Banks are the backbone of the economy. They keep money moving, credit flowing, and businesses running. When things go wrong, like during a pandemic or an inflation spike, banks feel the pressure first. And lately, that pressure has been building fast.
To keep up, banks are turning to automation. According to Gartner, 90% of financial institutions now utilize Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in some form. The global RPA market in financial services is expected to reach $ 2.06 billion by 2025, growing at a nearly 39% CAGR. RPA in banking has become essential. It helps banks handle tasks such as account opening, KYC checks, and customer service more efficiently and with fewer errors. That frees up staff to focus on real problems, not paperwork.
In this article, we will explore the role of RPA in the banking industry and its benefits to banks and financial institutions.
Drive Smarter Banking with Intelligent RPA Automation!
Partner with Kanerika to unlock automation-driven efficiency and growth.
What is RPA in Banking?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software bots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. In banking, where vast amounts of data and processes need to be managed daily, RPA has become a key enabler of efficiency, accuracy, and compliance. Instead of replacing people, RPA acts as a digital workforce that supports employees by handling routine work, freeing them up for more strategic and customer-focused roles.
According to Allied Market Research, the RPA and hyperautomation market in banking was valued at USD 745.4 million in 2021 and is projected to reach USD 7.1 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 25.7%. This rapid growth highlights how essential automation has become in modern banking operations.
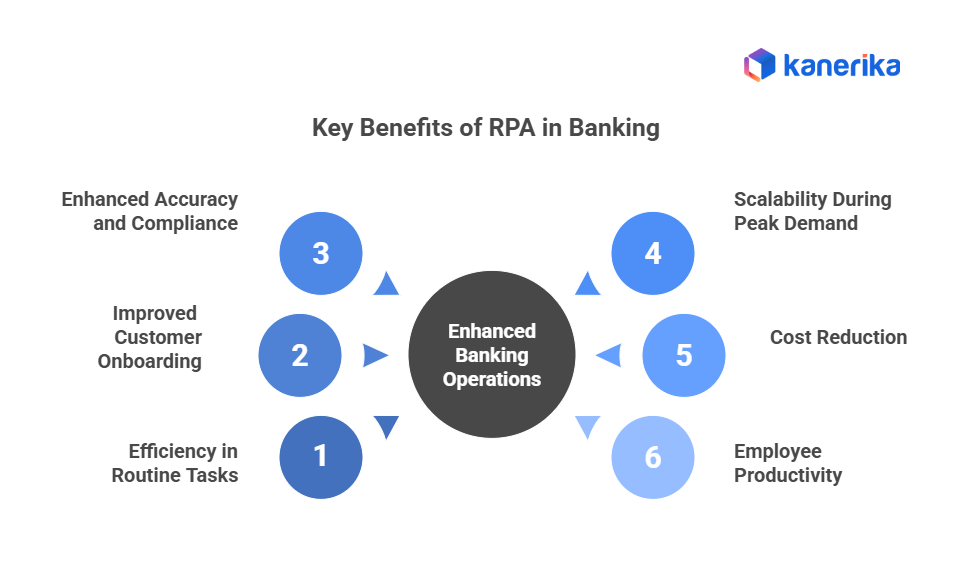
Key Benefits of RPA in Banking
- Efficiency in Routine Tasks
RPA bots can perform tasks such as data entry, report generation, and account updates at high speed, significantly reducing turnaround times.
- Improved Customer Onboarding
Processes such as Know Your Customer (KYC) verification and document validation are automated through bank verification services, allowing customers to open accounts faster and with fewer errors.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Compliance
Since bots follow predefined rules, they minimize human errors and help banks meet strict compliance requirements. Detailed logs created by RPA also make audits smoother.
- Scalability During Peak Demand
Banks can scale up their digital workforce by adding more bots during high-demand periods, such as year-end reporting or sudden surges in loan applications.
- Cost Reduction
By automating repetitive tasks, banks can reduce their reliance on temporary staff and lower operational costs without compromising service quality.
