Standing at the crossroads of AI implementation, businesses worldwide face a critical decision that could shape their competitive edge. According to Gartner’s 2024 CIO Agenda, 55% of organizations are actively implementing or planning to deploy open-source language models to drive innovation and reduce costs. Yet, the choice between Alpaca vs Llama AI remains a key decision that can significantly impact your operational efficiency, development costs, and market responsiveness.
Companies are increasingly integrating large language models (LLMs) to enhance operations and drive growth. For instance, Palantir Technologies has leveraged AI to accelerate its growth, reporting a significant revenue increase in the third quarter of 2024, surpassing analyst expectations. This growth is attributed to their AI initiatives, which have significantly improved operational efficiency and customer engagement.
Similarly, Bayer, a multinational pharm and biotech firm, has ventured into AI by collaborating with Microsoft to develop specialized AI models fine-tuned with industry-specific data. This initiative aims to address common challenges within industries, allowing collaboration and enhancing customer outcomes.
While tech giants invest billions in proprietary AI models, Stanford’s Alpaca and Meta’s Llama AI have emerged as powerful, cost-effective alternatives that democratize artificial intelligence for businesses of all sizes.
This comprehensive guide helps you make an informed decision between Alpaca vs Llama AI. We’ll explore their unique strengths, practical applications, and real-world performance metrics to determine which model better aligns with your business growth objectives.
Alpaca vs Llama AI: Understanding the Two Leading LLMs
Alpaca and Llama are two prominent large language models (LLMs) developed to advance AI’s capabilities in understanding and generating human-like text. Llama, created by Meta AI, was first released in early 2023 and was designed to provide high-performing language models in various sizes, including 7B, 13B, 33B, and 65B parameters. Known for its robust natural language processing abilities, Llama’s development aimed to offer a more accessible alternative for researchers, enabling a broader understanding and application of LLM technology.
Building on Llama’s foundation, Alpaca was developed by Stanford University and launched in March 2023 as a fine-tuned version of Llama’s 7B model. Alpaca stands out for its focus on instruction-following capabilities, making it effective for tasks where nuanced responses and task-specific comprehension are essential. By enhancing Llama’s original framework, Alpaca provides a streamlined, cost-effective solution for various applications, offering high performance with relatively lower computational requirements.
“Llama 3.1 now powers Meta AI, which is quickly becoming the most widely used AI assistant,”
– -Yann LeCun, Meta’s chief AI scientist
Transform Your Business with AI-Powered Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
Alpaca vs Llama AI: Architectural Differences
The architectural differences between Alpaca and Llama are subtle but significant, given that Alpaca is essentially a fine-tuned adaptation of Llama with modifications geared toward instruction-following tasks. Here’s a breakdown of how their architectures differ and how these distinctions align with their respective purposes.
Core Architecture
Both Llama and Alpaca are built on a transformer architecture—a powerful model design widely used in natural language processing tasks. This architecture supports capabilities like sequence-to-sequence learning, which is essential for text generation and understanding. However, while Llama is optimized for broad language comprehension, Alpaca’s fine-tuning focuses specifically on instruction-following, making slight alterations in training emphasis and response style to suit this purpose.
Model Adaptations and Layer Focus
Llama uses its transformer layers in a balanced way, focusing on extracting contextual relationships within a large corpus of internet text. This design allows Llama to perform well across a variety of language tasks such as content generation, translation, and summarization, without a specialized inclination toward instruction-following.
Alpaca, on the other hand, modifies this approach by retraining the model layers on instruction-following data derived from OpenAI’s text-davinci-003 responses. This adaptation adjusts certain attention weights in the transformer layers to prioritize task adherence and structured responses, making Alpaca effective in scenarios where detailed instructions and specific outcomes are required.
Parameter Tuning and Scaling
Llama is offered in multiple parameter sizes—7B, 13B, 33B, and 65B—giving users flexibility depending on computational resources and task complexity. This range allows it to scale up for highly complex tasks or down for lightweight applications.
Alpaca, meanwhile, is restricted to the 7B parameter size as it was developed by fine-tuning this specific model within the Llama family. Its 7B size emphasizes accessibility and cost-efficiency, focusing on lower-resource deployments while maintaining the ability to provide structured, instruction-focused outputs.
LLM Agents: Innovating AI for Driving Business Growth
Explore how LLM agents are transforming AI to fuel unprecedented business growth and innovation.
