What if your operations team could hand off dozens of routine tasks—and actually see results within weeks? Across industries, that’s no longer a future promise. According to PwC, 66% of companies using AI agents report measurable productivity gains, and 57% see clear cost savings.
So what are these “agents” really doing behind the scenes? How are they changing the way large organizations manage support, sales, logistics, and decision-making on a daily basis? And most importantly, how close are you to putting them to work in your own business?
Today’s AI agents span an impressive spectrum – from handling customer queries to delivering packages across cities. Through this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore real-world AI agent examples that are transforming industries, examine their key capabilities, and understand how these digital entities are evolving from simple rule-based systems into complex decision-makers capable of learning and adapting to new challenges.
Take Your Business to the Next Level with Powerful AI Agents!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are intelligent software systems designed to perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals autonomously. Think of them as digital workers that can sense, reason, and act based on programmed objectives – much like a human employee, but operating in the digital realm.
According to Deloitte’s Global State of AI Report 2023, businesses are rapidly integrating AI agents across critical operations – from customer service chatbots and virtual assistants to sophisticated algorithms managing supply chains and cybersecurity systems. These virtual workers excel at handling repetitive tasks, analyzing vast amounts of data, and making real-time decisions while maintaining consistent performance around the clock.
The surge in adoption stems from their proven ability to reduce operational costs, minimize human error, and significantly improve service delivery speeds. For instance, Fortune 500 companies implementing AI agents in customer service have documented response times dropping from hours to seconds, while maintaining higher customer satisfaction scores.
Key Characteristics of AI Agents
AI agents are sophisticated software systems characterized by six fundamental traits that make them invaluable in modern business applications. These characteristics work together to create systems that can operate independently, learn from experience, and adapt to changing conditions in real-time. Understanding these core traits is essential for organizations looking to leverage AI agents effectively in their operations.
1. Autonomy
Agents operate independently without constant human oversight, making decisions and executing tasks based on their programming.
Example: An autonomous trading bot that analyzes market conditions and executes trades 24/7 without human intervention, adjusting its strategy based on market volatility.
2. Reactivity & Environmental Awareness
The ability to monitor and respond to changes in their environment, processing inputs and adjusting behavior accordingly.
Example: A smart thermostat that continuously monitors room temperature, humidity, and occupancy patterns, automatically adjusting climate controls for optimal comfort and energy efficiency.
3. Goal-Oriented Behavior
Focused on achieving specific objectives through strategic decision-making and action planning.
Example: A warehouse robot that determines the most efficient picking route to fulfill multiple orders while avoiding obstacles and minimizing travel time.
4. Learning Capability
The power to improve performance through experience and feedback, continuously updating their decision-making models.
Example: A customer service chatbot that learns from past interactions to provide more accurate and relevant responses, recognizing patterns in customer queries and adapting its communication style.
5. Social Ability
Capacity to interact with humans and other AI agents, sharing information and coordinating actions.
Example: Multiple delivery drones working together to optimize delivery routes and avoid collisions while communicating with human dispatchers and each other.
6. Proactivity
Taking initiative to solve problems or improve processes without explicit instructions.
Example: A predictive maintenance system that identifies potential equipment failures before they occur and automatically schedules maintenance, ordering necessary parts in advance.
Generative AI Examples: How This Technology is Reshaping Creativity and Innovation
Redefining creativity and innovation, generative AI produces unique content, designs, and solutions across industries.
Types of AI Agents
1. Simple Reflex Agents
The most basic type of AI agents that operate on if-then rules, responding to current percepts without considering history or future implications. They’re like digital thermostats – straightforward and predictable in their actions based on preset conditions.
- Follows condition-action rules (if X happens, do Y)
- No internal memory or state tracking
- Best for simple, predictable environments Example: Basic chatbots that provide fixed responses to specific keywords
2. Model-Based Agents
These agents maintain an internal model of their environment, tracking how the world evolves and how their actions affect it. They can handle partial visibility by using their model to fill in missing information.
