Generative AI Models are igniting a revolution across industries, reshaping what’s possible in creativity, productivity, and innovation. Unlike traditional AI, which merely classifies or predicts, these models are architects of the new—imagining, composing, and bringing to life entirely original text, images, code, and more. Their transformative power is driving unprecedented demand, from content creation and software development to drug discovery and world-class design.
The market’s momentum is undeniable. By 2025, global investment in generative AI is forecasted to surge to an astounding $38 billion, with the horizon stretching toward a staggering $1 trillion by 2034. At the same time, Deloitte reports that breakthrough tools like Microsoft Copilot and ChatGPT are revolutionizing the workplace—streamlining meetings, distilling complex reports, and automating communications at scale.
Whether you are a pioneer, a builder, or a visionary leader, this guide will empower you to harness the full promise of generative AI models and elevate your work to new frontiers of innovation.
What Are Generative AI Models?
Generative AI models are computer programs that create new content by learning patterns from existing data. Think of them as highly sophisticated pattern-recognition systems that can produce original work rather than just analyzing or sorting information.
How Generative AI Models Work?
Core Concepts Behind Generative Models
Generative AI models create new content by learning patterns from massive amounts of existing data. Unlike traditional software that follows programmed rules, these models identify statistical relationships and use them to generate original text, images, music, or other content that resembles their training data.
- Neural Networks Foundation
At their core, generative models use neural networks – computer systems inspired by how the human brain processes information. These networks consist of interconnected nodes that process and transform data through multiple layers. Each layer learns increasingly complex patterns, starting with basic features and building up to sophisticated understanding of language, images, or other data types.
- Training on Massive Datasets
Generative models learn by analyzing enormous collections of data. Text models train on billions of web pages, books, and articles. Image models study millions of photographs and artworks. During training, the model repeatedly processes this data, adjusting its internal parameters to better predict and generate similar content.
Discriminative models classify or categorize existing data – they answer questions like “Is this email spam?” or “What object is in this photo?” Generative models create new data that didn’t exist before. They ask “What would a new email look like?” or “How can I create a realistic image of a cat?”
Key Techniques in Generative Models
- Transformers power most modern language models like GPT and Claude. They excel at understanding context and relationships between words across long passages of text. Transformers use an “attention mechanism” that helps the model focus on relevant parts of the input when generating each new word.
- Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) compress data into a simplified representation, then recreate it. They’re useful for generating variations of existing content and are often used in image generation and data compression applications.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) pit two neural networks against each other – a generator that creates fake content and a discriminator that tries to detect fakes. This competition drives both networks to improve, resulting in increasingly realistic generated content.
- Diffusion Models start with random noise and gradually refine it into coherent content through a series of small improvements. They’re behind many modern image generators and are known for producing high-quality, detailed outputs.
AI Agents Vs AI Assistants: Which AI Technology Is Best for Your Business?
Compare AI Agents and AI Assistants to determine which technology best suits your business needs and drives optimal results.
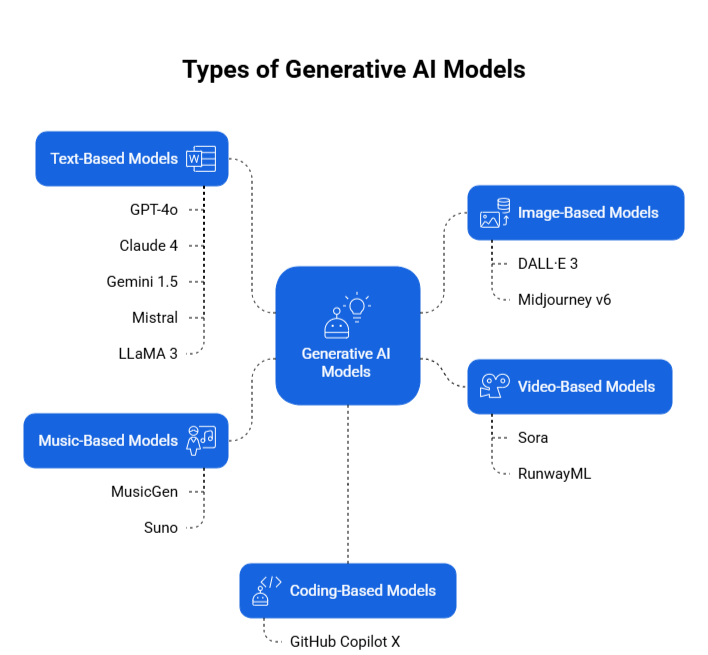
Types of Generative AI Models
- GPT-4o (OpenAI): This model can handle text, images, and voice. It’s fast, smart with reasoning, and works well for writing, answering questions, and more natural conversations.
