The insurance industry has been facing significant losses due to fraudulent claims. According to the Coalition Against Insurance Fraud, the figure can go as high as $308.6 billion annually. By implementing RPA fraud detection, insurers can bring down this number.
Traditional fraud detection methods have failed to identify, combat, and curb fraud due to their inflexibility, lack of core options like cross-integration, data analysis, and real-time behavioral profiling, and involve more human intervention. This has led to much time spent evaluating uneven patterns, missing out on subtle yet critical details, and, in most cases, resulting in significant financial losses.
Machine Learning (ML), a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI), along with Robotic Process Automation (RPA), has revolutionized the insurance industry and is effectively beneficial in fraudulent claim detection and prevention to facilitate the early detection of suspicious claims. It is one of the game-changing innovations that efficaciously saves time, money, and effort.

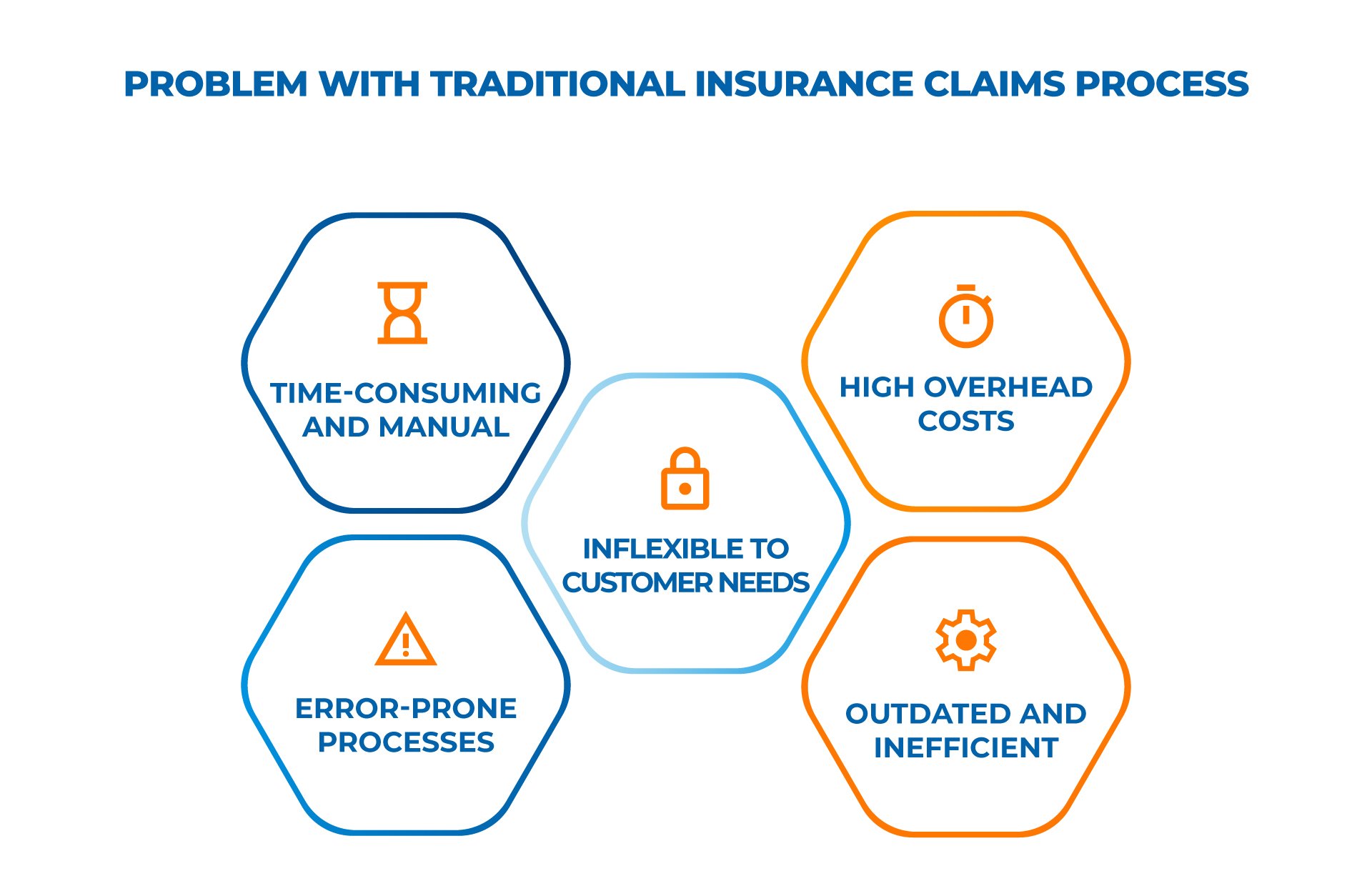
Problem with Traditional Insurance Claims Process
Traditional methods in insurance have been known to be time-consuming, manual, and prone to errors. These methods involve a lot of paperwork, leading to delays in processing claims and policy renewals. Moreover, the manual nature of these methods makes them prone to errors, which can be costly for both the insurer and the insured.