- Maintains internal state representation
- Can work with partially observable environments
- Predicts environmental changes Example: Self-driving cars that maintain a model of road conditions and traffic
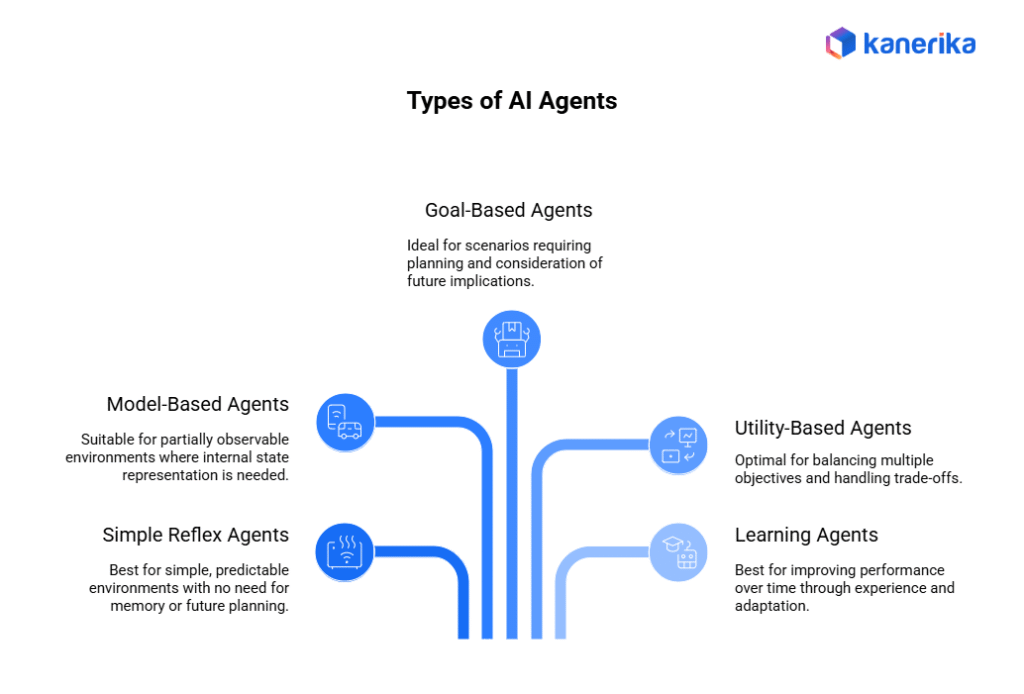
3. Goal-Based Agents
Operating with specific objectives in mind, these agents evaluate different scenarios to choose actions that help achieve their goals. They combine current conditions with goal information to make decisions.
- Considers future implications of actions
- Plans sequences of actions to reach goals
- More flexible than simpler agents Example: A delivery robot planning the most efficient route to multiple destinations
4. Utility-Based Agents
These sophisticated agents use utility functions to measure the desirability of different states, allowing them to choose optimal actions when faced with conflicting goals or uncertainty.
- Balances multiple objectives
- Handles trade-offs between competing goals
- Optimizes for best overall outcomes Example: Trading algorithms balancing risk and reward in investment decisions
5. Learning Agents
The most advanced type, these agents improve their performance through experience, modifying their behavior based on feedback and new information.
- Adapts behavior through experience
- Updates internal models and strategies
- Improves performance over time Example: Content recommendation systems that learn from user preferences and behaviors
Why Causal AI is the Next Big Leap in AI Development
Revolutionizing decision-making, Causal AI identifies cause-and-effect relationships to deliver deeper insights and accurate predictions.
AI Agent Examples: Industry-specific
1. Healthcare Applications
AI agents in healthcare combine medical knowledge with data analysis to support clinical decision-making and patient care. These systems process vast amounts of medical data to assist healthcare providers in diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient monitoring.
- Analysis of medical images and lab results
- Real-time patient condition monitoring
- Treatment effectiveness prediction
2. Finance Applications
Financial AI agents process massive amounts of market data to identify patterns, assess risks, and execute transactions. These systems operate at speeds and scales impossible for human traders, while maintaining strict compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Automated trading based on market conditions
- Real-time fraud pattern detection
- Credit risk assessment and scoring
3. Manufacturing Applications
In manufacturing, AI agents optimize production processes, maintain quality standards, and predict equipment maintenance needs. These systems help reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and maintain consistent product quality.