- Claude 4 (Anthropic): Known for being safer and more careful with answers. It can remember longer conversations and is often used in customer support or sensitive tasks.
- Gemini 2.5 (Google DeepMind): Designed to work closely with Google’s tools. It’s great for coding help, research, and pulling in search info for better answers.
- Mistral: A set of open-source AI models. Lightweight and flexible—good for companies that want more control over how AI runs on their own systems.
- LLaMA 3 (Meta): Built for developers. Easy to fine-tune and run without heavy computing power.
- DALL·E 3: Turn written prompts into images. Known for making creative and detailed visuals with good control.
- Sora: An early model for creating short video clips from text prompts. Still evolving but promising for marketing and content.
- Midjourney v6: Makes high-quality images, often used in design, branding, and creative projects.
- MusicGen / Suno: Create music by describing what you want in text—useful for content creators and musicians.
- RunwayML – Comprehensive video generation and editing tools for professional-quality content creation
- GitHub Copilot X: Helps developers write code, fix bugs, and suggest functions—all from inside their coding tool.
Each model has its strengths. Choosing the right one depends on what you’re building—words, pictures, music, or software.
Top 5 Generative AI Models of 2025
1. GPT‑4o (OpenAI)
- Multimodal powerhouse that handles text, images, audio, and video with a massive context window and enhanced reasoning skills.
- Excels at creative writing, code generation, and complex data interpretation—while being more cost-effective in API usage.
2. Gemini 2.5 Pro (Google DeepMind)
- A top-tier multimodal model offering robust reasoning and app-building capabilities, available via subscription.
- Integrated across Google products; excels at structured coding and multimodal input/output tasks.
3. Claude 4 (Anthropic)
- The latest release—Opus and Sonnet variants—offer exceptional reasoning, long-form memory, and the ability to summarize complex thought processes.
- Renowned for code generation and logical consistency, with “thinking summaries” that enhance transparency .
4. Mistral Medium 3 (Mistral AI)
- An open-access model delivering high performance “at or above” Claude Sonnet 3.7 on benchmarks—but at a more accessible price point.
- Available via major cloud platforms and supports enterprise-grade agents and coding workflows.
5. DeepSeek‑V3 (DeepSeek, China)
- A cost-efficient reasoning model gaining traction globally by offering performance comparable to top U.S. models—while minimizing GPU usage.
- Demonstrates the power of open, resource-efficient architectures in AI innovation.
Why These Models Matter
- Multimodality is no longer optional—leaders like GPT‑4o, Gemini, and Claude can handle text, visuals, and audio.
- Models such as Claude 4 and GPT‑4o have made strides in transparency and reasoning, reducing hallucinations and increasing trust.
- Open-access models like Mistral Medium 3 and DeepSeek-V3 highlight a trend toward affordable, efficient, and accessible AI without sacrificing quality.
Boost Your Business Impact with Advanced Generative AI Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
How Kanerika Is Applying Generative AI: Meet Alan, Susan, and Mike
At Kanerika, we’re not just exploring generative AI—we’re operationalizing it. With the launch of our AI agents Alan, Susan, and Mike, we’re solving real-world, labor-intensive challenges that consume valuable business time and resources. These intelligent agents reflect our commitment to innovation, automation, and enterprise growth through practical AI deployment.
Alan – The Legal Document Summarizer
Alan is designed to streamline legal workflows by transforming complex contracts and legal documents into concise, actionable summaries. Users can define simple, natural language rules to tailor outputs to specific requirements. Alan helps legal teams reduce review time, accelerate contract analysis, and enhance decision-making.
Susan – The PII Redactor
Susan addresses data privacy and compliance with precision. It detects and redacts personally identifiable information (PII) such as names, contact details, and ID numbers. By automating this critical task, Susan ensures documents are compliant with privacy regulations before sharing or storage—protecting sensitive data and organizational integrity.
Mike – The Proofreader
Mike focuses on accuracy and quality assurance. It validates numerical data, checks for arithmetic consistency, and identifies discrepancies across documents. Whether it’s reports, invoices, or proposals, Mike ensures that your documentation is reliable, professional, and error-free.
These AI agents are just the beginning of how we at Kanerika are leveraging generative AI to deliver tangible business value. We’re helping organizations reduce manual effort, improve compliance, and drive operational efficiency—one intelligent solution at a time.
Generative AI in Supply Chain Management: A Complete Implementation Guide
Learn how generative AI optimizes supply chains with improved forecasting, streamlined processes, and enhanced efficiency for better results.