Training Data Focus
The architectural and training distinctions also extend to data focus:
Llama is trained on a broad dataset from a diverse range of sources, enabling a wide understanding of language patterns and themes, making it effective for general-purpose applications.
Alpaca incorporates an additional layer of instruction-based fine-tuning, honing the model to provide coherent responses to specific instructions. This training methodology tweaks the Llama architecture to better recognize and follow sequential instructions, aligning with Alpaca’s intended use cases, such as code generation, guided explanations, and step-by-step educational assistance.
Application-Specific Optimization
Lastly, the optimization goals vary:
Llama is optimized for versatility, aiming to be a one-size-fits-all model with architecture suited for adaptability across diverse NLP tasks.
Alpaca incorporates optimized task-specific adjustments, which improve the transformer layers’ responsiveness to directives, effectively making it a specialized tool for businesses or applications needing structured, instructional responses.
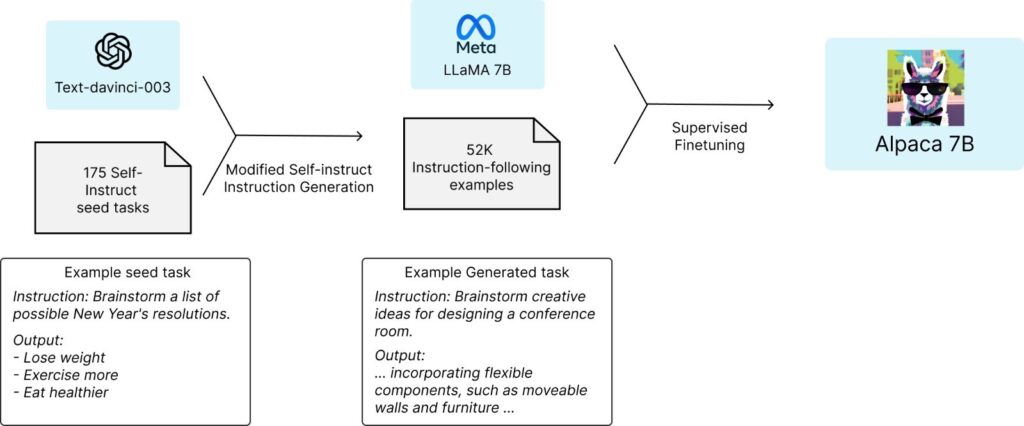
Source: Stanford Alpaca
Alpaca vs Llama AI: Key Differences Between the Two Language Models
Alpaca and Llama are two prominent large language models (LLMs) that, while related, exhibit distinct differences across various dimensions.
1. Development and Purpose
Llama: Developed by Meta AI, Llama (Large Language Model Meta AI) serves as a foundational model designed for versatility across a broad spectrum of natural language processing tasks. Its primary aim is to provide a robust, open-source alternative to existing large-scale models, facilitating research and application development.
Alpaca: Created by Stanford University, Alpaca is a fine-tuned version of Llama’s 7B model. It focuses on enhancing instruction-following capabilities, making it particularly adept at tasks requiring detailed and specific responses.
2. Training Data and Methodology
Llama: Trained on a diverse range of internet text, Llama’s training corpus encompasses approximately 1.4 trillion tokens. This extensive dataset enables the model to develop a broad understanding of language, catering to various applications.
Alpaca: Alpaca’s training involved fine-tuning the Llama 7B model using 52,000 instruction-following demonstrations generated from OpenAI’s text-davinci-003. This fine-tuning process enhances Alpaca’s performance in tasks that require following specific instructions.
3. Model Sizes and Parameters
Llama: Available in multiple sizes—7B, 13B, 33B, and 65B parameters—Llama caters to diverse computational needs and performance requirements. This scalability allows users to select a model size that aligns with their specific use cases and resource availability.
Alpaca: Fine-tuned specifically from the 7B Llama model, Alpaca offers a more lightweight and accessible option, particularly suitable for applications where computational resources are limited.
4. Capabilities and Performance
Llama: Exhibits strong general-purpose language understanding and generation capabilities, making it suitable for a wide array of tasks, including content creation, translation, and summarization.
Alpaca: Excels in instruction-following tasks, demonstrating performance comparable to larger models like OpenAI’s text-davinci-003 in specific scenarios. Its fine-tuning enhances its ability to generate detailed and contextually relevant responses based on user instructions.
