Imagine if you were given incentives on your car insurance for being a good driver – staying below speed limits, avoiding unexpected stops, and driving during low-risk periods.
Sounds like a good deal, right? That’s exactly what telematics enables in insurance.
It is also the entire business model of Allstate Insurance’s Drivewise Program – an excellent example of telematics in car insurance, transforming the way insurers engage with policyholders.
But how does it work? Drivewise users receive real-time feedback on their driving, allowing them to adjust their habits and potentially reduce their insurance premiums. This encourages both cost savings and a culture of safe driving.
According to Allied Market Research, the telematics insurance market is poised for substantial growth, expected to reach $13.78 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 19.5%.
To stand out in this market, telematics is a great strategy to offer more personalized and accurate insurance packages. Let’s explore some of the use cases of telematics in insurance as well as its impact in some other sectors.
What is Telematics in Insurance?
Here’s a simple explanation of how telematics in insurance works.
Imagine you and your friend both buy a car.
You are a calm driver, working from home and using the car only on weekends.
Your friend, on the other hand, drives his car to work all week and has a habit of taking over other people on the road.
As a result, he flags a higher likelihood of insurance claims.

Who do you think is paying the higher premium? Easy guess, right?
The use of telematics in insurance transforms how premiums are calculated. It involves the collection and analysis of driving data to determine insurance rates based on actual driving behavior rather than just demographic statistics or vehicle models.
Progressive Corporation’s Snapshot program is a stellar example of telematics in car insurance.
Using a telematics device, Snapshot gathers data on driving habits, enabling Progressive to offer discounts to safer drivers. Here’s how they collect the data:

- Mobile App: Drivers download an app that tracks their driving behavior, with agreed privacy terms. This represents the growing trend of mobile integration in telematics in the insurance industry.
- Plug-in Device: Similar to a USB device, this gadget plugs into the car and records driving data, a practical application of telematics in auto insurance.
- GPS Devices: These sophisticated devices monitor a driver’s location and movement, providing valuable data for telematics in car insurance.
- Onboard Sensors: These are embedded in vehicles to collect and transmit data, a key aspect of telematics in insurance.
- Mileage Detection: This function records and reports the distance driven, which is crucial for determining premiums in the telematics insurance market.
Use Cases of Telematics in Auto Insurance

Use Case 1 – Crash Data Reporting and Analysis
U.S. Department of Transportation statistics indicate that a car crashes every 10 seconds. This makes the need for efficient and accurate accident response more pressing than ever!
Telematics technology is revolutionizing this aspect.
The use of telematics in auto insurance for crash data analysis involves several key steps. Integrated algorithms in mobile apps or in-vehicle devices utilize sensor data to monitor crashes. Upon detecting an accident, the system promptly alerts trained agents who then confirm the incident and assess the required support level. This immediate connection to emergency services, facilitated by telematics, ensures rapid deployment to the crash site.
Post-accident, the telematics system facilitates the dispatch of towing services and communicates detailed incident reports to the insurance carrier. This report includes comprehensive data on the crash, vehicle damage, and any bodily injuries, allowing for the quick initiation of the claims process.
Also Read- Improved Processes: Streamlining Operations with Generative AI in Insurance
Use Case 2 – Theft Prevention with GPS Tracking
There is a significant global challenge of road safety and vehicle theft.
The World Health Organization highlights the gravity of the issue, with approximately 1.35 million people losing their lives on roads annually. Meanwhile, a vast majority are vulnerable road users, like pedestrians, motorcyclists, and cyclists.
So, the question arises – can telematics enable insurance companies, fleet operators, and vehicle owners to prevent injuries, deaths, and financial losses on the road?
The short answer is yes.
By integrating telematics, the landscape of vehicle safety and theft prevention is transforming.
Vehicles equipped with GPS trackers provide real-time geographical location data, enabling a swift response in case of theft or accidents.
Use Case 3 – Fraud Detection and Prevention

Telematics use tools like Safety Tag + Coloride to optimize fraud detection
When it comes to usage-based insurance (UBI), there is a risk of data manipulation by drivers seeking lower premiums.
This brings us to the significance of independent trip detection, a key feature enhancing the reliability of UBI.
While mobile-only offerings in telematics in the insurance industry indicate growing acceptance and potential, they also present certain limitations, particularly in fraud detection.
The issue with smartphone-based solutions is their susceptibility to manipulation; users can simply turn off their mobile devices, resulting in unrecorded trips.
However, innovations like the Safety Tag + Coloride are addressing these challenges head-on in telematics in car insurance.
Their independent trip detection functionality records and stores all vehicle movements, irrespective of whether a smartphone is connected. Once the device reconnects, the data is transmitted, providing a comprehensive record of all trips.
The implementation of such features in telematics for auto insurance is vital for sustaining the credibility of UBI.

