Introduction: The Transformative Power of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
What is RPA?
RPA utilizes software robots (“bots”) to automate repetitive, rules-based, high-volume digital tasks. These bots mimic human interactions with digital systems (opening applications, logging in, copy-pasting data, etc.) at high speed and without errors. RPA operates at the user interface level, enabling automation across various applications, including legacy systems, without complex integrations. It is a critical tool for digital workforce implementation.
Why RPA Matters in Today’s Business Landscape:
Businesses face pressure to be agile, cost-effective, and customer-centric. RPA is a fundamental tool for digital transformation and operational excellence, driving significant improvements in:
- Operational Efficiency: Tasks completed faster, leading to higher throughput.
- Accuracy: Elimination of human error in data entry and processing, improving data quality and compliance.
- Cost Reduction: Lower operating costs through reduced manual effort and rework.
- Employee Engagement: Freeing human talent from mundane tasks for more strategic, creative, and analytical work.
What You’ll Discover:
This article explores RPA use cases across business functions and industries, the evolution to intelligent automation, and key considerations for successful implementation.
Core Benefits of Implementing RPA
Implementing RPA yields numerous advantages across the organization:
| Benefit | Key Outcome / What it means |
|---|---|
| Increased Operational Efficiency | 24/7 processing, faster task completion, higher throughput, reduced backlogs. |
| Enhanced Accuracy and Quality | Elimination of human error, improved data integrity, reduced rework. |
| Significant Cost Savings | Reduced labor costs, lower operational expenses, high ROI. |
| Improved Compliance and Auditability | Consistent process execution, detailed audit trails, easier regulatory adherence. |
| Faster Processing Times | Accelerated workflows (e.g., invoice-to-cash), improved agility. |
| Better Employee Satisfaction | Humans freed from mundane tasks, focus on strategic work, increased morale. |
| Enhanced Customer Experience | Quicker responses, faster order fulfillment, accurate information, higher loyalty. |
| Scalability and Flexibility | Easy scaling up/down of bot workforce to meet fluctuating demands. |
Robotic Process Automation Use Cases Across Core Business Functions
RPA applications are universally beneficial across various business functions:
| Business Function | Key RPA Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Data Management & Entry | Data extraction & aggregation, migration, validation & cleansing, CRM de-duplication, website scraping. |
| Financial Operations & Accounting | Invoice & PO processing, AP/AR, payroll, expense management, financial reporting, treasury management. |
| Customer Service & Support | Query management, chatbot integration, onboarding, complaint handling, call center support. |
| Human Resources (HR) | Employee onboarding/offboarding, time & attendance, recruitment, employee data management. |
| IT Operations | Software testing, system setup, help desk & ticket management, monitoring, batch processing, legacy integration. |
| Compliance & Reporting | Regulatory data collection, audit trail generation, automated report generation, basic fraud detection. |
| Supply Chain & Logistics | Inventory management, order management & fulfillment, shipping tracking, supplier onboarding, BOM management. |
A. Data Management & Entry Automation
- Data Extraction & Aggregation: Automates extraction from documents, forms, and emails, consolidating into structured formats, often using OCR.
- Data Migration & Transfer: Reliably moves large datasets between systems, crucial for upgrades or integrations.
- Data Validation & Cleansing: Checks data against rules or other systems to identify and correct inconsistencies or duplicates.
- CRM Data De-duplication: Scans CRM systems to identify, merge, or flag duplicate customer records.
- Website Scraping: Gathers public information from websites for market research, competitive analysis, or lead generation.
- Kanerika Insight: Kanerika’s accelerators ensure seamless data flow for RPA, with pre-built solutions for extraction and validation.
B. Financial Operations & Accounting Automation
- Invoice & Purchase Order Processing: Automates data extraction, matching against POs, flagging discrepancies, and posting to accounting systems.
- Accounts Payable & Receivable: Automates vendor statement reconciliation, invoice generation, payment processing, and AR reconciliation.
