“Achieving great data governance standards is not only a possibility, it is also a responsibility. Technology’s potential is, and always must be, rooted in the faith people have in it” – Tim Cook, CEO, Apple
Yahoo’s exposed data breach of 2016 is a master class on data security best practices. The breach compromised the data of about 3 billion user accounts, nearly half of the world’s population. It exposed names, email addresses, telephone numbers, dates of birth, hashed passwords, and, in some cases, encrypted or unencrypted security questions and answers.
With over 2.5 quintillion bytes of data created each day, the digital universe is expanding at an unprecedented rate. However, this growth comes with significant risks; projected to escalate at its current trajectory, the annual financial toll from cyberattacks is expected to reach approximately $10.5 trillion by the end of 2025, marking a threefold surge from the figures recorded in 2015.
As businesses continue to navigate this complex landscape, implementing robust data security best practices is no longer optional; it’s a critical necessity. From multinational corporations to small enterprises, the need to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access has never been more acute.
Understanding Data Security Best Practices
In the digital era, your data security best practices are as crucial as its existence. Grasping its fundamentals and recognizing various data types is essential for robust protection.
Fundamentals of Data Protection
Data security is the practice of protecting digital information from unauthorized access, corruption, or theft. It is vital to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data—often summarized as the CIA triad of information security. Your strategies must include secure storage, stringent access controls, and comprehensive policies to safeguard data from end to end.
- Confidentiality: Only authorized individuals can access sensitive information
- Integrity: Your data should remain accurate and free from unauthorized modifications
- Availability: Legitimate users must have access to data whenever needed
Types and Sensitivity of Data
Understanding the types of data you handle can dictate the level of security needed. Data is often categorized into:
- Personal Data: Information related to an identifiable individual
- Financial Data: Details of financial transactions, credit card numbers, or bank accounts
- Health Data: Medical records that may require heightened security due to their sensitivity
Data sensitivity varies, with some categories requiring more stringent protection measures. For instance, health data may be subject to more rigorous regulations than other types due to the potential impact on privacy and personal well-being.
Secure Your Business Assets with Microsoft Purview’s Advanced Data Protection!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Purview implementation Services
1. Establishing a Security Framework
A security framework is integral to protecting your organization’s data and a key step in data security best practices. It sets a structured approach to align your security strategy with business objectives.
a. Defining Security Policies
Your foundation for a security framework begins with clear, enforceable security policies. Ensure that your policies are tailored to the unique needs of your business and that they address all facets of your operations, from employee conduct to data management.
- Identify key data assets and protection requirements
- Establish policies for access control, incident response, and data encryption
b. Risk Assessment and Management
Effective risk assessment and management are pivotal to a robust security framework. You should regularly assess your IT environment to identify vulnerabilities and threats.
- Conduct a thorough vulnerability assessment to identify and prioritize risks
- Implement risk management strategies to mitigate identified risks, including regular security policies and control updates.
Top 10 Data Governance Tools for Elevating Compliance and Security
Explore the top 10 data governance tools that enhance compliance, ensure data security, and streamline management for businesses of all sizes.
![]() Learn More
Learn More
2. Technical Measures for Protection
Implementing strong technical measures is vital for safeguarding your organization’s data. These measures serve as the backbone of a robust data security strategy.
a. Encryption and Tokenization
Your data remains secure through encryption, transforming readable data into an unreadable format that requires a key to unlock. Similarly, tokenization replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive equivalents, known as tokens, with no exploitable value.
b. Access Control Systems
Access control systems ensure that only authorized individuals can access your digital resources. These systems are typically categorized into:
- User-based controls, which define access per individual user
- Role-based controls, which grant access based on an individual’s role in your organization
Strict access controls prevent unauthorized data access and modification, as the CISA guidelines emphasize.
c. Intrusion Detection and Prevention
To promptly detect and respond to potential threats, your organization should employ intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS). These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and take immediate action to prevent a breach. According to Solutions Review, leveraging these systems is essential for a proactive defense against cyber threats.

