Consumer privacy has emerged as the bedrock of digital trust, dramatically influencing user confidence. For instance, Apple prioritizes user privacy through transparent data usage policies and secure encryption to protect users’ personal information. It significantly boosts consumer trust, highlighting the vital role of comprehensive data protection in forging strong, trustworthy digital connections. The introduction of stringent regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) marks a significant shift in how businesses approach data protection. GDPR and CCPA compliance are now critical benchmarks for businesses operating within and beyond the borders of Europe and California, underscoring the universal demand for transparency, security, and accountability in data handling practices.
Fundamentals of GDPR
If you are a business operating in the European Union (EU) or processing data of EU residents, you must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The GDPR is a comprehensive data protection law that came into effect on May 25, 2018, replacing the 1995 Data Protection Directive. Here are the key principles, data subject rights, and lawful basis for processing under the GDPR:
Key Principles
The GDPR is based on seven key principles that govern the processing of personal data. These principles are:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
- Purpose limitation
- Data minimization
- Accuracy
- Storage limitation
- Integrity and confidentiality (security)
- Accountability

Data Subject Rights
The GDPR provides data subjects with several rights that they can exercise against data controllers and processors. These rights include:
- Right to be informed
- Right of access
- Right to rectification
- Right to erasure (also known as the right to be forgotten)
- Right to restrict processing
- Right to data portability
- Right to object
- Right not to be subject to automated decision-making, including profiling

Lawful Basis for Processing
Under the GDPR, you must have a lawful basis for processing personal data. The lawful bases for processing are:
- Consent
- Contractual necessity
- Legal obligation
- Vital interests
- Public interest
- Legitimate interests
You must identify the lawful basis for processing personal data before you start processing it. Additionally, you must ensure that the processing is necessary, relevant, and proportionate to the purpose for which the data is being processed.

Fundamentals of CCPA
If you’re a business owner, it’s essential to understand the fundamentals of the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). This law gives California residents the right to know what personal information businesses collect about them and to request that the information be deleted. Here’s what you need to know about the CCPA.
Consumer Rights
Under the CCPA, California residents have the following rights:
- The right to know what personal information businesses have collected about them
- The right to request that businesses delete their personal information
- The right to opt out of the sale of their personal information
- The right to non-discrimination for exercising their privacy rights

Business Obligations
If your business collects personal information from California residents, you must comply with the following obligations:
- Provide notice to California residents about what personal information you collect, how it’s used, and with whom it’s shared
- Provide California residents with the right to opt out of the sale of their personal information
- Provide California residents with the right to request that their personal information be deleted
- Verify the identity of California residents who make requests to know, delete, or opt out
- Train employees who handle personal information on the requirements of the CCPA
- Update your privacy policy to comply with the CCPA.
Failure to comply with the CCPA can result in significant fines and legal action. Therefore, it’s essential to understand the law and take steps to ensure that your business is in compliance.

Compliance Roadmap
To ensure your organization is compliant with GDPR and CCPA, you need to follow a compliance roadmap. This roadmap includes several steps that you need to take to ensure that you are compliant with both regulations.
Data Mapping and Classification
The first step in the compliance roadmap is to identify all the personal data that your organization processes, stores, and transmits. You need to create a data inventory that includes all the personal data that you collect, where it is stored, who has access to it, and how it is used. You also need to classify the data based on its sensitivity and the risks associated with it. This will help you to determine the appropriate security measures that you need to implement to protect the data.

Privacy Notices and Policies
The second step is to review and update your privacy notices and policies to ensure compliance with GDPR and CCPA. Your privacy notice should be clear, concise, and easy to understand. It should explain what personal data you collect, why you collect it, how you use it, and who you share it with. It should also provide information about the individual’s rights, such as the right to access, rectify, and delete their personal data.
Data Protection Impact Assessments
The third step is to conduct a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA). A DPIA is a risk assessment that helps you to identify and mitigate the risks associated with processing personal data. You need to conduct a DPIA for all high-risk processing activities, such as processing sensitive data, using new technologies, or processing data on a large scale. The DPIA should identify the risks associated with the processing activity, evaluate the necessity and proportionality of the processing, and identify measures to mitigate the risks.