- Payroll Processing: Automates gathering time data, calculating pay, deductions, and generating payslips, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
- Expense Management: Automates initial review of expense reports, checks against policies, and flags violations.
- Financial Reporting: Automates data collection, reconciliation, and generation of standard financial reports, accelerating closing cycles.
- Treasury Management: Automates cash flow forecasting, investment tracking, and debt collection processes.
C. Customer Service & Support Automation
- Customer Query Management: Automates categorization of inquiries, provides templated responses, and routes complex queries to agents.
- Chatbot Integration: RPA enables chatbots to retrieve real-time data from backend systems to answer customer questions accurately.
- Customer Onboarding & Account Creation: Streamlines data input, identity verification (KYC), and account provisioning across multiple systems.
- Complaint Handling & Resolution: Automates logging, classification, routing of complaints, and initiates standard acknowledgments.
- Call Center Operations Support: Attended bots assist agents by retrieving customer data in real-time and automating data entry during or after calls.
D. Human Resources (HR) Automation
- Employee Onboarding & Offboarding: Automates data input into HRIS/payroll, system access provisioning, and document generation.
- Time & Attendance Management: Automates collection and validation of time data, calculation of hours, and integration with payroll.
- Recruitment Process Automation: Automates initial candidate screening, interview scheduling, and offer letter generation.
- Employee Data Management: Ensures data consistency across HR systems by automating updates for changes and periodic audits.
E. IT Operations Automation
- Automated Software Testing: Bots execute test scripts, input data, verify outputs, and log results for faster, more reliable testing.
- System Setup & Configuration: Automates user account creation, software installation, and system configuration across multiple machines.
- Help Desk & Ticket Management: Automates password resets, access requests, and routes complex tickets with pre-populated diagnostic information.
- Server & Application Monitoring: Automates collection and analysis of logs, generating alerts for anomalies or critical issues.
- Batch Processing & FTP Operations: Automates routine tasks like data backups, report generation, and scheduled file transfers.
- Legacy Application Integration: Bridges gaps between legacy and modern systems by interacting with UIs for data exchange.
- Kanerika Insight: Kanerika’s IT automation accelerators reduce manual effort, minimize errors, and enable IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives.

F. Compliance & Reporting Automation
- Regulatory Compliance Data Collection: Automates extraction and consolidation of data from various sources for regulatory reports (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Audit Trail Generation: Bots inherently provide detailed, immutable audit trails of all actions performed, simplifying compliance verification.
- Automated Report Generation & Distribution: Automates data compilation, report creation, and distribution to stakeholders.
- Fraud Detection: Automates initial transaction screening, flagging suspicious activities based on rules for human investigation.
G. Supply Chain & Logistics Automation
- Quality Control & Audit Automation: Automates data collection for quality checks and compliance reporting.
- Inventory Management: Monitors stock levels, forecasts demand, and automatically generates replenishment orders.
- Order Management & Fulfillment: Automates order processing, inventory allocation, pick list generation, and shipping notifications.
- Shipping & Logistics Tracking: Automates updates on shipment status across carrier portals and internal systems.
- Supplier Onboarding & Management: Automates vendor data input, contract management, and performance monitoring.
- Bill of Materials (BOM) Management: Automates updates and comparisons for BOMs across engineering, procurement, and production systems.
Here’s a revised RPA tools section for general use cases (not just supply chain):
Leading RPA Tools for Business Automation
Selecting the right RPA platform depends on your business needs, technical environment, and automation goals. Here’s what the major RPA tools offer:
UiPath
UiPath leads the market with its comprehensive automation capabilities and extensive integration options. The platform handles everything from invoice processing and data entry to customer onboarding and HR workflows. Moreover, its document understanding AI excels at processing unstructured data from emails, PDFs, and forms. UiPath’s large community and marketplace of pre-built automations accelerate deployment across departments.