3. Network Security
In the digital age, protecting your network is essential. Implementing robust security measures safeguards your sensitive data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
a. Firewalls and Virtual Private Networks
- Firewalls are your first line of defense in network security. They act as barriers between your internal and untrusted external networks, like the Internet. Firewalls can be hardware, software, or both, and they control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on an organization’s security policies. Ensure your firewall is properly configured to block undesired traffic without impeding legitimate communications for exceptional security.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) extend a private network across a public one. By using encryption and other security measures, a VPN allows you to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if your computing devices were directly connected to the private network. This secures your internet connection and helps protect your identity, even on an unsecured Wi-Fi network. With expert reviews and comparisons on Cybernews to help choose the best option, such as NordVPN and ExpressVPN, which offer robust encryption and secure connections.
b. Secure Socket Layer/Transport Layer Security
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are cryptographic protocols designed to communicate securely over a computer network. SSL is the older of the two protocols, while TLS is its successor and is more widely used today. You most frequently encounter these protocols while accessing secure websites, denoted by HTTPS in the URL.
- It’s critical to use the latest version of these protocols (TLS 1.3) to ensure the highest level of security. When setting up your SSL/TLS, generate or obtain a digital certificate from a reliable Certificate Authority (CA). This encrypts data and verifies the server’s identity to the client, fostering trust and integrity in data exchange.
4. Application Security
In ensuring the security of your applications, attention to secure coding and effective vulnerability management is crucial for protecting your software from cyber threats.
a. Secure Coding Practices
When you develop software, adopting secure coding practices is non-negotiable. A primary step is to educate your developers on principles like input validation, output encoding, and error handling to avoid common vulnerabilities. For instance, incorporating security training for developers should be a fundamental part of your development process. Also, utilize static and dynamic analysis tools that automatically identify potential security issues in your code.
b. Application Vulnerability Management
Your application vulnerability management process must include regular scans for weaknesses using automated tools. You should prioritize and address identified vulnerabilities based on their severity, with a process in place for patching them promptly. Additionally, keep an eye on third-party components, as they can be a common source of vulnerabilities. Automate monitoring your software dependencies to receive alerts when new vulnerabilities are disclosed.
5. End-User Education
Educating end-users is critical to fortifying your organization’s data security. Properly informed employees can act as a first line of defense against cyber threats.
Training and Awareness Programs
Training and awareness programs are fundamental components of end-user education. These programs are designed to familiarize you and your workforce with potential cybersecurity threats and the proper responses to them.
- Recognize Phishing Attempts: Learn to identify suspicious emails or links that can lead to security breaches
- Password Management: Understand the importance of strong password creation and the necessity of regular updates and usage of secure password managers only
- Safe Internet Practices: Navigate the web securely, recognizing unsafe websites and downloads that may harbor malware
These training programs must be:
- Regular: Ongoing training ensures information remains fresh and current
- Interactive: Engaging formats such as simulations and quizzes help you retain information
- Accessible: Material should be easy for users of all skill levels
By committing to regular and comprehensive training, you can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches caused by human error and build a more resilient security culture.
Data Governance Pillars: Building a Strong Foundation for Data-Driven Success
Discover the key pillars of data governance that enable organizations to achieve accuracy, compliance, and success in a data-driven world.
![]() Learn More
Learn More
6. Data Recovery Strategies
Data recovery strategies are critical for ensuring that in the event of data loss, your enterprise can quickly regain access to essential information and maintain business continuity.
a. Backup Solutions
Your backup solutions must be comprehensive and reliable. Implementing the 3-2-1 backup rule is vital: 3 copies of your data on 2 different media, with 1 stored offsite. Ensure periodic testing of backup systems to confirm data integrity and successful restoration.
- Frequency: Daily backups for active data; less frequent for archival data.
- Types:
- Full: All selected data is backed up.
- Incremental: Only new or changed data since the last backup
- Differential: New or changed data since the last full backup
b. Disaster Recovery Planning
Disaster recovery planning involves in-depth strategy and a prepared response for various scenarios. Your plan should include redundancy with diversity, using different recovery mechanisms and software to mitigate the chance of a single point of failure. Implement cryptographic checksums to detect corruption and establish a clear chain of command and action steps for recovery.
- Key Components:
- Risk Assessment: Identify likely scenarios and prepare accordingly
- Recovery Objectives:
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective): Target time to restore operations
- RPO (Recovery Point Objective): Maximum acceptable data lost
Your plan should be routinely updated and tested to ensure relevance and effectiveness in the face of new threats and evolving business processes.