Real-World Use Cases of Generative AI Models
1. Enterprise Tasks
- Helps employees write emails, reports, and slides faster using tools like Microsoft Copilot
- Summarizes long legal or financial documents into easy-to-understand notes
- Quickly finds HR policies, company updates, or files through AI chat tools
- Reduce time spent on repetitive writing tasks across departments
2. Marketing & Design
- Generate ad copy, product descriptions, and social media posts in seconds
- Create visuals, mockups, or banner designs without needing a design team
- Adjust campaigns easily for different audiences or platforms
- Speed up creative brainstorming with smart suggestions
3. Healthcare and Pharma
- Help researchers explore new drug ideas using AI-generated compounds
- Analyze medical scans faster with AI assistance
- Create fake but realistic patient data for safe testing and training
- Support doctors by providing quick summaries of medical texts or journals
4. Entertainment & Gaming
- Generate lifelike game characters or background stories
- Write in-game conversations that adapt to player actions
- Build game environments and levels without manual design
- Allow indie game makers to build rich worlds with fewer resources
5. Education
- Help teachers build quizzes, study guides, and classroom content
- Break down complex subjects into simpler language
- Translate learning material into different languages for wider access
- Provide students with personalized AI tutors that adjust to their level
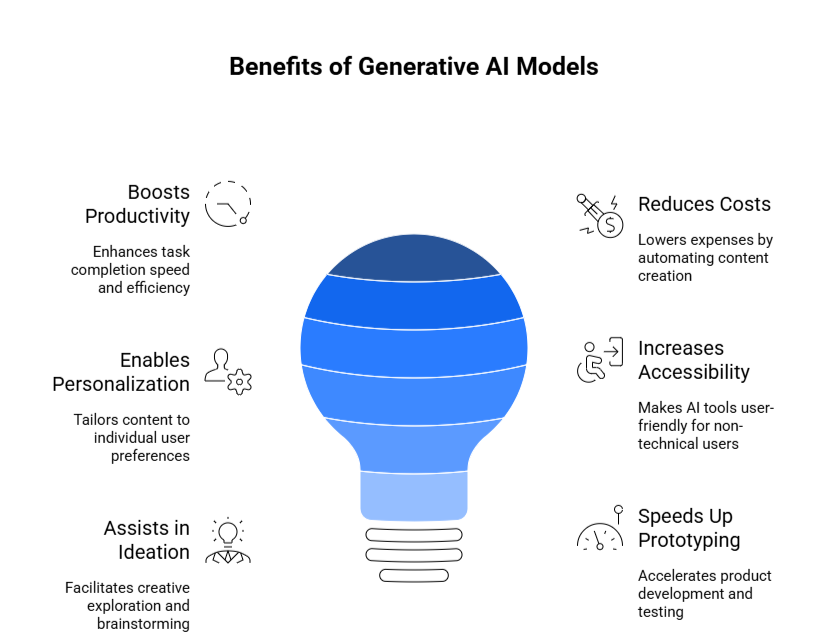
Benefits of Generative AI Models
1. Boosts productivity and creative speed
Generative AI helps complete tasks like writing, designing, or drafting ideas in minutes, allowing teams to move faster and focus on higher-value work.
2. Reduces cost of manual content creation
It can generate emails, product descriptions, images, or documents instantly—cutting down the need for repetitive manual work and lowering production costs.
3. Enables hyper-personalization at scale
With AI, you can tailor content to each user without writing everything from scratch, helping businesses connect with people more effectively.
4. Makes AI tools accessible to everyone
No-code interfaces let non-technical users explore ideas, generate content, or test features without needing programming skills.
5. Assists in ideation and design exploration
Whether you’re starting a project or exploring design options, generative AI offers quick drafts and variations to jumpstart the creative process.
6. Speeds up rapid prototyping
Teams can test early versions of products, interfaces, or campaigns faster—saving time and improving iteration cycles.
Risks and Ethical Concerns
While generative AI offers remarkable capabilities, it also presents significant challenges that individuals, organizations, and society must carefully consider. Understanding these risks is crucial for responsible AI adoption and development.