Best for: Enterprises automating complex, document-heavy processes across multiple departments
Automation Anywhere
Automation Anywhere‘s cloud-native platform delivers automation at scale with minimal infrastructure requirements. The Bot Store provides ready-made solutions for common business processes like expense reporting, employee onboarding, and customer service workflows. Its intuitive interface and strong AI capabilities make it accessible for both technical and business users.
Best for: Organizations prioritizing cloud deployment and rapid scaling across business units
Blue Prism
Blue Prism‘s enterprise-grade security and governance framework makes it ideal for industries with strict compliance requirements. Additionally, the platform provides robust audit trails, role-based access controls, and centralized bot management. Its digital workforce approach treats bots as virtual employees with defined roles and responsibilities.
Best for: Financial services, healthcare, and regulated industries requiring stringent security and compliance
Microsoft Power Automate
Power Automate integrates seamlessly with the Microsoft ecosystem, automating workflows across Office 365, Dynamics 365, and hundreds of third-party applications. Its low-code interface empowers business users to build automations without extensive coding knowledge. Desktop flows handle legacy application automation, while cloud flows connect modern apps and services.
Best for: Organizations heavily invested in Microsoft technologies seeking departmental automation
Choosing the Right RPA Platform
Consider these factors when selecting an RPA tool:
- Process complexity: Simple, repetitive tasks vs. complex workflows requiring AI and decision-making
- Technical capability: Developer resources available vs. need for citizen developer tools
- Infrastructure: Cloud preference vs. on-premises requirements
- Integration needs: Existing software ecosystem and legacy system requirements
- Budget: Total cost of ownership including licensing, infrastructure, and maintenance
- Scalability: Current automation scope vs. future expansion plans
Kanerika works with all major RPA platforms, helping clients select and implement the right solution based on their unique requirements. Moreover, our platform-agnostic approach ensures you get the best tool for your specific business challenges, not a one-size-fits-all solution.
Industry-Specific RPA Use Cases
RPA addresses unique challenges across various sectors:
| Industry | Key RPA Impact Areas |
|---|---|
| Financial Services & Banking | KYC/AML, loan processing, fraud detection, payment processing, wealth management. |
| Healthcare | Appointment scheduling, patient records, billing & coding, patient outreach. |
| Insurance | Claims processing, underwriting, policy administration, regulatory compliance. |
| Manufacturing | Invoice/PO processing, supply chain optimization, production tracking, BOM management. |
| Public Sector & Government | Benefit claims, tax processing, permit/license approvals, citizen data management. |
| Retail & E-commerce | Inventory & replenishment, order fulfillment, pricing & promotions, customer feedback. |
| Telecommunications | Invoice & billing, customer service, network performance reporting, service activation. |
| Higher Education | Admissions & enrollment, course registration, financial aid, tuition tracking. |
A. Financial Services & Banking
- KYC/AML & Customer Onboarding: Accelerates identity verification and streamlines onboarding processes.
- Loan & Mortgage Processing: Automates document collection, data validation, and eligibility calculations.
- Fraud Detection & Prevention: Enhances real-time transaction screening and flags suspicious activities.
- Payment Processing: Automates routing, clearing, settlement, and reconciliation of payments.
- Wealth Management: Automates investor data management, compliance checks, and portfolio reporting.
- Kanerika Insight: Kanerika offers specialized accelerators for financial services, enhancing fraud detection and reporting.
B. Healthcare
- Appointment Scheduling & Reminders: Automates scheduling, confirmations, and reminders to reduce no-shows.
- Patient Records & Data Management: Streamlines EHR updates and information transfer while adhering to HIPAA.
- Billing & Coding Automation: Automates claim processing, coding application, and payment reconciliation.
- Patient Outreach & Post-Treatment Care: Automates sending personalized instructions, reminders, and feedback surveys.
- Asset Tracking & Management: Monitors medical equipment and automates supply replenishment.

C. Insurance
- Claims Processing: Automates initial claims registration, data validation, and payment initiation for straightforward claims.
- Underwriting & Risk Assessment: Automates data gathering and analysis for risk assessment and policy eligibility.
- Policy Administration: Automates policy creation, servicing, renewals, and cancellations.