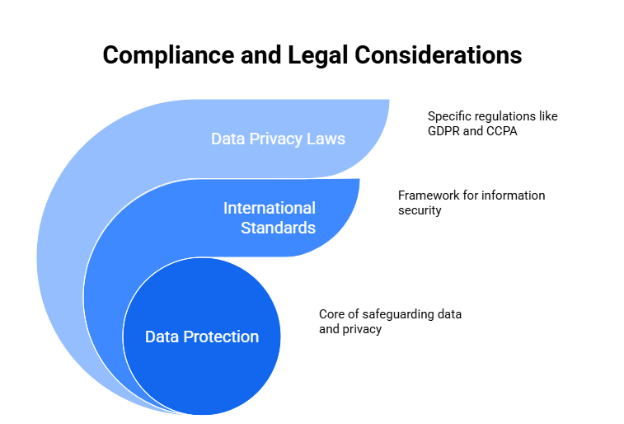
7. Compliance and Legal Considerations
Adhering to compliance and legal standards is crucial for safeguarding your data and respecting user privacy. This involves understanding and implementing international regulations and specific data privacy laws.
a. International Standards and Regulations
International standards, such as the ISO/IEC 27001, provide a framework for managing information security. They offer a set of best practices that you’re expected to integrate into your data security policies. Following these standards is a proactive measure to protect data and often a requirement to do business in certain jurisdictions.
For guidance on ethical concerns that interplay with technology and privacy, you can refer to insights from IEEE regarding the balance between ethical considerations and legal requirements.
b. Data Privacy Laws
You must be well-versed in data privacy laws such as Europe’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and other regional legislations. They impose specific obligations on both data collection and processing activities.
Understanding compliance with cybersecurity and privacy laws is critical due to the penalties for non-compliance, which can include substantial fines and reputational damage. Manufacturers, for instance, must adhere to various standards dictated by different governmental levels and industries.
8. Regular Audits and Monitoring
You must undertake regular security audits and implement continuous monitoring systems to bolster your data security. These actions ensure vulnerabilities are spotted promptly, and the integrity of your systems is maintained.
a. Audit Processes
Establish a Schedule: You should routinely conduct security audits to ensure all data security aspects are current and effective. A regular schedule typically includes annual comprehensive audits, with more frequent, targeted audits as needed.
Assessment Areas: In an audit, your focus should encompass several key areas:
- Risk Assessment: Identify new and emerging threats
- Review of Controls: Ensure access controls are working as intended
- Policy Compliance: Verify adherence to internal and external data security regulations
- Security Posture Analysis: Compare the results against established security baselines
Each audit should conclude with a detailed report outlining the findings and recommending enhancements.
b. Continuous Monitoring Systems
Real-time Alerting: Deploy systems that provide real-time alerts for potential security incidents. This enables quick response to threats.
- Traffic Anomalies
- Unauthorized Access Attempts
System Integration: Ensure your monitoring tools fully integrate your existing infrastructure. This integration allows for:
- Comprehensive Coverage: Monitoring should extend across all systems and networks
- Streamlined Response: Facilitate swift action in case of identified risks
Regular audits and continuous monitoring are non-negotiable facets of implementing robust data security best practices. They empower you with the insights to protect your assets and maintain stakeholder trust.
Microsoft Purview Information Protection: What You Need to Know
Explore how Microsoft Purview Information Protection safeguards your data with advanced classification, labeling, and compliance tools, ensuring secure and seamless data management.
![]() Learn More
Learn More
9. Incident Response Planning
When preparing for potential cybersecurity incidents, effective incident response planning is your linchpin to minimizing the impact on your organization. It requires methodical preparation and clear communication.