1. Misinformation and Deepfakes
The Problem
- AI can create fake news articles, false social media posts, and misleading information that appears authentic
- Deepfake technology produces convincing fake videos and audio of real people saying or doing things they never did
- Examples: Fake celebrity endorsements, fabricated political speeches, false news stories that spread rapidly online
Why It Matters
- Undermines trust in legitimate news and media sources
- Can influence elections and public opinion with false information
- Makes it harder for people to distinguish between real and fake content
- Damages reputations of individuals falsely depicted in deepfakes
Current Impact
- Political misinformation campaigns during elections
- Fake celebrity endorsements for scam products
- False emergency alerts and crisis information
2. Copyright Infringement and Intellectual Property Risks
The Problem
- AI models are trained on vast amounts of content from the internet, including copyrighted material
- Generated content may closely resemble existing copyrighted works without permission
- Unclear legal boundaries about what constitutes fair use in AI training and outputs
Why It Matters
- Artists, writers, and creators may lose income when AI reproduces their style or content
- Companies face legal risks when using AI-generated content commercially
- Original creators receive no compensation when their work influences AI outputs
Current Impact
- Ongoing lawsuits against AI companies by artists and publishers
- Getty Images suing Stability AI for using copyrighted images in training
- Writers and illustrators losing work to AI-generated alternatives
3. Bias in Training Data Leading to Biased Outputs
The Problem
- AI models learn from internet data that contains human biases and stereotypes
- These biases get embedded in the AI’s responses and generated content
- Can perpetuate discrimination against certain groups or communities
Why It Matters
- Reinforces harmful stereotypes about race, gender, age, and other characteristics
- Can lead to unfair treatment in hiring, lending, and other important decisions
- Excludes or misrepresents minority groups and perspectives
Current Impact
- AI image generators showing bias in depicting professionals by race and gender
- Language models providing different career suggestions based on perceived gender
- Hiring AI tools discriminating against certain names or backgrounds
4. Job Displacement in Creative Sectors
The Problem
- AI can now perform many tasks previously done by human creatives
- Writers, artists, designers, and other creative professionals face reduced demand for their services
- Companies may choose cheaper AI solutions over human talent
Why It Matters
- Threatens livelihoods of millions of creative workers
- May lead to loss of human creativity and cultural diversity
- Could create economic hardship for entire creative industries
Current Impact
- Stock photo companies reducing photographer contracts
- Marketing agencies using AI instead of copywriters
- Publishing houses considering AI-generated content over human authors
- Animation studios using AI for background art and simple animations
5. Privacy Concerns with Internal and Confidential Data
The Problem
- Employees may input sensitive company information into AI tools without realizing the privacy risks
- AI companies may store and potentially use this data for training or other purposes
- Confidential business information could be exposed or leaked
Why It Matters
- Trade secrets and proprietary information may be compromised
- Personal data of customers and employees could be exposed
- Companies may violate privacy regulations and face legal consequences
Current Impact
- Samsung employees accidentally leaked source code through ChatGPT
- Law firms concerned about client confidentiality when using AI tools
- Healthcare organizations worried about patient data privacy
- Financial institutions restricting AI use due to regulatory requirements
6. Regulatory Gaps and Uncertainty
The Problem
- Laws and regulations haven’t kept pace with rapid AI development
- Unclear legal responsibilities for AI-generated content and decisions
- Different countries developing conflicting AI regulations
Why It Matters
- Companies don’t know what’s legally allowed or prohibited
- Consumers have little protection against AI-related harms
- Innovation may be stifled by regulatory uncertainty
Current Impact
- EU working on comprehensive AI Act with strict requirements
- US considering various AI bills and executive orders
- China implementing its own AI regulations
- Companies struggling to comply with varying international requirements
What Can Be Done
- For Individuals
- Verify information from multiple sources before sharing
- Be aware of AI-generated content and deepfakes
- Protect personal information when using AI tools
- Support human creators and artists when possible
- For Organizations
- Implement clear AI usage policies and training
- Regularly audit AI systems for bias and accuracy
- Ensure data privacy and security measures
- Consider ethical implications before deploying AI solutions
- For Society
- Develop comprehensive AI regulations and standards
- Invest in education about AI risks and benefits
- Support affected workers with retraining programs
- Promote transparency in AI development and deployment
The Future of Generative AI Models
The next generation of generative AI promises to be more powerful, accessible, and integrated into our daily lives. These emerging trends will reshape how we interact with technology and transform entire industries.
1. Rise of Multi-Modal Models
AI systems are evolving to seamlessly integrate multiple modalities, enabling them to work with text, images, audio, and video all at once. These models can, for instance, analyze a photo, generate a detailed description in words, and even create a video based on the image’s content. Additionally, AI can take a written recipe and not only break it down into steps but also generate an engaging cooking video, complete with narration, making the cooking process more interactive and accessible.
