Enterprise RPA goes far beyond simple task automation. It’s a sophisticated business process automation methodology that employs software robots, or “bots,” to execute high-volume, repetitive digital tasks with the precision and reliability that large organizations demand. Unlike basic automation tools, enterprise-level RPA is architected specifically for the security, compliance, systems integration, and massive scale requirements that define modern enterprise operations.
What sets enterprise RPA apart is its remarkable accessibility. You don’t need coding expertise to configure RPA-driven workflows—if you can record a video on your smartphone, you can set up enterprise automations. Yet beneath this user-friendly interface lies robust infrastructure capable of orchestrating thousands of simultaneous automations while maintaining high availability and performance across global operations.
Transform Your Business with Automation!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Automation implementation Services
The Enterprise RPA Advantage: Three Deployment Models
Attended RPA: Human-Bot Collaboration
Attended RPA works alongside human employees, providing real-time assistance for interactive business processes. This model excels in customer service environments, IT helpdesks, and complex decision-making workflows where human oversight and intervention remain critical. The bot handles routine elements while humans focus on relationship-building and strategic thinking.
Unattended RPA: Autonomous Operations
Unattended RPA operates independently without human intervention, running based on pre-programmed triggers, data inputs, and schedules. Moreover, this model is ideal for back-office processes like data entry, financial reconciliation, IT system maintenance, and application integrations—delivering 24/7 operational continuity.
Hybrid RPA: The Best of Both Worlds
Hybrid RPA combines attended and unattended capabilities, enabling dynamic workflows where bots and humans collaborate seamlessly. Additionally, this adaptive approach reflects the reality of complex enterprise processes, delivering automated speed and efficiency alongside human judgment and creativity.
Benefits of RPA for enterprises

Transformational Business Benefits
Scale and Security Without Compromise
Enterprise RPA delivers rapid business process automation at massive scale while maintaining complete adherence to security and compliance requirements. Rather than weakening security, RPA actually strengthens it by deploying automations that protect sensitive data and eliminate risks associated with human error. The technology enables high-volume business processes to become elastic, handling any workload—planned or unplanned—in real time.
Productivity and Digital Transformation Acceleration
When combined with AI technologies, RPA becomes a cornerstone of digital transformation initiatives. Organizations experience immediate productivity gains from the speed, reliability, and precision of automated execution, while simultaneously freeing employees to focus on strategic, higher-value activities that drive innovation and growth.
Process and Cost Efficiencies Across Silos
RPA’s application-agnostic nature means it can seamlessly connect between software tools regardless of function or department. This capability eliminates technology silos without requiring changes to underlying systems, enabling enterprise-wide efficiencies and delivering substantial reductions in operating costs.
Guaranteed Compliance and Audit Readiness
For heavily regulated industries, RPA provides a compliance game-changer. Automated processes execute tasks exactly as prescribed every single time, generating complete, detailed audit trails of every action. This consistency enables industries like finance, healthcare, and life sciences to guarantee compliance while protecting sensitive data continuously.
Enhanced Employee Experience
By automating mundane, repetitive tasks, RPA frees human workers to engage in rewarding, fulfilling, and valuable work. Moreover, it helps in solving complex problems, making strategic decisions, and building meaningful relationships with customers and partners.
Industry-Specific Enterprise Applications
Financial Services: Precision at Scale
Financial services processes are natural candidates for RPA’s accuracy, security, and compliance capabilities. Customer onboarding becomes dramatically faster through automated data collection and verification. Furthermore, loan processing benefits from automated data entry and document verification for credit assessments, supporting faster decisions with higher accuracy. In regulatory reporting, RPA gathers and processes data while reducing human error and ensuring compliance requirements are consistently met.
Healthcare: Operational Excellence for Better Outcomes
Healthcare organizations use RPA to streamline administrative processes, reduce clinical workload, and support better patient care. Automation improves patient scheduling, speeds up claims processing, and ensures accurate data updates across electronic health record systems. This ensured accurate candidate evaluation, proper routing, and efficient candidate handling, ultimately enhancing the quality of hires, much as the attention to detail provided by the nursing essay writing service at Essaypro in delivering precise, well-structured academic support.