5. Multimodal Capabilities
Llama: Primarily a text-based model, Llama does not inherently support multimodal inputs or outputs. Its design focuses on text generation and understanding.
Alpaca: Similarly, Alpaca is centered on text-based instruction following and does not possess multimodal capabilities.
Source: Meta Llama
6. Use Cases and Business Applications
Llama: Due to its versatility, Llama is suitable for various applications, including:
- Content generation for marketing and communication
- Language translation services
- Summarization of large documents
- Development of chatbots and virtual assistants
Alpaca: With its enhanced instruction-following capabilities, Alpaca is particularly effective for:
- Generating code snippets based on specific requirements
- Providing step-by-step explanations for complex processes
- Assisting in educational tools that require detailed responses
7. Availability and Licensing
Llama: Released under a research-focused license, Llama is available for non-commercial use, primarily targeting the research community. Its open-source nature encourages collaboration and further development.
Alpaca: While Alpaca’s training data and methodology are publicly accessible, its model weights were initially withheld due to licensing constraints. This approach ensures compliance with usage policies while promoting transparency in research.
8. Latest Versions and Updates
Llama: As of 2024, Meta AI has released Llama 3, featuring significant improvements in performance and efficiency. The latest version includes enhanced training data and optimized architectures, resulting in better language understanding and generation capabilities.
Alpaca: Building upon the advancements in Llama 3, Stanford University has developed Alpaca 2, incorporating the latest training techniques and datasets to further enhance its instruction-following performance.
9. Performance Benchmarks
Llama: Demonstrates strong performance across various natural language processing benchmarks, showcasing its versatility and robustness in handling diverse tasks.
Alpaca: Excels in benchmarks that assess instruction-following and task-specific performance, highlighting its specialization in generating detailed and accurate responses based on user instructions.
10. Pricing and Licensing Considerations
Llama: Being open-source and available for research purposes, Llama does not entail direct licensing costs. However, deploying larger models may require substantial computational resources, leading to increased operational expenses.
Alpaca: Similarly, Alpaca is open-source and accessible for research and non-commercial use. Its lightweight nature, derived from the 7B Llama model, makes it more cost-effective in terms of computational resource requirements.
Mistral vs Llama 3: How to Choose the Ideal AI Model?
Discover key differences between Mistral and Llama 3 to choose the perfect AI model for your business needs.
| Aspect | Alpaca | Llama |
| Developed By | Stanford University | Meta AI |
| Purpose | Instruction-following and specific tasks | General-purpose language understanding |
| Training Method | Fine-tuned on Llama 7B with instruction data | Trained on diverse internet text |
| Parameter Sizes | Based on Llama 7B | Available in 7B, 13B, 33B, 65B |
| Best Use Cases | Code generation, step-by-step guidance | Content generation, translation, chatbots |
| Capabilities | Excels in instruction-following | Strong in general language processing |
| Multimodal Capabilities | Text-based only | Text-based only |
| Latest Version | Alpaca 2 | Llama 3 |
| Performance Strength | Detailed responses for specific tasks | Broad NLP tasks |
| Availability | Open-source, research-focused | Open-source, research-focused |
| Licensing | Free for research and non-commercial use | Free for research and non-commercial use |
| Computational Needs | Lightweight, lower resource requirements | Varies by model size; higher for larger models |
Boost Productivity and Scale Faster With Tailored AI Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
Alpaca vs Llama AI: Top Business Use Cases
Alpaca Use Cases
1. Customer Support Automation
Alpaca’s instruction-following capabilities make it suitable for automating customer support responses, especially for FAQs or troubleshooting guides. It can understand specific queries and provide accurate, step-by-step guidance.
2. Educational Content Creation
Alpaca can generate structured educational materials or tutorials based on instructions, making it useful for e-learning platforms and corporate training resources. Its ability to follow detailed prompts enables it to create tailored learning modules.
3. Code Assistance and Debugging
Developers can use Alpaca to generate code snippets, suggest fixes, or provide debugging tips. With its fine-tuning on instruction-following tasks, Alpaca is effective in generating responses specific to programming-related queries.
4. Product Recommendations
Alpaca is used in recommendation engines where it follows structured prompts to suggest products based on customer preferences, previous purchases, or search history.
5. Process Automation in Internal Tools
For internal company operations, Alpaca can automate repetitive and structured tasks, such as filling forms or handling standard workflows, by following pre-defined instructions.