- Employee Productivity
With routine tasks off their plate, employees can focus on higher-value activities, such as financial advising, customer service, and innovation.
RPA vs. Traditional Banking Automation
| Feature | Traditional Automation | RPA (Robotic Process Automation) |
| Execution Method | Uses built-in APIs or scripting behind the scenes | RPA bots mimic human keystrokes in the GUI |
| Integration Ease | Requires developer access and backend changes | Works with existing systems without coding |
| Scalability | Limited by custom development effort | Bots scale easily fast deployment across tasks |
| Adaptability | Rigid; requires recoding for changes | Flexible—adjust strategies via UI-level updates |
| Use Case Focus | Static repetitive tasks | Ideal for repetitive, multi-application workflows |
| Implementation Speed | Slower deployment due to development cycles | Rapid implementation through configuration |
| Cost Efficiency | High upfront programming costs | Bots scale easily for fast deployment across tasks |
RPA excels in flexibility and ease of deployment. Unlike traditional automation, which is often rigid and resource-heavy, RPA bots work through user interfaces, making them quicker to launch, easier to adapt, and more cost-effective. This is especially useful in banking, where legacy systems and frequent process changes make it challenging to maintain full-scale automation.
Enterprise RPA: The Complete Guide to Business Transformation
Discover how RPA transforms enterprises by automating workflows, improving efficiency, and driving growth.
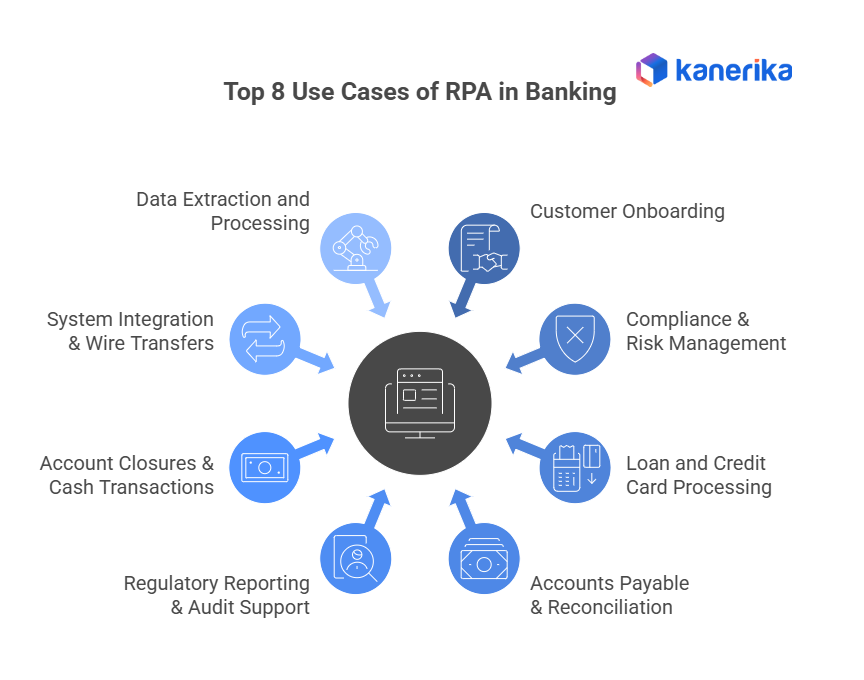
Top 8 Use Cases of RPA in Banking
1. Customer Onboarding
Opening a new account typically involves several steps, including collecting documents, verifying customer details, and updating core banking systems. RPA bots streamline this process by automatically extracting data, validating it against compliance rules, and entering it into the system. This reduces delays, improves accuracy, and delivers a smooth onboarding experience for customers. In many modernization projects, banks pair RPA with banking software development services to ensure these automated workflows integrate smoothly with existing core systems.
2. Compliance and Risk Management (KYC/AML)
Regulatory requirements, such as Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML), demand constant monitoring and meticulous record-keeping. RPA automates tasks such as screening customer data against global watchlists, flagging suspicious transactions, and maintaining detailed audit trails. This ensures faster compliance reporting while lowering the risk of penalties.