- Regulatory Compliance Reporting: Automates data collection and checks for industry-specific regulations.
- Kanerika Insight: Kanerika empowers insurers to automate claims processing and policy administration for faster service and reduced costs.
D. Manufacturing
- Invoice & Purchase Order Processing: Streamlines the procure-to-pay cycle for materials and services.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Enhances inventory management, demand forecasting, and logistics tracking.
- Production Tracking & Reporting: Collects data from MES/IoT sensors for real-time performance monitoring.
- Bill of Materials (BOM) Management: Automates updates and comparisons for BOMs across systems.
- Quality Control & Audit Automation: Automates data collection for quality checks and compliance reporting.
E. Public Sector & Government
- Benefit Claims Processing: Automates intake, eligibility checks, and payment initiation for various government benefits.
- Tax & Revenue Processing: Automates tax return processing, revenue collection, and refund calculations.
- Permit & License Application Approvals: Streamlines application processing, initial checks, and status updates.
- Citizen Data Management: Automates updates for citizen information across government systems.
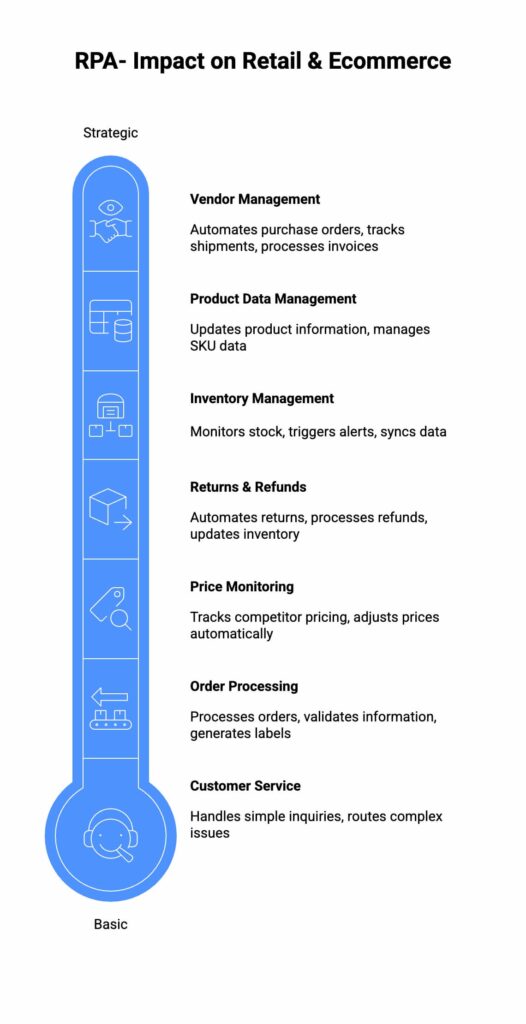
F. Retail & E-commerce
- Inventory Management & Replenishment: Monitors stock levels and automatically generates replenishment orders.
- Order Fulfillment & Tracking: Automates order processing, status updates, and shipping notifications.
- Pricing & Promotion Management: Automates price updates across platforms and manages promotional offers.
- Customer Feedback & Review Processing: Aggregates and analyzes customer feedback from various online sources.
G. Telecommunications
- Invoice & Billing Processing: Automates invoice generation, payment collection, and billing inquiry handling.
- Customer Service Operations: Enhances support for common queries and automates simple service activation.
- Network Performance Reporting: Generates automated reports on network health and service quality metrics.
- Provisioning & Service Activation: Automates customer service activation across multiple systems.
H. Higher Education
- Student Admissions & Enrollment: Automates application processing, data verification, and admissions notifications.
- Course Registration & Management: Streamlines student enrollments, add/drop requests, and course scheduling.
- Financial Aid Processing: Automates data collection, eligibility calculations, and disbursement of aid.
- Tuition & Payment Tracking: Automates payment tracking, reminders, and reconciliation with student accounts.