Vendor Management
The fourth step is to review and update your vendor management processes. You must ensure that your vendors also comply with GDPR and CCPA. Additionally, you must review your contracts with vendors to ensure they include appropriate data protection clauses.
Furthermore, conduct due diligence on your vendors to ensure they have appropriate security measures to protect the personal data they process on your behalf.
By following this compliance roadmap, you can ensure that your organization complies with GDPR and CCPA. This will help you protect your customers’ personal data and avoid costly fines and reputational damage.

Operationalizing Compliance
When it comes to operationalizing compliance with GDPR and CCPA, there are several key areas that you need to focus on. This includes training and awareness, data security measures, and incident response planning. By focusing on these areas, you can help ensure that your organization is fully compliant with these regulations.
Training and Awareness
One of the most important things you can do to operationalize compliance with GDPR and CCPA is to provide training and awareness to your employees. This should include training on how to handle personal data, as well as how to recognize and respond to data breaches. By providing this training, you can help ensure that your employees are fully aware of their responsibilities and obligations under these regulations.

Data Security Measures
Another key area to focus on when operationalizing compliance with GDPR and CCPA is data security measures. This includes implementing technical and organizational measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, and destruction. Some of the key data security measures that you should consider implementing include:
- Encryption of personal data
- Access controls to limit who can access personal data
- Regular security assessments and audits
- Monitoring of network activity to detect potential security breaches
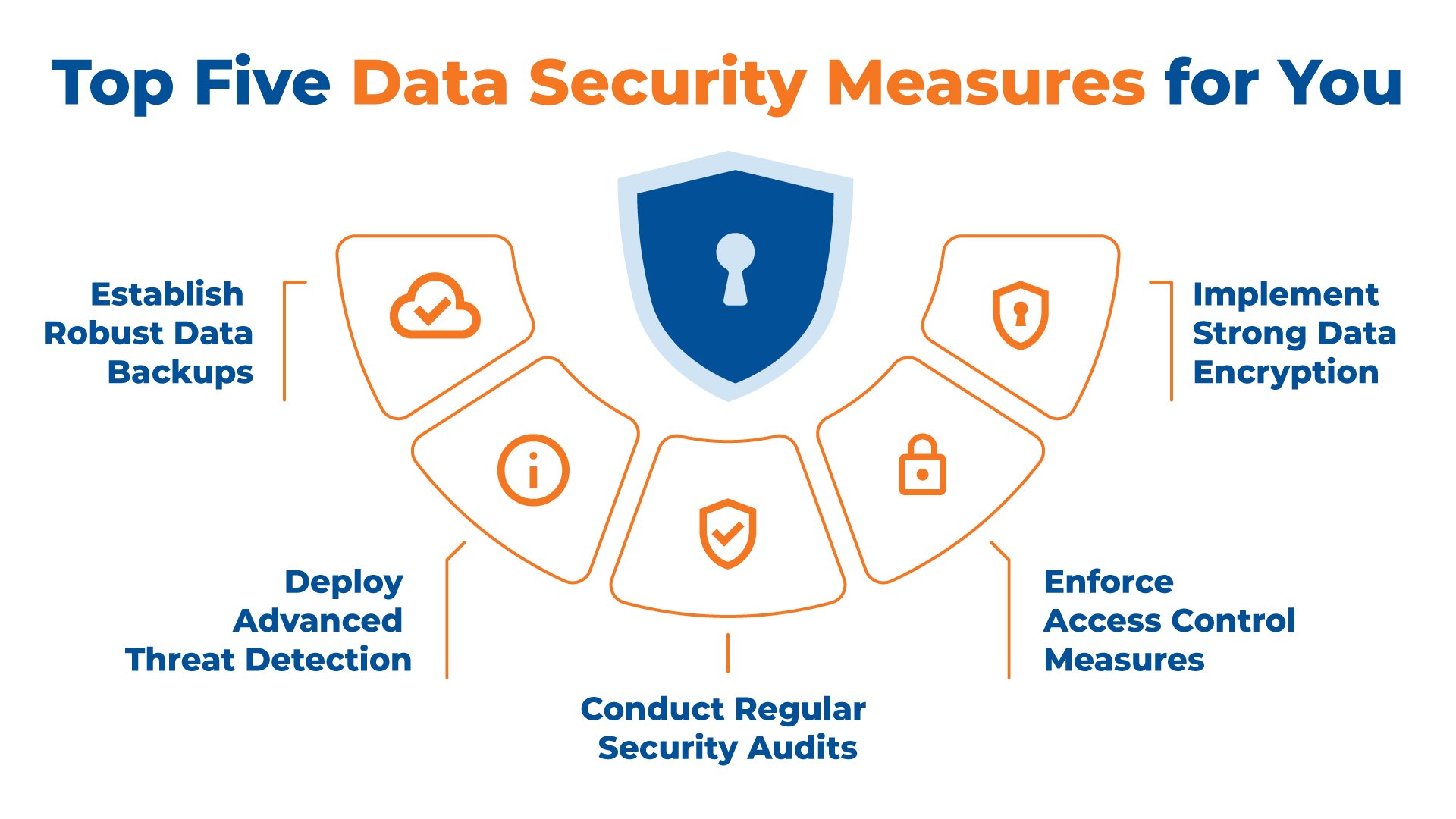
Incident Response Planning
Finally, it is essential to have an incident response plan in place in case of a data breach. This should include procedures for identifying and containing the breach and notifying affected individuals and regulatory authorities. By having an incident response plan in place, you can help ensure that your organization can respond quickly and effectively to any data breaches that may occur.
In conclusion, operationalizing compliance with GDPR and CCPA requires a focus on training and awareness, data security measures, and incident response planning. By implementing these measures, you can help ensure that your organization is fully compliant with these regulations and can protect personal data effectively.