a. Incident Management
Your incident management process is your structured approach following a security breach or attack. It encompasses several critical activities initiated by preparation. The foundation here is a comprehensive incident response plan, as highlighted by the ISACA guidance, which should outline identification, detection and analysis procedures, containment, eradication, and recovery. Ensure that your procedure details the following:
- Identification: Know your assets, threats, and vulnerabilities
- Analysis: Utilize tools and techniques to determine the nature of an incident
- Containment: Implement procedures to limit the extent of the incident
- Eradication: Remove elements responsible for the incident
- Recovery: Resume normal operations, confirming systems are no longer at risk
- Post-incident activities: Review and learn from the incident to improve future responses
| Incident Response Planning Overview | ||||
| Phase | Responsibilities | Actions | Communication | Tools/Resources |
| Preparation | IT Security Team | Develop and update incident response plan; Conduct training and simulations | Establish communication protocols; Create contact lists for key personnel | Incident response plan; Training materials |
| Identification | Security Analysts | Detect and determine the scope of the incident; Prioritize the incident based on impact | Notify incident response team and management | SIEM tools; Intrusion detection systems |
| Containment | Incident Response Team | Isolate affected systems to prevent spread; Implement temporary fixes | Update stakeholders on containment efforts | Forensic tools; Network segmentation tools |
| Eradication | IT and Security Teams | Remove malware or threats; Secure vulnerabilities that were exploited | Communicate eradication measures and status | Anti-malware tools; Patch management systems |
| Recovery | IT Department | Restore systems and data from backups; Monitor for anomalies | Inform stakeholders of recovery status and any impacts | Backup and recovery solutions; Monitoring tools |
| Lessons Learned | Entire Incident Response Team | Review and analyze the incident response; Update policies and procedures based on findings | Share lessons learned with the organization | Incident review reports; Updated incident response plan |
b. Communication Strategy
Your communication strategy during an incident is crucial. It determines the efficacy of your response and the trust of stakeholders. Begin by assigning clear roles and responsibilities to your incident response team. As recommended by Microsoft’s best practices, have a communication plan that includes:
- Internal Communication: Define who needs to be notified and how
- External Communication: Prepare templates for stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and the public
- Debriefs: Set structured times to update all parties involved
Ensure your communication is timely and accurate and preserves confidentiality where necessary.
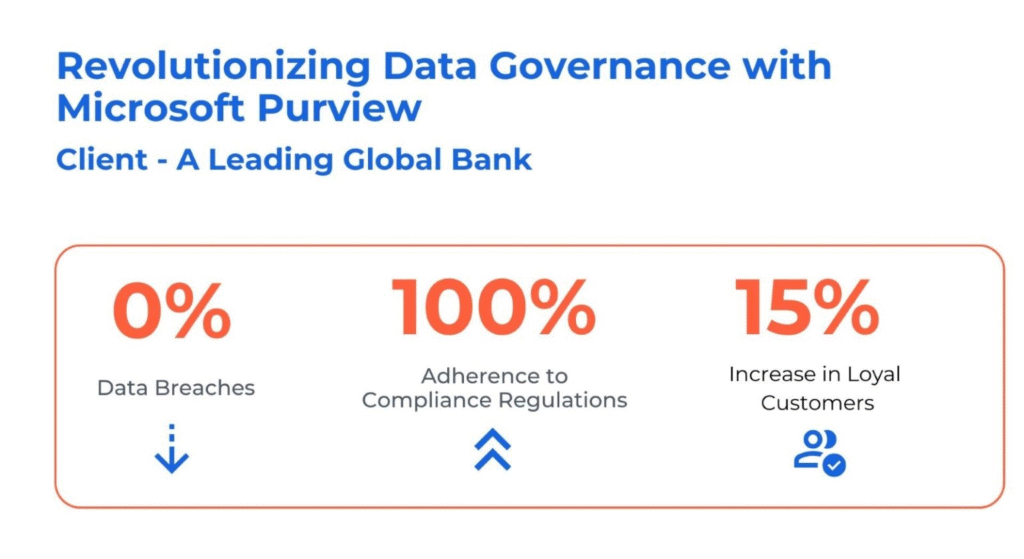
Case study: How Kanerika Empowers Clients with Robust Data Governance Solutions
The client, a global banking institution with nearly 9000 branches and 22000 ATMs worldwide, faced significant challenges in managing its distributed data environment. This included data silos, operational inefficiencies, and the complexities of adhering to stringent regulatory conditions such as privacy laws. These challenges were further exacerbated by the manual and labor-intensive processes of identifying and classifying sensitive data, increasing the risk of compliance breaches.