- Credential Management & Assessment: Automates grade processing and generation of transcripts/diplomas.
Beyond Basic RPA: Intelligent Automation & Kanerika’s Edge
Intelligent Automation (IA) combines RPA with AI/ML to handle complex, cognitive tasks and unstructured data.
The Evolution to Intelligent Automation (IA):
- Combining RPA with AI/ML: Gives bots “thinking” capabilities to handle complex processes.
- Handling Unstructured Data:
- OCR: Extracts text from scanned documents, PDFs, and images.
- NLP: Interprets, understands, and generates human language for emails, text fields, etc.
- ML: Allows bots to learn from data, identify patterns, and make predictions or decisions.
- Cognitive RPA: Bots that learn, make probabilistic decisions, and adapt to new scenarios.
- Hyperautomation: Orchestrating multiple technologies (RPA, AI, Process Mining, BPM) for end-to-end process transformation.
Comparison: Traditional RPA vs. Intelligent Automation (IA)
| Feature | Traditional RPA | Intelligent Automation (IA) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Capability | Mimics human actions (Rules-based) | Combines RPA with AI/ML for cognitive processing and learning |
| Data Handling | Primarily structured data | Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data (using OCR, NLP) |
| Decision Making | Explicit, predefined rules (“if-then”) | Learns from data, makes probabilistic decisions, adapts to new scenarios |
| Complexity of Tasks | Repetitive, high-volume, predictable tasks | Complex, cognitive tasks requiring human-like judgment |
| Learning & Adaptation | No inherent learning; requires reprogramming | Continuously learns and improves accuracy/efficiency |
| Scope of Automation | Task-specific or departmental | End-to-end process transformation (Hyperautomation) |
Kanerika’s Differentiated Approach to Digital Transformation:
- Holistic Digital Transformation Partner: Focuses on transforming end-to-end processes for strategic impact, not just isolated tasks.
- AI-Powered RPA Solutions: Integrates AI/ML for advanced analytics, predictive insights, and handling cognitive tasks.
- Industry-Specific Accelerators: Offers pre-built RPA components for rapid deployment in sectors like Finance, Healthcare, and Manufacturing.
- Custom RPA Development & Seamless Integration: Designs bespoke solutions and ensures integration with existing enterprise systems (ERP, CRM, legacy).
- Managed RPA Services: Provides ongoing monitoring, maintenance, optimization, and adaptation for continuous performance and ROI.
- Focus on Measurable Business Outcomes: Drives cost reduction, accuracy improvements, enhanced customer experience, and increased employee productivity.
Kanerika, leveraging its deep technology expertise, developed a tailored RPA solution for Trax. The “Rate Manager” was an automated auditing product that consolidated multiple rate sheets and agreements into a single online system, ensuring up-to-date rates and accommodating market disruptions. This rule-based engine compared invoices against agreed rates, flagging discrepancies and significantly reducing the manpower required for audits.
The outcome was a streamlined auditing process for Trax, with reduced costs, improved efficiency, and a move towards achieving a 100% “First Pass Yield”.
FAQs
What are the use cases for RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels at automating repetitive, rule-based tasks. Think data entry, invoice processing, or customer service chatbots – anything involving structured data and predictable steps. It frees human employees for higher-value work, improving efficiency and accuracy significantly. Essentially, RPA handles the tedious stuff so humans can focus on the strategic.
What is the main use of RPA?
RPA’s core function is automating repetitive, rule-based tasks typically handled by humans. This frees up employees for more strategic and creative work. Think of it as digital labor, handling things like data entry or invoice processing much faster and more accurately than a person. Essentially, it increases efficiency and reduces human error in mundane processes.
Where is RPA used in real life?
RPA’s real-world applications are incredibly diverse. Think of it automating repetitive computer tasks across industries – from processing invoices and claims in finance to managing customer service inquiries and scheduling appointments in healthcare. Essentially, anywhere a human interacts with software in a predictable, rule-based way, RPA can step in. This boosts efficiency and frees human workers for more complex, strategic work.