3. Loan and Credit Card Processing
Loan approvals and credit card issuance involve credit history checks, employment verification, and document validation—tasks that are traditionally time-intensive. With RPA, these steps can be automated, reducing processing time from several days to just a few hours. Customers benefit from faster decisions, while banks save costs and minimize human error.
4. Accounts Payable and Reconciliation
Managing vendor invoices, payments, and reconciliations is a repetitive yet critical task. Bots can automatically extract invoice details, match them with purchase orders, and process payments without manual input. They also reconcile transactions at scale, ensuring error-free financial records and freeing finance teams to focus on higher-value activities.
5. Regulatory Reporting and Audit Support
Banks generate numerous reports for regulators, internal audits, and stakeholders. Preparing these manually is time-consuming and prone to mistakes. RPA enables the automatic collection, consolidation, and generation of reports, ensuring accuracy, timeliness, and transparency. This not only simplifies audits but also builds trust with regulators.
6. Account Closures and Cash Transactions
Routine activities, such as closing dormant accounts or handling cash deposits and withdrawals, can consume a significant amount of employee time. RPA bots handle account closure requests by verifying outstanding balances, updating records, and sending confirmations. Similarly, automating cash transaction reporting enables banks to process high volumes efficiently without compromising security.
7. System Integration and Wire Transfers
Banks often rely on multiple legacy systems that don’t naturally integrate. RPA acts as a bridge, moving data seamlessly between systems and reducing the need for expensive IT upgrades. For wire transfers, bots can validate details, process payments, and generate reports within minutes, ensuring compliance with service-level agreements.
8. Data Extraction and Processing
Banks deal with vast amounts of unstructured data from forms, contracts, and customer communications. Using Optical Character Recognition (OCR) combined with RPA, institutions can capture, process, and organize this information quickly. This reduces manual entry by up to 90% while improving data accuracy for downstream processes.
Real-World Examples of RPA in Banking
1. HDFC Bank – Streamlined Loan Processing
HDFC, one of India’s largest private banks, addressed a bottleneck in loan applications that required employees to spend roughly 40 minutes each to process. With RPA from AutomationEdge, the bank automated 15+ key workflows across retail and corporate banking. The outcome? Processing time was halved to about 20 minutes, and the system achieved 100% error-free transparency.
2. UBS – Quick Crisis Response with RPA
During a surge in loan applications triggered by pandemic relief needs, UBS partnered with Automation Anywhere to rapidly increase processing capabilities in just six days. The bank reduced loan request handling time from 30–40 minutes down to just 5–6 minutes—an exceptional gain in both agility and customer service.
3. Postbank (Bulgaria) – Loan Admin Efficiency
Postbank automated 20 loan administration steps that once required seven employees, four hours a day. RPA completed them 2.5 times faster and diverted only 5% of cases to human review, massively increasing throughput and accuracy.
4. SS&C GlobeOp – Faster Syndicated Loan Processing
As a global fund administrator, SS&C GlobeOp needed speed and precision for syndicated loan documents. By deploying Blue Prism bots, they achieved a 57% faster processing time, eliminated manual corrections (100% accuracy), and redeployed 30% of staff to higher-value work.
Kanerika’s Impact on Banking Efficiency Through RPA
At Kanerika, we specialize in RPA solutions for the banking and financial services industry, helping institutions streamline operations and reduce inefficiencies. Our automation expertise encompasses critical processes such as accounts payable, compliance checks, loan processing, and customer onboarding, delivering faster cycles, fewer errors, and significant cost savings.
We take a consultative approach, designing automation strategies that align with our clients’ goals and existing systems. By ensuring seamless integration, scalability, and security, we empower banks to build smarter and more agile operations, allowing teams to focus on innovation and customer service while automation handles repetitive tasks.
RPA Integration Tools Used by Kanerika
1. UiPath
UiPath’s hyperautomation platform helps banks automate high-volume tasks like KYC, loan processing, and reconciliations. With AI integration and strong governance, it enables large-scale, compliant automation.