- Real-time quality control monitoring
- Production line optimization
- Predictive maintenance scheduling
4. Transportation Applications
Transportation AI agents coordinate complex mobility systems, from individual vehicles to entire traffic networks. These systems optimize routes, manage traffic flow, and ensure safe operation of autonomous vehicles.
- Self-driving vehicle navigation and control
- Smart traffic light management
- Fleet routing and logistics optimization
5. Retail Applications
AI agents in retail are transforming both online and physical shopping experiences. These systems analyze customer behavior, optimize inventory, and provide personalized shopping experiences while helping retailers make data-driven decisions about merchandising and operations.
- Automated reordering systems
- Demand prediction and planning
- Personalized shopping recommendations
6. Education Applications
Educational AI agents are revolutionizing learning by providing personalized instruction, automated assessment, and adaptive content delivery. These systems help educators scale their impact while offering students customized learning experiences based on their individual needs and progress.
- Personalized Learning
- Automated grading systems
- Study habit analysis and recommendations
15 Best AI Agents for Business Automation
Customer Service Automation Agents
1. Zendesk AI Agent
Automated support agent that handles customer tickets without human input. Routes complex issues to the right teams while resolving simple problems instantly.
Key Features
- Automated ticket classification and routing
- Multi-language customer response generation
- Escalation management with smart handoffs
Use Cases
- Handle 80% of routine support tickets automatically
- Provide 24/7 customer service coverage
- Reduce response time from hours to seconds
2. Intercom Resolution Bot
AI customer service agent that manages live chat conversations. Understands context across multiple messages and resolves issues in real-time.
Key Features
- Contextual conversation management
- Real-time issue resolution
- Customer data integration
Use Cases
- Answer product questions during sales conversations
- Process refunds and account changes
- Qualify support requests before human handoff
3. Ada
E-commerce focused customer service agent that processes orders and handles returns. Works across web, mobile, and social media platforms.
Key Features
- Transaction processing capabilities
- Multi-platform deployment
- Order status and tracking updates
Use Cases
- Process returns and exchanges automatically
- Handle shipping inquiries and updates
- Manage account modifications and billing questions
Sales Process Automation Agents
4. 11x Alice & Julian
Two specialized sales agents working together. Alice finds and contacts prospects while Julian qualifies inbound leads and books meetings.
Key Features
- Dual agent sales system
- Prospect research and outreach automation
- Meeting scheduling and qualification
Use Cases
- Generate qualified sales meetings on autopilot
- Follow up with cold leads using personalized messaging
- Qualify website visitors and demo requests
5. Artisan
Autonomous outbound sales agent that researches prospects and manages entire sales sequences. Handles everything from lead research to follow-up campaigns.
Key Features
- Prospect research and data enrichment
- Personalized outreach campaign management
- Performance tracking and optimization
Use Cases
- Scale outbound sales without hiring more reps
- Research and contact potential customers automatically
- Manage complex sales sequences across multiple touchpoints
6. Salesforce Agentforce
CRM-integrated sales agents that work inside your existing Salesforce setup. Updates records, manages pipeline activities, and executes sales processes automatically.
Key Features
- Native Salesforce CRM integration
- Pipeline management automation
- Deal progression tracking
Use Cases
- Update CRM records after sales calls automatically
- Move deals through pipeline stages based on activities
- Generate sales reports and forecasting data
7. Drift
Conversational marketing agent that captures and qualifies website visitors. Routes high-value prospects to sales teams while nurturing others automatically.
Key Features
- Website visitor identification
- Lead qualification scoring
- Automated meeting booking
Use Cases
- Convert website traffic into qualified leads
- Book sales meetings while prospects are browsing
- Segment leads based on company size and buying intent
Boost Productivity and Efficiency with Next-Gen AI Agents!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
Business Process Automation Agents
8. Lindy
No-code platform for building custom business automation agents. Creates workflows that connect different software tools and handle multi-step processes.
Key Features
- No-code agent builder
- 2,500+ software integrations
- Multi-step workflow automation
Use Cases
- Automate invoice processing and approvals
- Manage employee onboarding workflows
- Handle data entry between different systems
9. Oracle Miracle Agent
Enterprise automation agents built into Oracle’s business software. Handles finance, HR, and supply chain processes without manual intervention.