What is the RPA case?
An RPA case, simply put, is a specific task or process that Robotic Process Automation (RPA) software is designed to handle. It’s a defined set of actions, like data entry or invoice processing, automated to improve efficiency and accuracy. Think of it as a single, pre-programmed “job” for the RPA “robot.” Each case requires careful planning and configuration to ensure successful automation.
In which cases RPA will not apply?
RPA isn’t a magic bullet; it struggles with tasks needing genuine human judgment, complex decision-making, or unstructured data. It also falters when processes are highly inconsistent or frequently change, as reprogramming becomes too costly. Essentially, if the task requires creativity, critical thinking, or adapting to unpredictable situations, RPA is unsuitable.
What are the UiPath use cases?
UiPath automates repetitive digital tasks, freeing up human employees for more strategic work. Think mundane data entry, invoice processing, or even complex software interactions – anything with a clear, repeatable digital workflow. It improves efficiency, reduces errors, and boosts productivity across various departments. Essentially, if a computer screen can do it, UiPath can likely automate it faster and more accurately.
What is the use case of RPA in HR?
HR uses Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. This frees up HR staff to focus on strategic initiatives like employee engagement and development. Think automating onboarding paperwork, data entry, or even initial candidate screening – boosting efficiency and reducing errors. Essentially, RPA handles the tedious, letting humans handle the human-centric aspects.
What is the use case of automation?
Automation boosts efficiency by handling repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers for more creative and strategic endeavors. It minimizes errors inherent in manual processes, ensuring greater accuracy and consistency in output. Ultimately, automation allows businesses to scale operations more effectively and deliver improved products or services at lower costs. It’s about optimizing resource allocation for better overall performance.
What are the RPA use cases in banking?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in banking streamlines repetitive tasks, freeing human employees for more complex work. Think account opening, KYC checks, and fraud detection – all areas where RPA bots excel at accuracy and speed. This boosts efficiency, reduces operational costs, and improves customer service by handling routine inquiries swiftly and reliably. Ultimately, it allows banks to focus on strategic initiatives and innovation.
What is an RPA used for?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is used to automate simple, repetitive tasks that people do on computers. Think of it as a software robot that can click, type, and move data across applications. This helps businesses finish tasks faster and more accurately, letting employees focus on more important work.
In which scenarios can RPA be helpful?
RPA is helpful for tasks that are repetitive, rule-based, and happen often. It can automate things like data entry, generating reports, or moving information between systems. Essentially, if a human performs the same computer steps over and over, RPA can take over. This frees up staff for more complex work.
What are the 5 uses of robots?
Robots have five main uses: automating manufacturing processes, performing dangerous tasks like space or underwater exploration, assisting in healthcare (e.g., surgery and delivery), handling logistics and delivery in warehouses, and providing everyday services such as cleaning or customer support.
Is RPA a form of AI?
No, RPA itself is not a form of AI. RPA automates repetitive tasks by following fixed, step-by-step rules you set. AI involves systems that can learn, understand, and make decisions on their own. While RPA can use AI for smarter automation, it doesn’t possess intelligence by itself.
What are the 7 general use cases for prompts in Generative AI?
Prompts are used across seven key areas for Generative AI: generating new content (text, images, code), brainstorming ideas, and answering questions. They also help AI summarize information, translate languages, rewrite existing text, and follow specific instructions or commands.
What are three types of RPA?
RPA generally comes in three types: * Attended bots assist people on their desktops with specific tasks, often triggered by a user. * Unattended bots work independently in the background, fully automating complete processes without human intervention. * Hybrid bots combine both, allowing a seamless handover between human and bot tasks for complex workflows.
What are the 6 AI use case primitives?
AI’s six core capabilities are: Classification (sorting into categories), Regression (predicting numbers), and Clustering (grouping similar items). It also handles Anomaly Detection (finding unusual patterns), Recommendation (suggesting things), and Generation (creating new content like text or images).
Which tool is used for RPA?