Cross-Compliance Strategies
If your organization is already GDPR compliant, you are on the right track to becoming CCPA compliant. However, there are still some differences between the two regulations that you need to be aware of. Here are some strategies that can help you comply with both rules.
Similarities and Overlaps
There are some similarities between the GDPR and CCPA regulations that can help you comply with both. For instance, both regulations require you to provide data subjects with the right to access their personal data, the right to delete their personal data, and the right to opt out of the sale of their personal data. Therefore, if your organization has already implemented processes to comply with these requirements under GDPR, you can leverage those processes to comply with CCPA as well.

Harmonizing GDPR and CCPA Requirements
While there are similarities between the GDPR and CCPA, there are also some differences that you need to address. For example, CCPA requires businesses to disclose the categories of personal information that they collect, whereas GDPR requires businesses to disclose the purposes for which they collect personal data. Therefore, you need to harmonize these requirements to comply with both regulations.
One way to harmonize these requirements is to create a table that lists the categories of personal information that you collect and the purposes for which you collect it. This table can help you comply with both CCPA and GDPR requirements, as well as help you understand the data flows within your organization.
Another way to harmonize these requirements is to create a data inventory that lists all the personal information that you collect, store, and process. This inventory can help you understand the data flows within your organization, as well as help you comply with both CCPA and GDPR requirements.
By implementing these cross-compliance strategies, you can ensure that your organization is compliant with both GDPR and CCPA regulations.

Monitoring and Maintaining Compliance
Ensuring GDPR and CCPA compliance is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and maintenance. Here are some key considerations to help you stay on top of compliance requirements.
Audits and Assessments
Regular audits and assessments are essential to maintaining compliance with GDPR and CCPA. Conducting audits can help you identify areas where you may be falling short of compliance requirements, and assessments can help you determine the effectiveness of your compliance program.
During audits, it is important to review your data processing activities, data protection policies, and data breach response plans. You should also assess the adequacy of your data protection measures and identify areas where you may need to improve.

Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a key component of maintaining GDPR and CCPA compliance. You should regularly review and update your data protection policies and procedures to ensure they are up to date with the latest compliance requirements.
Continuous improvement can also involve implementing new technologies and tools to enhance your data protection measures. For example, you may want to consider implementing data encryption or data loss prevention tools to protect your data better.
Regular training and education for employees is also critical to maintaining compliance. Employees should be trained on data protection policies and procedures, as well as the importance of data privacy and security.
By implementing regular audits and assessments and continuously improving your data protection measures, you can help ensure ongoing compliance with GDPR and CCPA requirements.