Use Case 4 – Risk Assessment for Young and High-Risk Drivers
Within the use of telematics in insurance, one significant challenge is the higher insurance costs faced by certain demographics, particularly young male drivers aged 18 to 25.
Historically, this group has been associated with a higher frequency of accidents, leading to inflated insurance rates.
However, telematics in auto insurance presents a revolutionary solution.
The integration of telematics devices allows these drivers to demonstrate safer driving habits than what statistical averages might suggest. By monitoring their actual driving behavior, telematics in car insurance provides a platform for young and high-risk drivers to potentially lower their insurance premiums.
Beyond tracking driving habits, telematics technology encompasses on-board diagnostics (OBD), capable of identifying and predicting mechanical issues before they escalate.
The importance of this feature cannot be overstated, especially when considering heavy vehicles like 18-wheelers. OBD systems can detect early signs of critical failures in brakes, engines, or other systems, allowing for timely maintenance and averting potential disasters.
Use Case 5 – Enhanced Fleet Management and Safety

Statistics reveal that fleet vehicles utilizing telematics experience 20% to 25% fewer collisions.
Telematics devices offer fleet managers a comprehensive, real-time view of each vehicle’s location, fuel usage, and idle times. This granular data is instrumental in optimizing route planning and scheduling, leading to increased productivity, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced profitability.
Moreover, telematics significantly reduces the time fleet managers spend coordinating drivers and loads. Enhanced route evaluation leads to greater efficiency and more accurate Estimated Time of Arrivals (ETAs).
Telematics also ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, such as tracking driver hours through electronic logging devices (ELDs).
Telematics also supports innovative approaches like gamification strategies, rewarding drivers for safe practices. This has proven to reduce dangerous driving behaviors by up to 34%.
Business Case Studies of Insurance Tech Implementation
In the first instance, a leading insurance company was facing difficulties in financial modeling and forecasting.
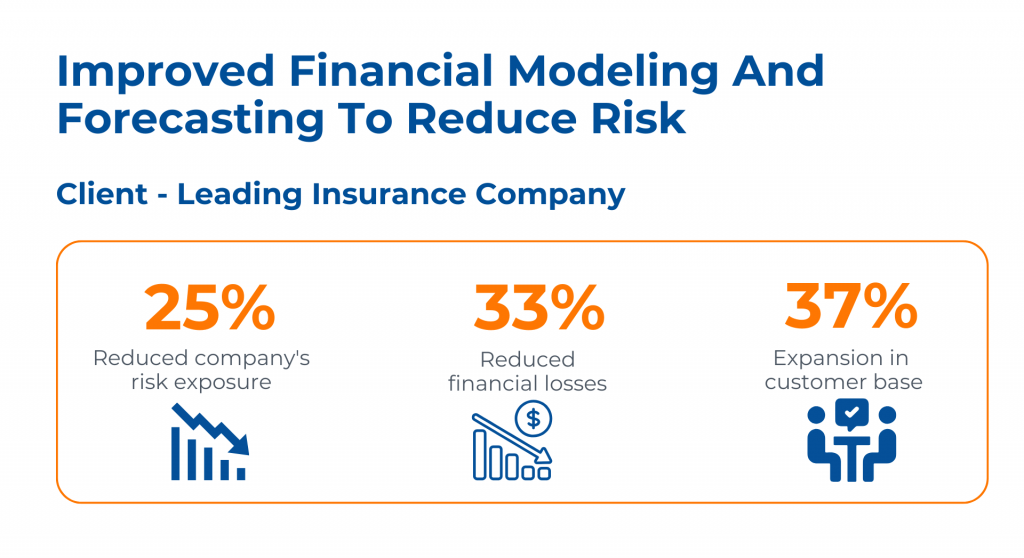
To resolve this, Kanerika implemented advanced AI data models to conduct thorough financial analysis. Leveraging Machine Learning algorithms like Isolation Forest and Auto Encoder, the company successfully mitigated fraudulent activities and could forecast better financial models.
As a result, the company experienced a notable 25% reduction in risk exposure and a corresponding 33% decrease in financial losses. Additionally, there was a substantial 37% growth in the customer base.
In another case, a prominent global insurance leader encountered challenges associated with manual data integration, leading to errors and potential compliance risks.
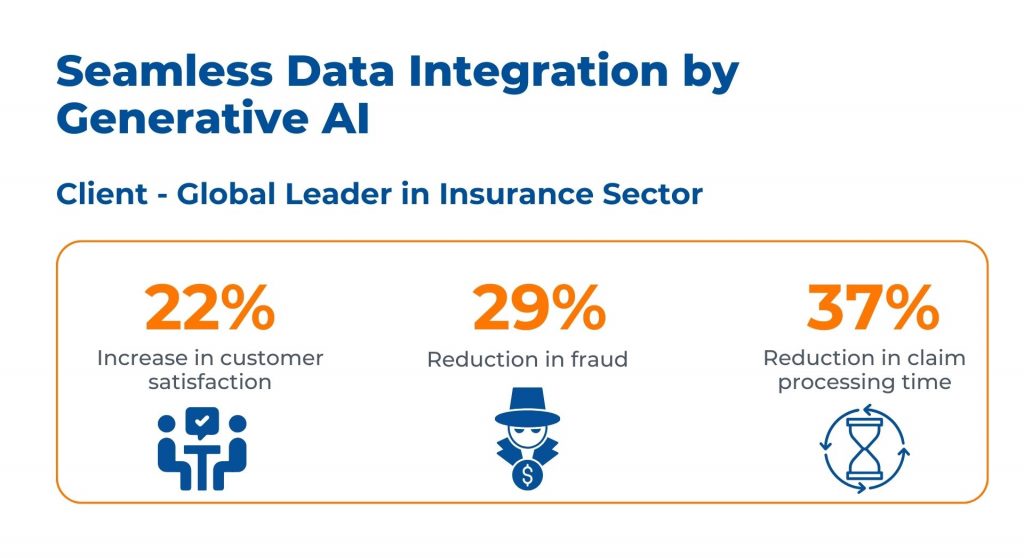
To address these issues, Kanerika implemented strategic solutions, automating data extraction through Kafka and standardizing data using Talend.
Utilizing advanced AI models such as TensorFlow and PyTorch, the integration process was streamlined, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
As a result of these initiatives, the company witnessed a remarkable 22% increase in customer satisfaction and a significant 29% reduction in fraudulent activities. Additionally, there was a notable 37% decrease in claim processing time.
Impact of Telematics on Other Insurance Sectors
Telematics in Health Insurance
Health insurers have always relied heavily on data to assess risk and determine coverage. Traditional factors like age, medical history, and lifestyle choices have been standard in profiling applicants.
However, telematics changes this.
By integrating data from fitness monitors, health insurance companies can now access detailed insights into an individual’s physical activities and overall fitness.
This enables the creation of activity-based reward programs and offers discounts to those willing to share such information.