Manufacturing: From Factory Floor to Executive Suite
Manufacturing enterprises apply RPA throughout operations to reduce costs, improve productivity, and accelerate time-to-market. Inventory management automation monitors stock levels, handles reorders, and reconciles inventory to maintain optimal levels while preventing shortages or overstock situations. Order processing automation handles purchase orders, invoices, and shipment tracking with improved accuracy and faster fulfillment times. Quality control benefits from automated data collection and analysis for product inspections, ensuring compliance with standards while reducing manual oversight requirements.
Customer Service: Efficiency Meets Excellence
RPA transforms customer service by simultaneously increasing operational efficiency and improving customer satisfaction. Automated inquiry handling through intelligent chatbots responds to routine questions instantly or routes complex issues to appropriate agents. Ticketing and issue resolution systems automatically log complaints, categorize them, and route them to support teams, dramatically reducing response times. Customer onboarding becomes smoother and faster through automated data entry and verification processes.
How to Use DAX Calculated Columns & Tables in Microsoft Fabric
How to use DAX Calculated Columns and Tables inside Microsoft Fabric’s semantic model, explore practical use cases, and highlight where this functionality fits.
The AI-RPA Convergence: Next-Generation Automation
Modern enterprise RPA doesn’t operate in isolation—it works in concert with artificial intelligence to create Intelligent Automation platforms that handle increasingly complex business processes. This convergence represents a fundamental shift in automation capabilities.