Several tools are used for Robotic Process Automation (RPA). The most widely recognized and used include UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism. These platforms help businesses automate repetitive digital tasks.
What are 10 amazing examples of robotic process automation in practice?
RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks across many sectors. Practical examples include processing invoices, onboarding new employees, managing customer service inquiries, migrating data between systems, and generating regular reports. It also handles IT support tickets, updates patient records, reconciles financial accounts, processes insurance claims, and automates supply chain orders.
What are the 4 stages of process automation?
Process automation typically involves four main stages. First, you identify and understand your current tasks to see what can be automated. Next, you design and build the automated solution. Finally, you put it into use, then monitor and improve its performance over time.
What are three examples of automation?
Automation uses technology to perform tasks automatically without human intervention. Three examples include robotic arms on a factory assembly line, smart home devices automatically adjusting thermostats or lighting, and automated customer service chatbots or phone systems. These help make processes faster and more efficient.
In which cases will RPA not apply?
RPA won’t apply to tasks needing human judgment, understanding complex situations, or interpreting highly varied information. It’s also not suited for processes that constantly change or involve physical work outside of digital systems. For very rare or one-time tasks, other solutions are usually more efficient.
Can RPA be replaced by AI?
No, AI doesn’t typically replace RPA. Instead, AI often enhances RPA, allowing it to automate more complex tasks requiring decision-making or understanding. RPA excels at repetitive, rule-based processes, while AI adds intelligence. They are powerful when used together.
What is RPA useful for?
RPA is useful for automating repetitive computer tasks that follow clear steps. Think of it as software robots handling high-volume data entry, form filling, or moving information between different systems. This helps businesses work faster, reduce errors, and allows people to focus on more complex, creative work.
What are the top 5 RPA use cases?
The most impactful RPA use cases span multiple industries and deliver immediate ROI:
1. Invoice Processing & Accounts Payable – Bots extract data from invoices, match them with purchase orders, and process payments automatically. This eliminates manual data entry and reduces processing time by 70-80%.
2. Customer Onboarding – Automated verification of customer documents, background checks, credit checks, and account setup across systems. What took days now happens in hours.
3. Order Processing & Fulfillment – From order validation to inventory checks to shipping label generation, RPA handles the entire workflow across multiple systems without human intervention.
4. Data Migration & System Integration – Moving data between legacy systems and modern platforms while maintaining accuracy. RPA bridges gaps where APIs don’t exist.
5. Regulatory Compliance & Reporting – Automated data collection, report generation, and audit trail creation ensures consistent compliance without overwhelming your team.
At Kanerika, we’ve automated over 150+ processes across these use cases, delivering 40% growth in employee productivity and 25-70% cost efficiency for our clients.
Which industries benefit most from RPA?
While RPA delivers value across all sectors, certain industries see exceptional returns:
Financial Services leads adoption with 78% of firms implementing RPA for loan processing, fraud detection, and regulatory reporting. The heavily regulated nature and high transaction volumes make automation essential.
Healthcare uses RPA to handle claims processing, patient registration, and medical records management – reducing administrative burden by 50-60% and allowing staff to focus on patient care.
Retail & Ecommerce leverages RPA for inventory synchronization, order processing, and customer service automation – critical for handling peak shopping seasons and multi-channel operations.
Manufacturing deploys RPA for quality control checks, supply chain coordination, and production scheduling – improving operational efficiency by 35-40%.
Logistics & Supply Chain automates shipment tracking, route optimization, and invoice reconciliation – essential for managing complex, time-sensitive operations.
Kanerika has successfully delivered RPA solutions across all these industries, with proven expertise in Automation Anywhere, UiPath, and Blue Prism platforms. Our industry-specific approach ensures we understand your unique challenges and regulatory requirements.
How much does RPA implementation cost?
RPA implementation costs vary significantly based on project scope and complexity:
Small-Scale Deployments (1-5 bots): $25,000 – $75,000 Ideal for departments testing RPA with straightforward processes like data entry or report generation.