GDPR vs. CCPA
When it comes to privacy regulations, GDPR and CCPA are two of the most well-known and important laws. While both laws aim to protect individuals’ personal data, there are some key differences between them.
Scope of Applicability
GDPR applies to all companies that process personal data of EU residents, regardless of the company’s location. CCPA, on the other hand, applies to companies that do business in California or collect personal information of California residents, regardless of the company’s location.
Definition of Personal Data
GDPR defines personal data as any information that can identify a natural person. CCPA defines personal information as information that identifies relates to, describes, is capable of being associated with, or could reasonably be linked, directly or indirectly, with a particular consumer or household.

Consumer Rights
Under GDPR, individuals have the right to access, correct, delete, and restrict the processing of their personal data. Individuals also have the right to data portability and to object to the processing of their personal data. CCPA grants consumers the right to know what personal information is being collected about them. It also gives them the right to request deletion of their personal information and the right to opt-out of the sale of their personal information.
Penalties
GDPR violations can result in fines of up to 4% of a company’s global annual revenue or €20 million, whichever is greater. CCPA violations can result in fines of up to $7,500 per violation.
GDPR vs. CCPA- A Table
| Aspect | GDPR | CCPA |
|---|---|---|
| Geographical Scope | Applies to entities processing the personal data of EU residents, regardless of the entity’s location. | Applies to for-profit businesses operating in California that meet certain criteria (e.g., revenue, data processing volume). |
| Personal Data Scope | Broad definition of personal data, including any information related to an identifiable individual. | Focuses on personal information that identifies, relates to, or could reasonably be linked with a particular consumer or household. |
| Rights of Individuals | Includes rights to access, rectification, erasure (right to be forgotten), restriction on processing, data portability, and objection to processing. | Includes rights to know, delete, and opt out of the sale of personal information. A right to non-discrimination for exercising their rights. |
| Opt-in/Opt-out | Requires prior consent for data processing with a clear affirmative action (opt-in). Specific conditions for children’s data. | Consumers have the right to opt out of the sale of their personal information. Opt-in consent is required for minors under 16. |
| Data Protection Officer | Mandatory for certain organizations to appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO). | No specific requirement for a DPO, but businesses must provide methods for consumers to exercise their rights. |
| Breach Notification | Requires notification within 72 hours of becoming aware of the data breach if it is likely to result in a risk to the rights and freedoms of individuals. | Requires businesses to notify consumers of data breaches but does not specify a strict timeframe. |
| Penalties | Severe penalties for non-compliance, including fines up to €20 million or 4% of the annual global turnover, whichever is greater. | Civil penalties for violations, with fines up to $7,500 per intentional violation and $2,500 per unintentional violation. Consumers can also bring private actions for certain breaches. |

Importance of Partnering with Data-Compliant Vendors
Partnering with data-compliant vendors is a pivotal strategy for businesses navigating the complex terrain of data privacy regulations. In an era where data breaches can lead to significant financial penalties and irreparable damage to reputation, choosing vendors that adhere to stringent data protection standards like GDPR and CCPA becomes essential. Such partnerships ensure that every aspect of data handling, from collection to processing and storage, aligns with global privacy laws, safeguarding sensitive information against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Furthermore, working with compliant vendors demonstrates a commitment to data security and privacy, fostering trust among customers and stakeholders. This not only helps in maintaining regulatory compliance but also enhances corporate integrity and customer confidence, key components for success in the digital marketplace.
Partnering with Kanerika: Your Pathway to Compliance
Kanerika emerges as an exemplary partner in this context, offering GDPR- and SOC-compliant (Service Organization Control Type 2) solutions tailored to businesses aiming for the highest standards of data privacy and security. Here’s how Kanerika stands out as your ideal data security partner:
- Expertise in Data Privacy Regulations: Kanerika’s deep understanding of GDPR, CCPA, and other data protection laws ensures that your business’s data handling practices are fully compliant.
- Robust Data Protection Solutions: Leveraging cutting-edge technologies and methodologies, Kanerika implements comprehensive data security measures tailored to your business’s specific needs.
- Transparent and Compliant Practices: Kanerika’s commitment to transparency and compliance is reflected in its clear privacy policies, consent management processes, and the appointment of experienced DPOs.
- Responsive DSAR Processing: Kanerika’s efficient handling of DSARs underscores its commitment to respecting individuals’ data rights.
- Continuous Compliance Monitoring: With regular reviews and updates of data protection policies, Kanerika ensures your business remains aligned with the latest regulatory requirements.