Llama Use Cases
1. Content Generation for Marketing
Llama’s broad natural language capabilities make it effective for generating high-quality marketing content, such as blog posts, social media captions, or newsletters, that engage customers and boost brand awareness.
2. Customer Service Chatbots
Llama can serve as the foundation for conversational chatbots that handle customer inquiries, providing coherent responses and answering frequently asked questions to enhance customer service.
3. Document Summarization
With its strong language processing skills, Llama can summarize lengthy documents or reports, making it ideal for industries needing quick and comprehensive summaries of dense information, like finance or legal sectors.
Source: Meta Llama
4. Language Translation Services
Llama can support businesses in translating documents, messages, or customer inquiries in multiple languages, facilitating global customer engagement and communication.
5. Sentiment Analysis for Customer Insights
By analyzing customer reviews or social media feedback, Llama can help businesses gauge customer sentiment, allowing them to adapt products and services to better meet client expectations.
Claude 3.5 vs GPT-4o: Key Differences You Need to Know
Uncover the essential differences between Claude 3.5 and GPT-4 to make an informed AI model choice.
Kanerika: Your #1 Choice for AI Implementation Services
Kanerika stands as your premier partner for AI implementation, offering unparalleled expertise in crafting advanced, innovative AI solutions tailored to meet specific business needs. As a leading AI services provider, we bring a wealth of experience, having delivered numerous successful AI projects across industries including banking, retail, manufacturing, and logistics. Our team specializes in leveraging cutting-edge AI technologies, such as ChatGPT, Llama, Alpaca, and Claude, to design and implement custom AI models that align perfectly with your business goals.
Our solutions focus on enhancing productivity and efficiency while optimizing resources and reducing costs, enabling your organization to achieve significant operational improvements. Whether you’re aiming to automate processes, enhance customer engagement, or gain deeper insights from your data, Kanerika’s AI expertise ensures that you receive tailored, high-impact solutions. Partner with Kanerika and experience the transformative power of AI in driving your business forward with confidence and innovation.
Drive Innovation and Growth With Cutting-Edge AI Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Alpaca and Llama AI model?
Alpaca is a fine-tuned version of Meta’s Llama 7B model, developed by Stanford specifically for instruction-following tasks. While Llama is a general-purpose model trained on diverse internet text, Alpaca enhances Llama’s instruction-following abilities for tasks requiring detailed, step-by-step responses.
Is Alpaca AI good?
Yes, Alpaca AI is highly effective for instruction-following tasks. Its fine-tuning makes it ideal for scenarios where structured, directive responses are needed. Alpaca’s performance on such tasks rivals that of larger models like GPT-3.5, offering a lightweight yet powerful solution for applications with specific instructional needs.
What does Llama AI stand for?
Llama stands for “Large Language Model Meta AI.” Developed by Meta AI, it’s designed as a versatile language model capable of handling various natural language processing tasks, from summarization to content generation, and aims to provide a robust, open-source option for research and application development.
Is Llama better than GPT?
Whether Llama is better than GPT depends on the use case. GPT models like GPT-4 offer advanced capabilities, especially in generative tasks, while Llama is a more open-source, accessible alternative suited for research and specific NLP tasks, allowing users flexibility in customization for diverse applications.
Is Alpaca AI free?
Yes, Alpaca AI is free and open-source for research and non-commercial use. It was released by Stanford as an accessible alternative to commercial models, making advanced instruction-following capabilities available to researchers and developers who seek lightweight, cost-effective AI solutions.
Is Llama AI free?
Llama AI is also free and open-source, with Meta making it available primarily for research purposes. While it’s accessible without cost for non-commercial use, its licensing terms restrict direct commercial deployment, aligning it more with research and development applications in the AI community.
Is Llama owned by Meta?
Yes, Llama is developed and owned by Meta AI, the artificial intelligence division of Meta (formerly Facebook). Meta’s goal with Llama is to provide a powerful, open-source language model that advances research and accessibility in AI applications while remaining available for non-commercial use.
Is Llama better than Alpaca?
Llama and Alpaca each excel in different areas. Llama is more versatile for general NLP tasks, while Alpaca is specialized for instruction-following, making it better for applications needing clear, directive responses. Choosing between them depends on whether general language processing or specific, instructional output is prioritized.