Key Features
- End-to-end process automation
- Enterprise software integration
- Financial and HR workflow management
Use Cases
- Process expense reports and reimbursements
- Manage employee benefit enrollments
- Handle purchase order approvals and vendor payments
10. Microsoft Copilot Vision Agents
Business automation agents that work across Microsoft 365 and Dynamics 365. Takes ownership of complete tasks and updates systems automatically.
Key Features
- Cross-platform Microsoft integration
- Task ownership and completion
- Automated data updates
Use Cases
- Update customer records after service interactions
- Generate and distribute reports automatically
- Manage project timelines and resource allocation
11. Workday AI Agents
HR automation agents that handle employee requests and workforce management. Processes everything from time-off requests to performance reviews.
Key Features
- Employee self-service automation
- Workforce analytics and reporting
- Performance management workflows
Use Cases
- Process vacation requests and schedule coverage
- Handle new hire paperwork and system access
- Generate compliance reports and audit trails
Development and Technical Agents
12. Google Jules
Autonomous coding agent that writes complete software features. Analyzes existing code, plans implementations, and delivers working solutions.
Key Features
- Complete feature development
- Codebase analysis and planning
- Independent task execution
Use Cases
- Build new product features from requirements
- Fix bugs and optimize existing code
- Generate technical documentation automatically
13. Devin AI
Full-stack software engineering agent that builds applications from start to finish. Handles everything from planning to deployment.
Key Features
- End-to-end application development
- Multi-language programming support
- Deployment and testing automation
Use Cases
- Build complete web applications from specifications
- Create APIs and database integrations
- Handle software testing and quality assurance
Analysis and Intelligence Agents
14. Observe.AI
Real-time conversation analysis agent for sales and support teams. Monitors calls, provides coaching suggestions, and generates performance insights.
Key Features
- Real-time call monitoring and coaching
- Automated conversation summaries
- Performance analytics and insights
Use Cases
- Coach sales reps during live customer calls
- Generate call summaries and action items automatically
- Track compliance and quality metrics
15. n8n AI Agents
Custom research and data collection agents built on the n8n automation platform. Gathers information from multiple sources and organizes findings automatically.
Key Features
- Custom agent development platform
- Multi-source data collection
- Automated research workflows
Use Cases
- Monitor competitor pricing and product changes
- Gather market research from multiple sources
- Track industry news and trends automatically
AI Image Recognition: The Future of Visual Intelligence
Transforming visual analysis, AI image recognition deciphers images to drive smarter decisions across industries.
Revolutionizing AI Agents: Microsoft’s Latest Copilot Studio Enhancements
Microsoft’s Copilot Studio is redefining how AI agents are created and deployed. From autonomous operations to multi-modal interactions, here’s how the latest updates empower organizations to build next-generation AI agents.
1. Knowledge-Powered Agents
Elevate Agent Intelligence with Advanced Tuning and RAG Enhancements
- What’s New: Leverage the latest generative models, enriched Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), and analytics on knowledge sources.
- Key Features: Curate knowledge, fine-tune responses, and use Azure AI Search indexes to access custom knowledge bases.
- Best For: AI agents handling complex queries in customer service, support, or research roles.
2. Autonomous Agents
Create AI That Works for You—No Prompts Needed
- What’s New: Build agents that autonomously complete tasks without manual intervention.
- Key Features: Configure agents from scratch or customize prebuilt models in Copilot Studio.
- Best For: Automating repetitive workflows, enhancing productivity, and saving time.
3. Multi-Modal Agents
Expand AI Capabilities Beyond Text-Based Interactions
- What’s New: Enable agents to process voice commands and analyze uploaded images.
- Key Features: Integrate generative AI into IVR systems and interactive apps, supporting voice and visual inputs.
- Best For: Voice-enabled AI agents for customer support, interactive user experiences, and image-based data queries.
4. Enterprise-Grade Multi-Channel Agents
Build Scalable AI Agents with Microsoft 365 SDK
- What’s New: Develop enterprise-grade agents for Teams, Copilot, and web platforms using the SDK in C#.
- Key Features: Seamlessly connect Copilot Studio agents with Azure AI services like Semantic Kernel or AI Foundry.
- Best For: Enterprise deployments requiring robust, multi-channel, and scalable AI solutions.
