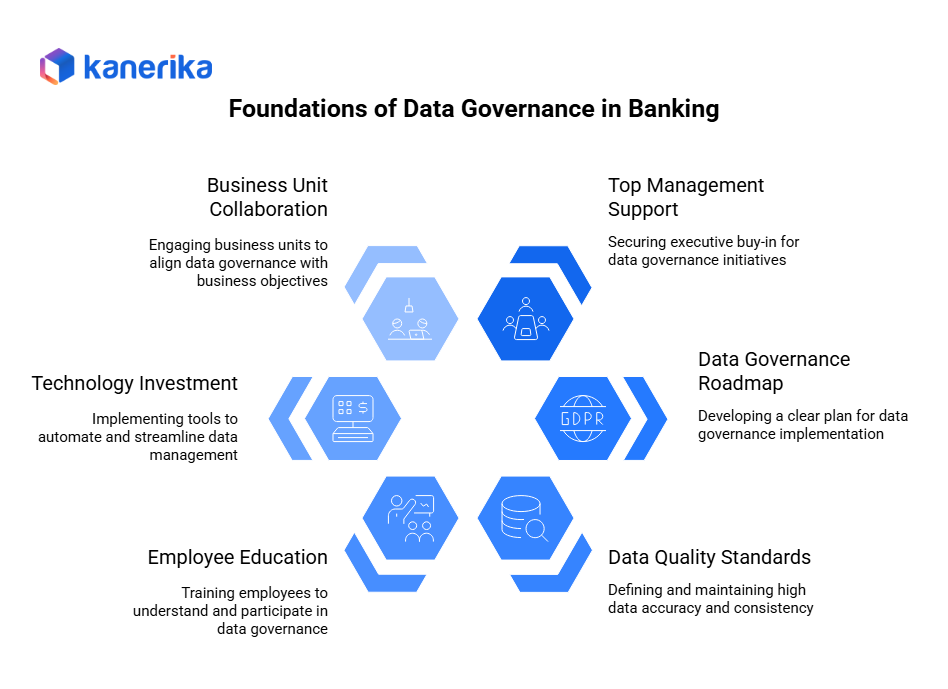
Key Solutions to Address Data Governance Challenges in Banking
To address the challenges faced in implementing data governance in the banking industry, organizations can adopt the following solutions:
1. Secure top management support: Gain buy-in from executives by emphasizing the importance of data governance and its impact on business outcomes.
2. Create a data governance roadmap: Develop a clear plan outlining the steps, activities, and timeline for implementing data governance.
3. Establish data quality standards: Define data quality measures and implement processes to monitor, validate, and improve data accuracy and consistency.
4. Educate and train employees: Conduct training programs to raise awareness about data governance, its benefits, and the role of employees in its implementation.
5. Invest in data governance tools and technology: Implement data governance software and platforms that automate and streamline data management processes.
6. Collaborate with business units: Engage business leadership to ensure their active participation in data governance initiatives and promote alignment with business objectives.
Real-World Case Studies
Banks across the world are investing heavily in modern data governance to improve compliance, reduce risk, and enable better decision-making. The following real case studies show how leading institutions are putting governance into action.
Case Study 1: HSBC – Enterprise Data Governance Framework
HSBC partnered with Collibra to build a unified data governance framework across its global operations. As a result, the bank significantly improved its ability to manage complex data assets, strengthen compliance, and standardize data definitions. Moreover, HSBC enhanced the quality and transparency of risk reporting by implementing lineage tracking and stewardship workflows. This move enabled faster regulatory reporting and reduced audit effort.
Case Study 2: ING – Governance for BCBS 239 Compliance
ING needed better control over its risk data to meet BCBS 239 obligations. Therefore, the bank redesigned its governance model to ensure accurate risk aggregation, complete lineage documentation, and consistent data across all risk domains. Through centralized data oversight and improved metadata management, ING strengthened its reporting accuracy and operational resilience. This approach also improved cross-team collaboration and reduced the time required for regulatory submissions.
Case Study 3: Capital One – Cloud-First Governance with AI
Capital One adopted a cloud-first strategy and built an AI-driven data governance system on AWS. Consequently, the bank automated metadata tagging, lineage extraction, and data classification at scale. This automation reduced manual effort, improved data discoverability, and enhanced security for sensitive financial data. In addition, Capital One’s governance model now supports real-time analytics, fraud detection, and consumer protection use cases.
Data Security Best Practices: Steps for Protecting Information
Implement key data security best practices like encryption, access control, and regular audits to safeguard sensitive information and prevent breaches.