In addition, traditional methods of insurance are not very flexible. They are designed to handle a limited range of scenarios and cannot adapt to changing customer needs. For example, if customers want to customize their policy, they may have to go through a lengthy process of filling out forms and waiting for approval.
Furthermore, traditional methods in insurance are not very cost-effective. They require a lot of resources, such as staff, paper, and storage space. This can result in high overhead costs, which can be passed on to the customer through higher premiums.
The Role of RPA Fraud Detection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has become an essential tool for insurance companies to detect and prevent fraud. RPA uses software robots to automate repetitive tasks and processes, reducing the risk of human error and increasing efficiency. By implementing RPA fraud detection, insurance companies can improve their ability to identify and investigate fraudulent claims.
Here are some ways that RPA can be used in fraud detection:
- Data analysis: RPA can analyze large amounts of data quickly and accurately, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity.
- Claims processing: RPA can automate the workflow, ensuring that all claims are reviewed and processed consistently and efficiently. This reduces the risk of fraudulent claims slipping through the cracks.
- Risk assessment: RPA can help insurance companies assess the risk of a fraudulent claim by analyzing various data points such as the claimant’s history, the type of claim, and other relevant factors.
- Compliance monitoring: RPA can monitor compliance with regulations and policies, ensuring that all claims are processed according to the rules and regulations set forth by the insurance company and regulatory bodies.
Overall, RPA is a valuable tool for insurance companies to improve their fraud detection capabilities. By automating repetitive tasks and processes, RPA can free up human resources to focus on more complex tasks such as investigating potential fraud cases.
Read More – Telematics in Insurance: How It Works and Benefits You
Also Read – Automation In Insurance: Use Cases, Benefits, and Strategies

The Three Stages of RPA in Insurance Claims
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) transforms the insurance industry by automating time-consuming and repetitive tasks. In the context of insurance claims, RPA can streamline the claims process, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. The implementation of RPA in insurance claims can be divided into three stages:
1. Basic Automation: In the first stage, RPA automates simple and repetitive tasks, such as data entry, document processing, and basic calculations. This stage uses rule-based bots that follow pre-defined workflows. Basic automation can reduce the time required to process a claim and minimize errors caused by manual data entry.
2. Advanced Automation: In the second stage, RPA automates more complex tasks, such as fraud detection, risk assessment, and decision-making. This stage is characterized by using cognitive bots to learn from data and make decisions based on predefined rules. Advanced automation can improve the accuracy and consistency of claims processing and reduce the risk of fraud.
3. Intelligent Automation: In the third stage, RPA is integrated with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to create intelligent bots for end-to-end claims processing. This stage is characterized by using bots to analyze unstructured data, such as images and videos, and make complex decisions based on context. Intelligent automation can significantly reduce the time and cost required to process a claim and improve the customer experience.
Leading Technologies in RPA and Machine Learning
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Machine Learning (ML) are leading technologies transforming the insurance industry. RPA is a software technology that automates repetitive tasks by mimicking human actions, while ML is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time.
1. Optical Character Recognition (OCR):
OCR technology enables machines to recognize and extract text from images and documents. This technology can automate the processing of claims and policy documents.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP is a technology that enables machines to understand and interpret human language. In the insurance industry, it can automate customer service and claims processing.
3. Predictive Analytics:
Predictive analytics is a technology that uses statistical algorithms and ML techniques to analyze data and predict future events. It can identify fraudulent claims and predict customer behavior.
4. Chatbots:
Chatbots are computer programs that simulate human conversation. They are being used in the insurance industry to automate customer service and claims processing.
5. Image Analysis:
Image analysis is a technology that enables machines to analyze images and identify objects and patterns. This technology is used in the insurance industry to automate processing claims and policy documents.