Real Examples in Development
- GPT-4 already combines text and images, with video capabilities coming soon
- Google’s Gemini can process text, images, audio, and code simultaneously
- OpenAI’s Sora creates videos from text descriptions
Why It Matters
- More natural interactions – speak, show, or type to get what you need
- Richer creative possibilities combining different media types
- Better accessibility for people with different abilities and preferences
2. More Open-Source Alternatives with Fine-Tuning Support
Free AI models are now available for companies and individuals to customize for specific needs. Tools for training AI on specialized data, like medical or legal documents, have become more accessible. Community-driven development is making AI more democratic and transparent, ensuring broader participation and ethical innovation.
Real Examples in Development
- Meta’s LLaMA models becoming increasingly powerful and free to use
- Hugging Face providing platforms for sharing and customizing AI models
- Stability AI making image generation tools freely available
Why It Matters
- Reduces costs for businesses wanting custom AI solutions
- Gives more control over data privacy and security
- Enables innovation in specialized fields like healthcare and education
3. Edge Deployment (On-Device AI)
AI technology is now evolving to run directly on your phone, laptop, or smart device—without requiring an internet connection. This means you get instant responses with complete privacy, as your data never leaves your device. These on-device AI assistants are designed to function seamlessly even when you’re offline, offering both speed and security wherever you are.
Real Examples in Development
- Apple’s on-device AI for Siri and photo recognition
- Google’s Pixel phones running AI locally for camera features
- Microsoft integrating AI directly into Windows operating system
Why It Matters
- Complete privacy – your personal information stays on your device
- Faster responses without waiting for internet connections
- Works anywhere, even in areas with poor connectivity
4. Integration into Everyday Platforms
AI is now built into everyday tools—emails write themselves, CRMs predict customer needs, and search engines deliver smart, personalized answers to complex questions.
Real Examples in Development
- Microsoft integrating AI into Office 365 (Word, Excel, PowerPoint)
- Google adding AI to Gmail, Google Docs, and Google Sheets
- Salesforce embedding AI throughout their business software
Why It Matters
- No need to learn new AI tools – it’s built into what you already use
- Seamless workflow integration makes you more productive
- AI becomes invisible and helpful rather than a separate tool
5. Better Guardrails for Trust, Accuracy, and Ethics
AI systems should clearly signal uncertainty when applicable, include built-in fact-checking and source verification, and have strong safeguards against bias, misinformation, and harmful content.
Real Examples in Development
- Constitutional AI that follows ethical guidelines in its responses
- AI systems that cite sources and show confidence levels
- Watermarking technology to identify AI-generated content
Why It Matters
- Builds trust in AI systems for important decisions
- Reduces spread of misinformation and harmful content
- Makes AI safer for use in sensitive areas like healthcare and education
Transform Your Business with Kanerika’s Generative AI Solutions
At Kanerika, we deliver customized generative AI solutions designed to meet the unique needs of businesses across industries like logistics, manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and beyond. Whether it’s streamlining operations, optimizing processes, or creating tailored customer experiences, our AI-driven tools empower you to achieve operational excellence and stay ahead in competitive markets.
Our solutions adapt to your specific challenges, offering benefits like predictive analytics for logistics, inventory optimization for manufacturing, smart pricing strategies for retail, and personalized care in healthcare. By harnessing generative AI, we enable your business to forecast trends, reduce costs, and unlock growth opportunities with precision and efficiency.
Kanerika’s commitment lies in crafting solutions that address your unique requirements. With our expertise, you gain the flexibility and innovation needed to transform your operations, enhance decision-making, and deliver value to your stakeholders. Let’s build a smarter, more efficient future for your business together.
Transform Your Business with AI-Powered Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
FAQs
What is a generative AI model?
Generative AI models are algorithms designed to create new content—such as text, images, audio, or code—based on patterns learned from large datasets.
How do generative AI models work?
They use deep learning architectures like transformers to analyze massive amounts of data and generate content by predicting the most likely next elements in a sequence.
What are common examples of generative AI?
Examples include ChatGPT for text, DALL·E for images, GitHub Copilot for code, and MusicLM for music generation.
Are generative AI models always accurate?
No. While they are powerful, generative models can produce incorrect, biased, or misleading content, especially if not properly trained or aligned.
What data are generative AI models trained on?
They are typically trained on diverse, large-scale datasets pulled from the internet, books, code repositories, and more—depending on the model’s purpose
Can generative AI replace human creativity?
Generative AI can assist and augment human creativity but doesn’t truly “understand” content or intent. It’s a tool, not a replacement.
What are the ethical concerns around generative AI?
Key concerns include data privacy, intellectual property issues, misinformation, deepfakes, and bias in outputs