Generative AI has revolutionized enterprise automation by enabling natural language automation assistance, auto-generation of functional automations, and self-healing automations that auto-recover from application changes. This advancement has cut execution failures by over 50% while dramatically accelerating the automation development lifecycle.
The emergence of AI agents represents the next frontier. These sophisticated systems harness large language models to make decisions, learn from data, interact through natural language, and take action to achieve business goals. At the process level, agentic workflows intelligently choose RPA bots to execute specific tasks, creating dynamic, adaptive automation systems that can handle unprecedented complexity.
RPA technology is constantly evolving, with vendors introducing new features and capabilities to improve the user experience and expand the scope of Automation. For example, some RPA software can now integrate with machine learning algorithms to improve decision-making and predictive capabilities.
AI for Startups: How to Leverage Artificial Intelligence to Grow Fast
How startups can tap into the power of AI, the tools they can use, the challenges to keep in mind, and some real-world examples.
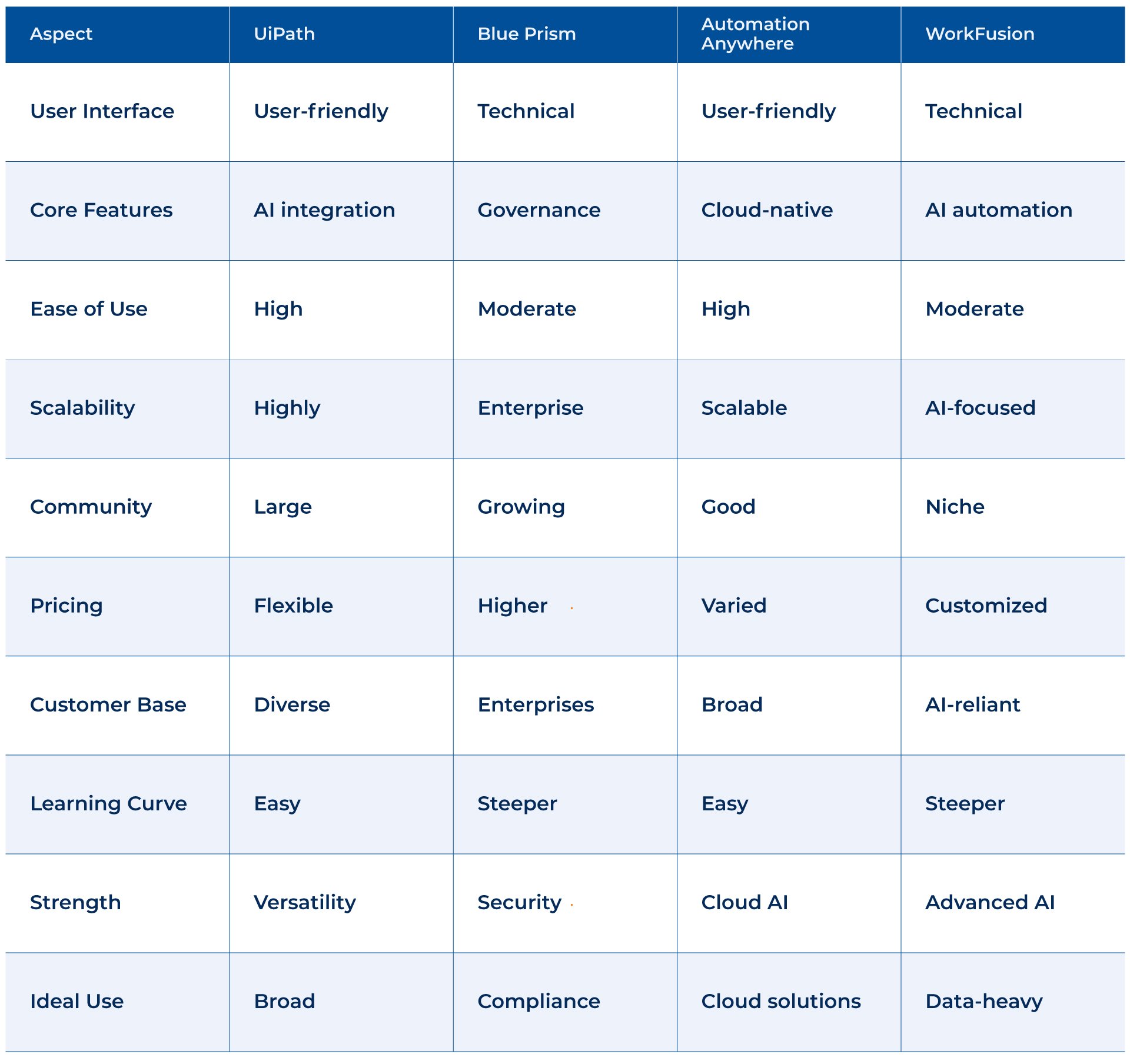
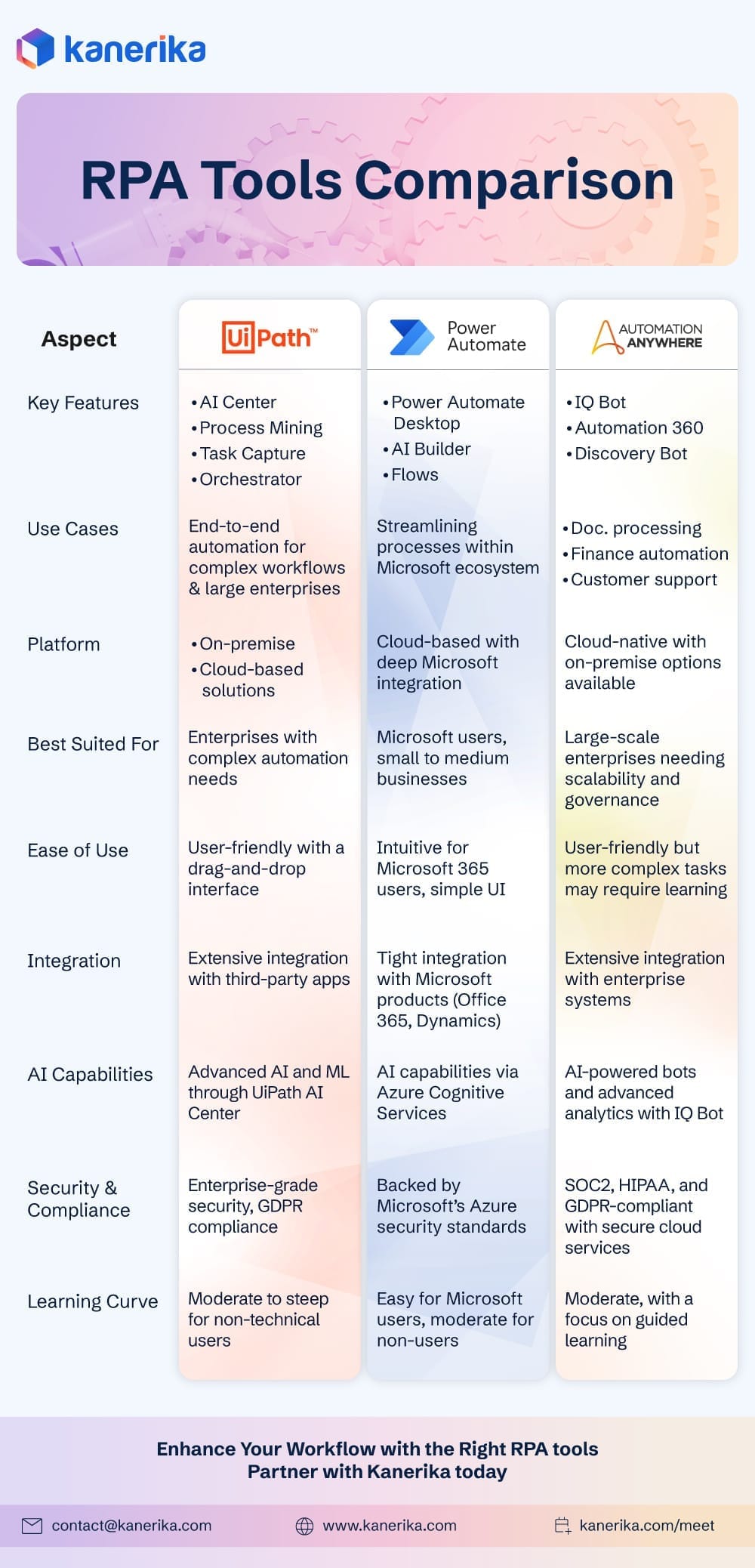
Key Players in the RPA Market
Many players in the RPA market range from prominent enterprise software vendors to specialized RPA startups. Some of the key players in the market include:
- UiPath is a leading RPA software vendor that offers a comprehensive platform for automating business processes.
- Automation Anywhere: another major player in the RPA market, offering various automation solutions for businesses of all sizes.
- Blue Prism: a UK-based RPA vendor that provides a scalable, secure, and centralized platform for automating business processes.
- WorkFusion is a cloud-based RPA platform combining RPA with machine learning and analytics to automate complex business processes.