Kanerika addressed these challenges by:
- Implementing a data discovery process using Purview’s Data Map to automatically identify and classify data assets, providing a comprehensive view of data sources and transformations.
- Enhancing data governance with Purview’s Policies, ensuring the proper classification and handling of personal data (PII, PCI, PHI), thus improving visibility and auditability.
- Automating data lineage and streamlining the flow from sources through different layers in the Lakehouse, enhancing transparency and compliance.
Establishing data sharing rules to safeguard sensitive information and ensuring proper access to authorized stakeholders, preventing unauthorized access and data mishandling.
Prevent Data Security Risks in Your AI with Kanerika’s Robust Governance Solution
As AI adoption accelerates, so do the risks tied to data exposure, poor governance, and regulatory gaps. For enterprises, effective data governance is no longer optional—it’s essential for survival. Kanerika, a leading data and AI solutions company, helps organizations secure their data ecosystems with enterprise-grade tools that go beyond surface-level fixes.
At the heart of Kanerika’s offering is a powerful trio: KANGovern, KANComply, and KANGuard—a comprehensive suite built on the foundation of Microsoft Purview. These solutions work together to maintain data integrity, enforce compliance, and block unauthorized access across the full data lifecycle.
Whether it’s controlling shadow AI risks, ensuring regulatory readiness, or improving decision-making through clean, reliable data—Kanerika’s integrated approach delivers. Businesses can confidently embrace AI without compromising security or control. With Kanerika, data stays secure, usable, and in the right hands—every step of the way.
FAQs
What are some best practices for data security?
Data security boils down to proactive defense. Prioritize strong, unique passwords and multi-factor authentication for all access points. Regularly update software and hardware to patch vulnerabilities, and implement robust access controls to limit who sees what data. Finally, back up your data regularly and securely, off-site if possible, to protect against loss.
What are the 7 principles of data security?
Data security boils down to seven key ideas: Confidentiality (keeping data secret), Integrity (ensuring data accuracy), Availability (making data accessible when needed), Authentication (verifying user identity), Authorization (controlling access levels), Non-repudiation (preventing denial of actions), and Accountability (tracking who did what). These principles work together to protect data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. Essentially, they ensure data remains reliable and trustworthy.
What are the four 4 elements of data security?
Data security isn’t just one thing; it’s a layered approach. Think of it as four key pillars: Confidentiality (keeping data secret), Integrity (ensuring data accuracy), Availability (making sure data’s accessible when needed), and Authenticity (verifying the data’s source and legitimacy). These four elements work together to protect your valuable information.
What are the 3 types of data security?
Data security isn’t just one thing; it’s a layered approach. We typically categorize it into confidentiality (keeping data secret), integrity (ensuring data accuracy and trustworthiness), and availability (making sure authorized users can access data when needed). These three work together to protect your information. Think of them as the pillars holding up your data’s safety.
What are the 5 ways to secure data?
Data security is a multi-layered approach. It relies on strong passwords and multi-factor authentication to control access. Encryption safeguards data both at rest and in transit, while regular backups ensure recovery from loss or breaches. Finally, robust security policies and employee training are crucial for effective data protection.
What are the basics of data security?
Data security boils down to protecting your information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. This involves strong passwords, updated software, and careful consideration of where and how you store data. Think of it as building a layered fortress around your valuable information, with multiple defenses to thwart potential threats. Regular vigilance and updates are key to maintaining this fortress.
What is the best practice for information security?
Best information security practices center around a layered defense. This means combining robust technical controls (like firewalls and encryption) with strong user training and security policies. Ultimately, it’s about minimizing risk by proactively identifying and managing vulnerabilities across all aspects of your systems and operations. Regular risk assessments and ongoing monitoring are crucial.
What is the best method to secure your data?
There’s no single “best” method, but a layered approach is key. This means combining strong passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), regular software updates, and robust antivirus/anti-malware protection. Consider also data encryption, especially for sensitive information. Ultimately, security is a continuous process of vigilance and adaptation.
Which of the following are security best practices?
Security best practices boil down to minimizing vulnerabilities and maximizing resilience. This means regularly updating software, using strong, unique passwords, and employing multi-factor authentication wherever possible. Ultimately, it’s about building layered defenses against threats, both internal and external.