Telematics in Life Insurance
Similarly, life insurance is undergoing a revolution with telematics. Insurers can use wearable technology to track clients’ lifestyle and health markers, offering more tailored life insurance plans.
By understanding an individual’s activity levels and health habits, telematics in life insurance ensures that policies are reflective of actual lifestyle risks.
Telematics in Home Insurance

Telematics allows companies to monitor home conditions to reduce insurance claims
In 2024, 69.91 million households in the US will be actively using smart home devices.
These tools can relay critical information about a home’s condition, such as the state of electrical systems or HVAC maintenance. This data aids insurers in assessing the risk of insuring a particular property, potentially leading to lower premiums for well-maintained homes.
Additionally, telematics can alert both homeowners and insurers to necessary maintenance, thereby reducing the likelihood of insurance claims.
When it comes to commercial property insurance, telematics continuously monitors the condition of crucial safety systems like fire alarms and water leak detectors.
Real-time alerts not only inform insurers about the risk profile of the property but also provide early warnings for potential claims.

Kanerika: Your Partner in Insurance Technology
Telematics devices, though transformative in providing real-time insights into driving habits, bring forth a major challenge – data privacy and management. Moreover, the need to share this data with various parties for analysis and insight generation adds a layer of complexity.
Partnering with Kanerika will take care of all these issues so that insurance companies can focus on their tasks better.
Kanerika ensures robust data privacy and security, employing advanced encryption and anonymization to protect user information while complying with regulations.
With Kanerika, insurance technology is just a click away.
Explore Kanerika’s scalable and customizable solutions today!