Comparative Analysis of Enterprise RPA Products
Enterprise Deployment Strategy: A Roadmap to Success
1. Stakeholder Engagement from Day One
Successful enterprise RPA deployment begins with comprehensive stakeholder engagement. Involve HR early to address workforce concerns, bring in diverse voices from across departments, and identify automation champions who can influence change. Moreover, this inclusive approach shapes robust strategies and ensures organization-wide buy-in.
2. Establish a Center of Excellence
Create an organization-wide center of excellence (CoE) focused on effectiveness and governance. This hub establishes standards for compliance, security, and continuous improvement across the automation lifecycle. The CoE propagates best practices, tools, and templates while ensuring consistent, high-quality automations throughout the organization.
3. Strategic Vendor Selection
Choose a vendor that aligns with long-term automation and business goals. Evaluate solutions based on:
- Transparent Pricing Models: Avoid unexpected costs as deployment scales
- Continuous Innovation: Select vendors committed to advancing RPA capabilities
- Comprehensive Support: Ensure robust customer support and training programs
- Enterprise Security: Prioritize solutions with strong security architecture
- Flexibility: Choose platforms supporting both attended and unattended automation
- Accessibility: Look for low-code/no-code options enabling citizen developers
- Scalability: Ensure infrastructure can grow with expanding automation needs

4. Process-Focused Implementation
Begin with processes that yield the greatest ROI. Some organizations start small with attended automation, allowing workforce familiarization with RPA. However, the most successful enterprise deployments take comprehensive approaches, redesigning processes from scratch to fully incorporate automation tools and capture maximum value immediately.