Kanerika’s Innovative Strategy for Implementing RPA in Insurance
As a leading provider of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Machine Learning (ML) solutions in the insurance industry, we at Kanerika focus on delivering cost-effective and efficient services tailored to the unique requirements of each of our clients. Our approach involves:
- Offering highly customizable RPA solutions for strategic efficiency.
- Applying our deep industry expertise to tailor solutions to client needs.
- Ensuring our RPA solutions are scalable and seamlessly integrated with existing systems.
- Using ML algorithms to enhance accuracy in predicting claims and detecting fraud.
- Boosting operational efficiency by automating routine tasks.
- Improving customer experiences with faster, more accurate responses.
- Collaborating with insurers to develop specific ML and RPA strategies.
- Leveraging our expert team for targeted automation and solution development.

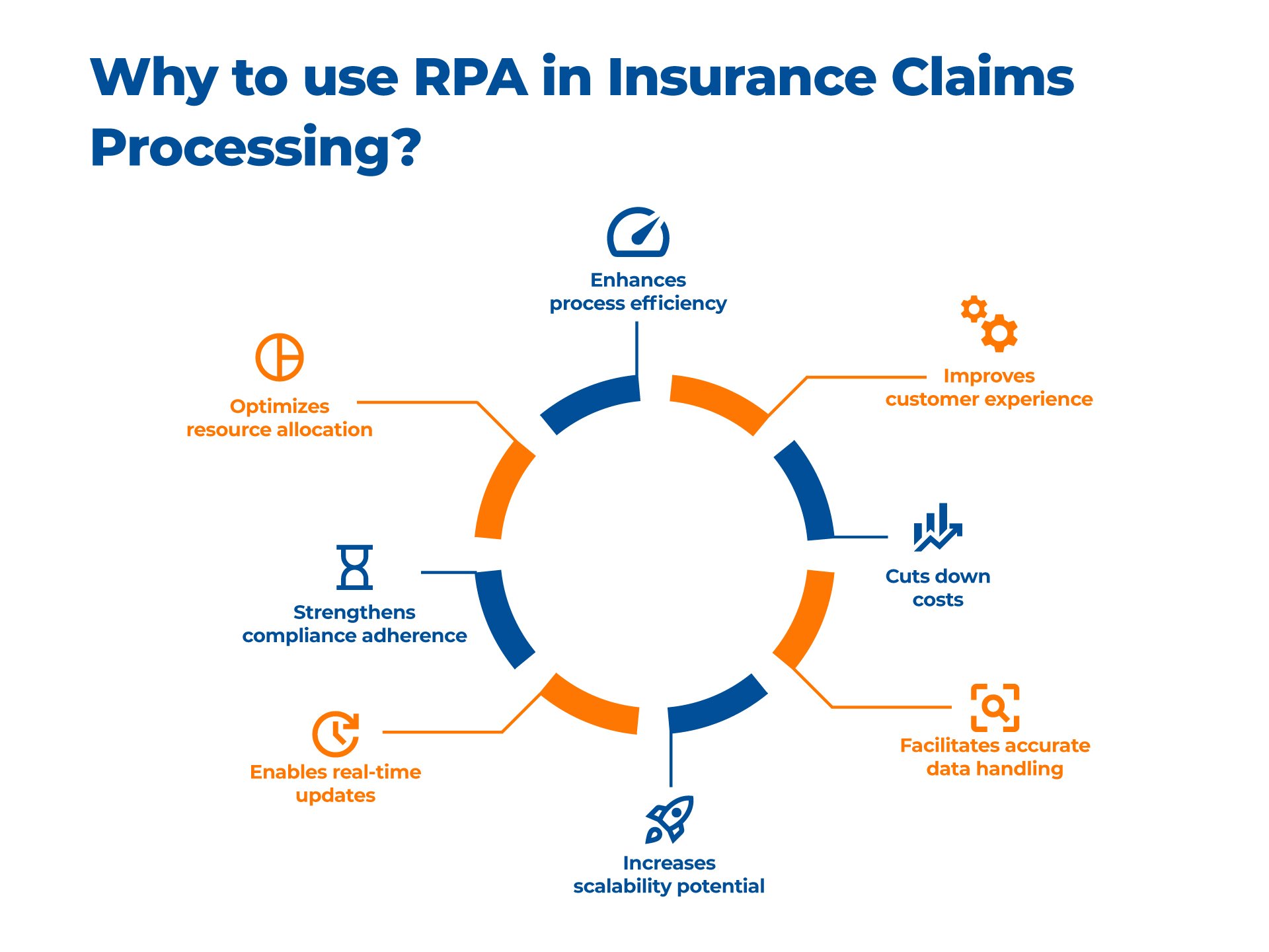
The Future of RPA in Insurance Claims
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is making waves in the insurance industry, significantly impacting claims processing. This technology can revolutionize insurance claim processing by accelerating the process, enhancing efficiency, and reducing error susceptibility.