FAQs
What is GDPR & CCPA compliance?
GDPR (EU) and CCPA (California) are laws protecting personal data privacy. GDPR sets stricter, broader rules for companies handling EU residents’ data, while CCPA focuses on California residents’ rights regarding their personal information. Compliance means following these laws meticulously to avoid hefty fines and reputational damage. Essentially, both ensure individuals control how their data is used.
What is GDPR compliance?
GDPR compliance means following the EU’s strict rules on how businesses handle personal data. It’s about protecting individuals’ privacy rights by ensuring data is collected lawfully, securely stored, and only used for specified purposes. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, so it’s crucial for any organization dealing with EU citizens’ data. Think of it as a high bar for data protection and responsible handling of personal information.
What are the 7 main principles of GDPR?
GDPR’s core is about giving individuals control over their personal data. It achieves this through principles like lawfulness, fairness & transparency; purpose limitation (data only for stated reasons); data minimization; accuracy; storage limitation; and integrity & confidentiality. Finally, accountability ensures organizations are responsible for compliance. These collectively build a framework for ethical and responsible data handling.
What does the CCPA stand for?
CCPA stands for the California Consumer Privacy Act. It’s a landmark law giving California residents significant control over their personal data. Essentially, it’s about your right to know what information companies collect about you and how they use it. This empowers consumers to protect their privacy within California.
What is the full form of GDPR?
GDPR stands for General Data Protection Regulation. It’s essentially a comprehensive EU law designed to protect the personal data and privacy of individuals within the European Union and the European Economic Area. In short, it’s about giving people more control over their information.
What is the CCPA data privacy Act?
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a groundbreaking US law giving California residents more control over their personal data. It lets you know what information companies collect about you, demand they delete it, and opt-out of data sales. Essentially, it puts consumers in the driver’s seat regarding their digital footprint within the state. It’s a significant step towards greater online privacy.
What rights are introduced by GDPR and CCPA?
GDPR and CCPA both grant individuals more control over their personal data. GDPR focuses on broad data protection rights across the EU, including access, rectification, and the “right to be forgotten.” CCPA, specific to California, emphasizes the rights to know, delete, and opt-out of data sales. Essentially, both aim to empower individuals, but with slightly different scopes and approaches.
What is the fine for CCPA vs GDPR?
The CCPA and GDPR have vastly different penalty structures. CCPA fines focus on intentional non-compliance and can reach up to $7,500 per violation. GDPR penalties are significantly higher, potentially reaching €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover, depending on the severity and nature of the breach. Essentially, GDPR’s fines reflect its stricter enforcement and broader scope.
What is CCPA in accounting?
CCPA, or the California Consumer Privacy Act, doesn’t directly impact accounting *procedures* but significantly affects how businesses handle consumer data. It mandates transparency and consumer control over personal information, impacting how accounting firms manage client data and potentially influencing financial reporting related to data breach costs or compliance investments. Essentially, it’s about data privacy’s impact on the business, not the accounting *method*.
What is the US equivalent of the GDPR?
The US doesn’t have a single, unified law like the GDPR. Instead, it relies on a patchwork of federal and state laws, like CCPA in California, offering varying levels of data protection across different sectors. This makes a direct equivalent impossible, creating a more fragmented and often less comprehensive data privacy landscape. Think of it as many smaller pieces instead of one big puzzle.
What type of data should be secured?
Essentially, any data that could cause harm if exposed needs securing. This includes personally identifiable information (PII), financial details, intellectual property, and sensitive business data. The key is to assess the potential damage from a data breach – the higher the risk, the higher the security measures should be. Think about what could hurt your business or individuals if leaked.
What is GDPR and CPRA?
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is the EU’s comprehensive law safeguarding personal data privacy for its citizens. CPRA (California Privacy Rights Act) is a similar, but state-level, US law offering Californians strong data protection rights. Both aim to give individuals more control over their personal information, but differ in their scope and specific enforcement mechanisms. Essentially, they’re both about boosting data privacy, but one is global (GDPR) and one is California-specific (CPRA).
How many data protection principles are there?
There isn’t a single universally agreed-upon number of data protection principles. Different regulations and frameworks highlight varying aspects of data protection, resulting in different lists of principles. However, core concepts like fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, and data minimization consistently appear across most frameworks. The precise count depends on how broadly you define each principle.