2. Automation Anywhere
Automation Anywhere combines AI and cloud-native bots to streamline workflows, including fraud detection, customer service, and compliance checks. Its fast deployment ensures quick ROI for banks.
3. IBM Robotic Process Automation
IBM RPA brings AI-driven accuracy to compliance, reporting, and back-office banking operations. It integrates well with legacy systems, making modernization easier without major system changes.
4. AkaBot
AkaBot offers flexible UI and API automation, along with pre-built solutions for banking needs such as onboarding, payments, and reporting. It delivers speed and versatility with minimal setup time.
5. Microsoft Power Automate
Power Automate is a low-code platform that connects seamlessly with Microsoft 365 and Azure. It simplifies approvals, document processing, and monitoring while ensuring secure, scalable automation.
RPA in Finance: Benefits, Best Practices & Applications
Explore how RPA improves finance by enhancing efficiency, reducing errors, and delivering business value.
Case Study: Automating Invoice Processing for a US-Based Financial Institution
Client Overview
A mid-sized financial institution in the United States was facing delays and inefficiencies in its accounts payable operations. The AP team manually processed thousands of invoices received via email, leading to slow turnaround times, frequent errors, and strained vendor relationships.
Challenge
The client needed a solution to reduce manual workload, improve accuracy, and speed up invoice processing. Their existing system lacked automation, and the volume of incoming invoices was growing steadily.
Kanerika’s Approach
Kanerika deployed a custom RPA in banking solution that used bots to extract invoice data from emails, validate it using rule-based logic, match it with purchase orders, and update records in the finance system. The automation was seamlessly integrated with the client’s existing software, incorporating OCR for data capture, real-time tracking, and automated approval workflows—all without requiring manual intervention.
Results
- 80% reduction in invoice turnaround time
- 50% boost in operational efficiency
- 30% increase in supplier engagement
- Near-zero error rates in invoice data entry
Outcome
The client now processes invoices faster and more accurately. Staff are freed from repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on strategic work. The automation also improved vendor satisfaction and positioned the company for future scalability.
Navigating the world of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in banking can be challenging, making it essential to choose a partner with proven expertise. That’s where Kanerika stands out. With deep proficiency across leading RPA platforms, including Automation Anywhere, UiPath, and Blue Prism, we act as your trusted co-pilot in driving automation success.
With over 150 automated processes, more than 1,000 bots deployed, and a team holding over 30 RPA certifications, we combine breadth and depth of experience to deliver measurable results. Partner with us to unlock efficiency, accuracy, and scalability in your banking operations.
Boost Efficiency and Cut Costs with Smart RPA Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika to bring expertise in deploying RPA for measurable results.
FAQs
Which banking processes can be automated using RPA?
RPA works best for processes that are repetitive, rules based, and data intensive. Common examples include account opening, loan application processing, KYC verification, compliance checks, invoice management, and report generation. Since bots interact through the user interface, they can be deployed without changing core systems.
2. How reliable is RPA for sensitive financial operations?
RPA is highly reliable because it follows defined rules with consistency and precision. Every action performed by a bot is logged, which helps in maintaining audit trails and ensuring compliance. This makes it suitable for handling sensitive tasks in banking.
3. How long does it take to implement RPA in a bank?
Implementation is usually much faster compared to traditional IT projects. A small pilot can often be launched within a few weeks, and larger rollouts may take only a few months depending on the complexity of the processes involved.
4. How is RPA different from traditional automation?
Traditional automation often requires coding and direct integration with backend systems, which can be time consuming. RPA, on the other hand, mimics human actions on the screen, making it quicker to implement and easier to adapt when processes change.
5. Will RPA lead to job losses in banking?
RPA is not meant to replace people but to assist them. By taking over repetitive work, bots allow employees to focus on strategic tasks and customer service. In most cases, RPA improves job satisfaction by reducing manual, error prone activities.