Mid-Scale Projects (5-20 bots): $75,000 – $250,000 Suitable for cross-departmental automation including invoice processing, customer onboarding, and inventory management.
Enterprise-Scale Programs (20+ bots): $250,000 – $1,000,000+ Comprehensive automation across multiple business units with complex integrations and governance frameworks.
Cost Components:
- Software licensing (per bot/per year)
- Development and configuration
- Integration with existing systems
- Training and change management
- Ongoing maintenance and support
The ROI Reality: While initial costs seem significant, most Kanerika clients see 200-300% ROI within 18-24 months through labor savings, error reduction, and productivity gains. Our solutions typically deliver 25-70% cost efficiency improvements, meaning your investment pays for itself quickly.
Kanerika offers transparent pricing and works with clients to phase implementations, allowing you to start small, prove value, and scale strategically.
Can RPA work with legacy systems?
Yes – and this is actually one of RPA’s greatest strengths. Unlike traditional integration requiring APIs or middleware, RPA works at the user interface level, meaning it can automate virtually any system a human can access.
How RPA Handles Legacy Systems:
- Screen scraping: Bots read data directly from application screens, even mainframe terminals
- Keyboard/mouse automation: Mimics human interactions without requiring system modifications
- OCR capabilities: Extracts data from scanned documents or images within legacy applications
- No API required: Works with systems that have no integration capabilities
Common Legacy Scenarios:
- Mainframe applications (AS/400, COBOL systems)
- Desktop applications without web interfaces
- Proprietary vendor software with no APIs
- Green-screen terminal systems
- Legacy ERP systems being phased out
Real-World Example: Kanerika implemented RPA for a logistics client still using a 1990s-era warehouse management system. The bots automated data transfer between the legacy WMS and their modern TMS without requiring expensive system upgrades or custom integration development.
The Business Case: Rather than spending millions replacing legacy systems, companies use RPA as a bridge technology – extending the life of existing investments while gaining automation benefits. This is particularly valuable when planning eventual system modernization, as RPA provides immediate relief while you plan long-term infrastructure changes.
At Kanerika, we’ve successfully automated processes across DOS-based systems, AS/400 mainframes, and decades-old proprietary applications – proving that legacy infrastructure doesn’t have to block your automation journey.
What's the difference between RPA and AI?
RPA and AI are complementary technologies that serve different purposes – and increasingly work together:
RPA (Robotic Process Automation):
- Follows explicit, rule-based instructions
- Handles structured, repetitive tasks
- Requires clear “if-then” logic
- Works with predictable inputs and outputs
- Examples: Data entry, form filling, report generation
AI (Artificial Intelligence):
- Learns from patterns and makes decisions
- Handles unstructured data and exceptions
- Adapts to new scenarios without reprogramming
- Works with ambiguous inputs requiring judgment
- Examples: Sentiment analysis, fraud detection, predictive forecasting
Think of it this way:
- RPA = Digital Assistant that follows your exact instructions perfectly, every time
- AI = Smart Assistant that understands context and makes judgment calls
Where They Work Together (Intelligent Automation): Modern automation combines both:
- Document processing: AI extracts data from varied invoice formats → RPA enters it into accounting systems
- Customer service: AI chatbot handles inquiries → RPA pulls customer data and processes requests
- Fraud detection: AI flags suspicious transactions → RPA initiates investigation workflows
Kanerika’s Approach: We implement both RPA and AI based on your specific needs. For the insurance client facing fraud challenges, we deployed AI/ML-driven RPA that combined:
- Predictive analytics and deep anomaly detection (AI)
- Natural Language Processing for document understanding (AI)
- Automated claim processing workflows (RPA)
- Image recognition for document verification (AI)
The result: 25% improvement in operational efficiency, 36% cost savings, and 20% faster claim processing.
Bottom line: You don’t need to choose between RPA and AI. The question is which processes need rule-based automation, which need intelligent decision-making, and which benefit from both. Kanerika helps you architect the right solution mix for maximum business impact.