5. Performance Measurement and Optimization
Implement robust KPI tracking and analytics systems to monitor bot performance, uptime, and ROI. Use this data continuously to optimize processes and refine automation strategies. Regular stakeholder feedback ensures automations evolve to address emerging opportunities and challenges.
Transform Your Business with Automation!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Automation implementation Services
Enterprise RPA- Challenges & Case Studies
Implementing RPA in an enterprise requires careful planning and execution. Identifying the right processes and workflows to automate and ensure that the RPA solution is integrated with other systems and applications is essential.
One effective strategy for implementing RPA is to start with a pilot project and gradually scale up. This allows you to test the solution in a controlled environment and identify any issues or challenges before rolling it out to the entire organization.
Another important consideration is to involve stakeholders from across the organization in the implementation process. This includes IT, operations, finance, and other departments the Automation may impact. By applying these stakeholders early on, you can ensure that the RPA solution is aligned with the overall digital transformation strategy of the enterprise.
In conclusion, leading RPA software providers offer a range of solutions that can help enterprises automate tasks and workflows. By evaluating these solutions based on your specific needs and requirements and following effective implementation strategies, you can achieve significant productivity, efficiency, and cost savings.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Learning from the success stories of other enterprises can help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure a successful RPA deployment. Here are a few case studies and success stories to inspire you:
- IBM: IBM used RPA to automate its finance processes, resulting in a 90% reduction in processing time and a 50% reduction in costs.
- Walmart: Walmart used RPA to automate its HR processes, resulting in a 70% reduction in processing time and a 40% reduction in costs.
- Accenture: Accenture used RPA to automate its invoice processing, resulting in a 70% reduction in processing time and a 90% reduction in errors.
The Future of Enterprise RPA
The RPA landscape continues evolving rapidly, with AI-driven advancements pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Enterprise solutions are maintaining market leadership by specifically designing for enterprise requirements, featuring extensive integrations, robust training programs, and the scalability to support massive use cases.
Looking ahead, the integration of RPA with AI agents and multi-agent systems promises to transform enterprise automation entirely. These systems will not just execute predefined tasks but dynamically adapt to changing business conditions, make intelligent decisions, and collaborate seamlessly with human workers to achieve business objectives.
Kanerika: Your Trusted Strategic Partner for RPA Implementation
As enterprises look to scale automation and drive meaningful transformation, having the right strategic partner can make all the difference. Kanerika stands out as a trusted expert in RPA implementation, having enabled numerous organizations to reimagine their processes through intelligent automation.
At Kanerika, our approach to automation is insight-driven and outcomes-focused. We begin by deeply understanding your unique business processes, identifying areas where automation can deliver maximum value. Then, leveraging a blend of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI), we craft a customized automation roadmap tailored to your specific goals—whether it’s enhancing productivity, improving compliance, or enabling innovation.
Our team of specialists brings years of experience and stays at the forefront of emerging technologies to ensure our clients benefit from the latest advancements. From rapid prototyping to full-scale deployment, Kanerika’s RPA solutions are built for scalability, resilience, and measurable impact.
Proven Success: Transforming Recruitment with RPA in HR
A powerful example of our impact can be seen in this case study, where we helped a leading HR firm streamline recruitment processes using RPA. By automating resume screening, interview scheduling, and candidate communication, the organization was able to reduce processing time by 70% and dramatically improve candidate experience—all without increasing headcount.
Whether you’re just beginning your automation journey or looking to scale enterprise-wide, Kanerika is the partner you can rely on for intelligent, future-ready automation solutions that drive real business transformation.