Choose Kanerika for Advanced Data Governance Solutions
At Kanerika, we pride ourselves on delivering tailored, innovative solutions for your data governance needs. Our expertise lies in creating automated, integrated, and responsive data governance frameworks that enhance data quality and security while aligning perfectly with your business objectives. Therefore, by leveraging our proprietary consulting frameworks and composable solution architecture, we help you reduce operational costs and improve decision-making with confidence.
With our global presence and extensive experience across various industries, we bring best practices and insights from top brands worldwide to your organization. Moreover, our commitment to continuous improvement and client satisfaction ensures that your data governance initiatives are not only implemented successfully but also optimized for long-term success.
Strengthen Compliance and Security with Next-Gen Data Governance
Partner with Kanerika Today.
FAQs
What is data governance in banks?
Data governance in banks is the set of policies, processes, and technologies that ensure the accuracy, security, and proper use of financial data. It’s essentially about establishing clear ownership and accountability for all bank data to comply with regulations and safeguard customer information. This includes defining data quality standards, managing access rights, and tracking data lineage. Ultimately, it’s about building trust and minimizing risk.
What are the 4 pillars of data governance?
Data governance rests on four key pillars: accountability, ensuring clear ownership and responsibility for data; compliance, adhering to regulations and internal policies; data quality, maintaining accuracy and reliability; and security, protecting data from unauthorized access and breaches. These pillars work interdependently to ensure trustworthy and valuable data.
What are the 5 C's of data governance?
Data governance isn’t just about rules; it’s about cultivating a culture of trust and accountability around data. The 5 C’s – Compliance, Completeness, Consistency, Confidentiality, and Correctness – represent the pillars of this culture, ensuring data quality and ethical use. Each “C” works interdependently to build a robust and reliable data ecosystem. Think of them as the essential building blocks for trustworthy data management.
What does governance mean in banking?
In banking, governance is essentially the system of checks and balances ensuring responsible management. It dictates how banks are directed, controlled, and held accountable to stakeholders – from shareholders to customers and regulators. Strong banking governance minimizes risk, protects assets, and maintains public trust. Ultimately, it ensures the bank operates ethically and sustainably.
What is the main role of data governance?
Data governance ensures data quality and trustworthiness. It’s about establishing clear rules and processes for how data is handled throughout its lifecycle, from creation to disposal. This ultimately protects an organization’s reputation, ensures regulatory compliance, and supports better decision-making. In short, it’s about maximizing the value and minimizing the risk associated with data.
What is IT governance in banking?
IT governance in banking ensures technology supports business goals, manages risks, and complies with regulations. It’s essentially a framework for aligning technology strategy with the bank’s overall objectives, from cybersecurity to customer data protection. This involves setting clear responsibilities, policies, and processes across all IT functions. Ultimately, it’s about building trust and stability within the bank’s digital ecosystem.
What are examples of data governance?
Data governance isn’t just about rules; it’s about actively managing data’s entire lifecycle. Examples include defining who owns and can access specific data, establishing clear data quality standards (accuracy, completeness), and implementing processes for data security and privacy compliance. Ultimately, it ensures your data is reliable, trustworthy, and used responsibly.
What is called data governance?
Data governance is essentially establishing a set of rules and processes to manage an organization’s data effectively. It ensures data quality, consistency, and security, ultimately boosting trust and decision-making. Think of it as creating a roadmap for how data is used, accessed, and protected throughout its lifecycle. This includes defining roles, responsibilities, and policies for data handling.
What is data management in banking?
Data management in banking is the careful handling of all customer and financial information. It ensures accuracy, security, and regulatory compliance, which is crucial for preventing fraud and maintaining customer trust. This involves everything from storing transaction records securely to utilizing data for better risk assessment and personalized services. Ultimately, it underpins the entire banking operation.
What are the data domains in banking?
Banking data spans several key areas. It includes customer information (demographics, accounts), transactional data (deposits, withdrawals, loans), market data (interest rates, economic indicators), and operational data (internal processes, risk management). Understanding these domains is crucial for effective banking operations and compliance. These data types are interconnected and provide a holistic view of the bank’s activities and customer relationships.
What is data governance principle?
Data governance principles are the foundational rules guiding how an organization manages its data. They ensure data quality, consistency, and compliance, acting as a roadmap for data handling across the entire lifecycle. These principles dictate who can access, use, and modify data, fostering trust and accountability. Ultimately, they aim to maximize the value of data while minimizing risks.
What do you mean by bank governance?
Bank governance is essentially the system of rules, practices, and oversight that ensures a bank operates safely, soundly, and ethically. It involves the board of directors, senior management, and internal controls all working together to protect depositors’ money and maintain public trust. Good governance prevents mismanagement and promotes transparency and accountability. Ultimately, it’s about responsible leadership in the financial industry.