FAQs
Which type of insurance uses telematics?
Telematics insurance uses technology to track your driving habits. This means your insurer monitors things like speed, acceleration, and braking through a device in your car or smartphone app. Your premiums are then adjusted based on your driving score, rewarding safer drivers with lower costs. It’s a data-driven approach to making car insurance more personalized.
What is telematics and how does it work?
Telematics is essentially using technology to remotely monitor and manage vehicles or other assets. It works by collecting data (location, speed, fuel consumption, etc.) via sensors and transmitting it wirelessly for analysis. This data provides insights for improved efficiency, safety, and cost reduction. Think of it as giving your vehicle a digital brain and a constant report card.
What are the disadvantages of telematics?
Telematics, while offering many benefits, also presents drawbacks. Privacy concerns arise from the constant tracking of vehicle data and driver behavior. There’s also the potential for system malfunctions or hacking, leading to data breaches or operational failures. Finally, the reliance on technology can create a new layer of complexity and associated costs.
Why do I need telematics?
Telematics gives you superpowers over your vehicles. It transforms raw data into actionable insights about driver behavior, vehicle performance, and location, boosting efficiency and safety. Essentially, it helps you optimize your fleet’s operations and reduce costs, from fuel savings to preventative maintenance. Think of it as having a constantly watchful, data-driven co-pilot for all your vehicles.
Who uses telematics?
Telematics isn’t just for trucking fleets anymore! Anyone benefiting from location tracking, vehicle diagnostics, or driver behavior monitoring uses it. This ranges from individual drivers wanting safer habits to large corporations managing sprawling fleets and optimizing logistics. Essentially, anyone wanting better control and insight into their vehicles and drivers benefits.
Does Allianz use telematics?
Yes, Allianz offers telematics programs in several regions, though availability depends on your location and specific policy. These programs typically use mobile apps or devices to track driving behavior, potentially leading to discounts for safe driving. Essentially, it’s a way Allianz uses technology to better assess and reward responsible drivers.
Where are telematics used?
Telematics finds a home wherever location, behavior, and condition data matter. Think vehicle fleet management optimizing routes and fuel efficiency, but also in asset tracking (think shipping containers), personal safety devices, and even agricultural machinery monitoring crop health. Essentially, any moving or monitored object benefits from its data-gathering capabilities. The applications are surprisingly diverse and constantly expanding.
Is telematics an IoT?
Telematics is essentially a specialized application *within* the broader Internet of Things (IoT). It focuses specifically on the remote monitoring and management of vehicles and their assets. While all telematics is IoT, not all IoT is telematics; IoT encompasses a far wider range of connected devices and applications. Think of telematics as a niche subset of the IoT ecosystem.
Is telematics hardware or software?
Telematics isn’t purely hardware or software; it’s a *system*. Think of it like a car: the hardware is the GPS device and sensors, while the software processes that data, providing insights and services. Essentially, it’s the integrated combination of both working together.
What is black box telematics?
Black box telematics is essentially a device in your vehicle that secretly monitors your driving habits. It records data like speed, braking, acceleration, and location, often transmitted to a company for analysis. This information is used primarily for insurance purposes – to assess risk and potentially adjust premiums based on driving behavior. It raises privacy concerns for some drivers due to the constant data collection.
Is telematics a tracking device?
No, telematics is more than just a tracking device. It’s a broader system using GPS and other sensors to collect vehicle data, analyzing it for various purposes. Think of a tracker as a single function; telematics is the entire suite of services built around that data – from fleet management to driver behavior analysis. It uses tracking as *one* component to deliver a complete picture.
What data does telematics collect?
Telematics gathers a wealth of vehicle data. This includes location (GPS), driving behaviors like speed and acceleration, engine performance metrics, and even potentially driver habits through things like phone usage detection. Essentially, it creates a detailed record of the vehicle’s operation and its driver’s actions. This data can be used for various purposes, from insurance to fleet management.
What is the full form of telematics?
Telematics isn’t an acronym with a readily available “full form” like many others. Instead, it’s a portmanteau combining “telecommunications” and “informatics.” Think of it as the merging of remote communication technologies with data processing and analysis. Essentially, telematics uses wireless tech to collect, transmit, and interpret data about moving objects.
How are telematics used?
Telematics essentially turns your vehicle into a data-generating machine. It uses sensors and GPS to track location, driving behavior, and vehicle health. This information is then used for everything from optimizing routes and improving fuel efficiency to providing roadside assistance and preventing theft. Ultimately, it enhances safety and improves management of fleets or individual vehicles.
What does telematics record?
Telematics systems record a vehicle’s location, speed, and driving behavior. This data includes things like acceleration, braking patterns, and even mileage. Essentially, it creates a detailed digital log of every trip, offering insights into driving habits and vehicle performance. This information can be useful for insurance, fleet management, or personal vehicle diagnostics.