Transform Your Business with Automation!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Automation implementation Services
FAQs
How can RPA be used in business?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive, rule-based tasks across your business. Think of it as a digital workforce handling things like data entry, invoice processing, and customer service interactions – freeing up human employees for more strategic work. RPA boosts efficiency, reduces errors, and speeds up operations significantly, leading to cost savings and improved accuracy. Essentially, it’s about automating the mundane to unlock human potential.
What are the three types of RPA?
RPA isn’t neatly divided into just three types, but we can categorize it based on functionality. You have attended, where a human initiates and monitors the process; unattended, running completely autonomously; and hybrid, combining both approaches for optimal efficiency depending on the task’s complexity and need for human oversight. Essentially, it’s a spectrum of automation, not fixed categories.
What does RPA mean in business?
RPA, or Robotic Process Automation, is essentially having software “robots” handle repetitive, rule-based tasks in your business. Think of it as automating the mundane, freeing up human employees for more strategic and creative work. This boosts efficiency and accuracy while reducing operational costs. Ultimately, RPA streamlines your business processes.
Which RPA tool is in demand?
The “hottest” RPA tool constantly shifts, but UiPath and Automation Anywhere consistently lead in market share and job postings. Demand depends heavily on your specific industry and skillset – some niches favor niche tools. Ultimately, mastering a popular platform opens more opportunities.
How does RPA automate business processes?
RPA uses software robots to mimic human actions on computers. These “bots” follow pre-programmed rules to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks like data entry or invoice processing. This frees up human employees for more strategic and complex work, boosting efficiency and accuracy. Essentially, RPA acts as a digital workforce handling mundane tasks.
Where is RPA mostly used?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) thrives in areas with repetitive, rule-based tasks. Think data entry, invoice processing, or customer service interactions – anything easily structured into digital workflows. Essentially, RPA excels where human labor is tedious and prone to error, freeing up employees for higher-value work. It’s rapidly expanding into diverse sectors including finance, healthcare, and manufacturing.
What language is used in RPA?
RPA isn’t tied to a single language. It uses a mix of technologies, often including visual scripting and integration with various programming languages like Python or C# depending on the specific RPA tool and its advanced features. Think of it as building software with visual blocks, often supplemented by code for more complex tasks.
What are the applications of RPA in industries?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive tasks across various sectors. Imagine it as a digital worker handling data entry, invoice processing, or customer service requests – freeing up human employees for more strategic work. Industries like finance, healthcare, and manufacturing benefit hugely from increased efficiency and reduced errors. Essentially, RPA automates the mundane, boosting productivity and accuracy.
What is the future of RPA?
RPA’s future is bright but evolving. We’ll see a shift from simple task automation towards more intelligent, AI-powered systems that handle complex decisions and integrate seamlessly with existing business processes. Hyperautomation, combining RPA with other technologies, will be key. Ultimately, RPA will become an invisible, integral part of how businesses operate.
How many companies are using RPA?
Precise numbers on RPA adoption are elusive because many deployments are internal and unreported. However, thousands of organizations globally, spanning various sizes and industries, utilize Robotic Process Automation. Growth is rapid, so any specific count quickly becomes outdated. The key takeaway is widespread and accelerating usage.
Where does RPA work best?
RPA shines brightest in handling repetitive, high-volume tasks with clearly defined rules, like data entry or invoice processing. It’s less effective where human judgment or complex problem-solving is crucial. Essentially, RPA excels at automating the *mundane*, freeing up human workers for more strategic activities. Think structured data and predictable processes.
What is RPA in business analysis?
In business analysis, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is like having a digital assistant that handles repetitive, rule-based tasks. It automates things previously done manually, freeing up analysts to focus on higher-level problem-solving and strategic work. This boosts efficiency and reduces errors in processes like data entry and report generation. Essentially, RPA is a tool that empowers business analysts to work smarter, not harder.
What is the main purpose of RPA?
RPA’s core aim is to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks typically handled by humans. It frees up human workers for more complex and creative endeavors. This boosts efficiency and accuracy by eliminating human error in these routine processes, ultimately saving businesses time and money. Think of it as a digital workforce handling the mundane.