Kanerika’s AI Agent Suite: Purpose-Built Solutions for Businesses
Each agent integrates into your current workflows to boost efficiency and productivity across different business functions.
1. DokGPT – Intelligent Information Retrieval
DokGPT lets you find information from documents using everyday language. It works with multiple file types and languages, giving you quick insights without complex search commands. Perfect for businesses with lots of documents, it helps employees locate relevant information fast.
2. Karl – Intelligent Data Analyzer
Karl turns your plain language questions into clear data insights. It creates visual charts and trends that make data easy to understand for anyone on your team. Great for making data-driven decisions without needing specialized analysts.
3. Alan – Legal Document Summarizer
Alan breaks down complex legal documents into clear summaries. It reads through long contracts and legal texts, pulling out the key information you need. Saves legal professionals time by cutting down manual document review.
4. Susan – Personal Information Redactor
Susan finds and removes personal information from documents automatically. It keeps you compliant with data protection rules like GDPR and HIPAA. Helps businesses maintain privacy standards without manual work.
5. Mike – Document Accuracy Checker
Mike catches mathematical errors and formatting problems in your documents. It explains what’s wrong and suggests fixes, helping you create accurate documents. Useful for teams that need precise documentation.
6. Jennifer – Phone Call Manager
Jennifer handles phone calls through voice commands. It can schedule meetings and gather information, keeping your team organized without extra staff. Good for businesses wanting to automate routine phone tasks.
Why Small Language Models Are Making Big Waves in AI
Discover how small language models are driving innovation with efficiency and accessibility in AI.
Experience the Future of Business with Kanerika’s Agentic AI Expertise
Kanerika brings deep expertise in agentic AI and AI/ML, helping businesses across manufacturing, retail, finance, and healthcare transform the way they operate. Our purpose-built AI agents and custom generative AI models are designed to solve real business challenges—removing bottlenecks, improving decision-making, and boosting operational efficiency.
From faster information retrieval and real-time data analysis to video intelligence, smart surveillance, and inventory optimization, our solutions enable organizations to streamline workflows and cut costs. We also support advanced capabilities like sales and financial forecasting, arithmetic data validation, vendor evaluation, and smart product pricing—empowering teams to focus on growth while AI takes care of complexity.
As trusted partners of Microsoft and Databricks, we deliver solutions backed by the highest quality and security standards, including CMMI Level 3, ISO 27001, ISO 27701, and SOC 2 certifications. With Kanerika, enterprises gain AI-driven innovation with confidence, reliability, and scale.
Partner with us to drive productivity, optimize resources, and redefine what’s possible for your business with AI.
Streamline, Optimize, and Scale with AI-Powered Agents!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of an agent in AI?
An AI agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions to achieve specific goals. For example, a self-driving car uses sensors and AI algorithms to navigate roads autonomously, making real-time decisions to ensure safety and efficiency.
Is Alexa an AI agent?
Yes, Alexa is an AI agent. It interacts with users through natural language processing, understanding commands, and performing tasks like playing music, controlling smart devices, and answering queries. Its ability to adapt and learn over time makes it an intelligent agent.
Is ChatGPT an AI agent?
Yes, ChatGPT is an AI agent. It uses natural language processing to generate human-like responses based on user inputs. As a conversational AI, it assists in tasks like answering questions, brainstorming ideas, and providing recommendations.
How do AI agents work?
AI agents work by perceiving inputs from their environment, processing the information using algorithms, and acting to achieve defined objectives. They rely on sensors, data, and predefined rules or learning models to make decisions and perform tasks autonomously.
What are the types of AI agents?
AI agents include simple reflex agents, model-based agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, and learning agents. Each type varies in complexity, with learning agents being the most advanced, capable of adapting and improving over time.
How to create an AI agent?
Creating an AI agent involves defining its purpose, gathering data, designing algorithms or models, and programming it to interact with its environment. Tools like Python, TensorFlow, or OpenAI APIs can be used to develop and train AI agents effectively.
What are the functions of an AI agent?
AI agents perform functions like data analysis, decision-making, task automation, and interaction with users. They can optimize processes, predict outcomes, provide insights, and enhance user experiences in fields like customer service, healthcare, and logistics.