Here are some ways in which RPA can transform the insurance claims process:
- Faster Claims Processing: RPA technology can automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks involved in claims processing, such as data entry, document verification, and claim assessment. This can significantly reduce the time taken to process claims and improve customer satisfaction.
- Improved Accuracy: RPA technology can eliminate errors caused by manual data entry and reduce the risk of fraudulent claims. This can help insurance companies save money and improve their bottom line.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: RPA technology can improve the overall customer experience by providing faster claims processing, personalized communication, and real-time updates on claim status.
- Cost Savings: RPA technology can help insurance companies save costs by reducing the need for manual labor and improving the efficiency of claims processing. This can lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in the insurance industry has proven to be highly beneficial. RPA has the potential to automate repetitive and mundane tasks, reduce errors, and increase efficiency. It can also help insurance companies save time and money while improving customer satisfaction.
By implementing RPA, insurance companies can streamline their processes, improve their workflows, and reduce their employees’ workloads. This technology can also help insurance companies stay competitive by providing faster and more accurate services to their customers.
As the technology continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how it transforms the insurance landscape in the years to come.

FAQs
What is RPA in cyber security?
RPA, or Robotic Process Automation, in cybersecurity isn’t about robots fighting hackers directly. Instead, it automates repetitive security tasks like log analysis and vulnerability scanning, freeing up human analysts for more complex threats. This boosts efficiency and reduces human error, a significant weakness in many security systems. Think of it as automating the grunt work so human experts can focus on strategic defense.
Which automation technique is used for fraud detection?
Fraud detection often leverages a combination of automation techniques. Machine learning algorithms are key, analyzing vast datasets to identify unusual patterns indicative of fraud. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can automate repetitive tasks like flagging suspicious transactions for human review. This blended approach boosts efficiency and accuracy in identifying fraudulent activities.
Is there an AI tool to detect fraud?
Yes, several AI tools can help detect fraud. These tools analyze vast datasets to identify unusual patterns and anomalies indicative of fraudulent activity, far exceeding human capabilities. Their effectiveness depends on the quality of the data fed to them and the specific type of fraud being targeted. Essentially, AI acts as a powerful magnifying glass, highlighting potentially suspicious transactions or behaviors.
What are the three types of RPA?
RPA isn’t neatly divided into just three types, but we can categorize it based on capabilities. There’s attended RPA, where a human initiates and often monitors the process; unattended RPA, running completely independently; and hybrid RPA, blending both approaches for optimal efficiency depending on the task. These distinctions highlight the spectrum of automation, from simple human-assisted tasks to fully autonomous processes.
Is RPA a coding?
No, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) isn’t traditional coding. It uses visual tools and pre-built modules to automate tasks, rather than writing lines of code from scratch. Think of it as “programming without programming”—you’re instructing a robot, not building one from the ground up. This makes it much faster to implement than custom software development.
What is the example of RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive digital tasks, like filling out online forms or extracting data from emails. Think of it as a software robot mimicking human actions on a computer. A good example is automatically processing invoices: RPA software reads the invoice, extracts key data, and updates accounting systems, eliminating manual data entry. This frees up human employees for more strategic work.
How secure is RPA?
RPA’s security depends heavily on how it’s implemented. While the bots themselves aren’t inherently vulnerable, weak access controls, insufficient monitoring, or integration with insecure systems create significant risks. Robust security measures, like strong authentication and encryption, are crucial for a secure RPA deployment. Ultimately, RPA security is only as strong as its weakest link.
What are the vulnerabilities of RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) bots are vulnerable to the same security risks as any software, including malware infection and unauthorized access if not properly secured. They’re also limited by their programmed instructions, failing when encountering unexpected data or process variations. Finally, their reliance on existing systems means RPA inherits and potentially amplifies vulnerabilities present in those underlying systems. Essentially, RPA’s security is only as strong as its design and the systems it interacts with.
What is the difference between RPA and SOAR?
RPA automates *repetitive, rule-based tasks* within a single application, like filling out forms. SOAR, on the other hand, orchestrates *complex, security-focused workflows* across multiple systems, often involving human intervention and decision-making. Think of RPA as a tireless clerk, while SOAR is a security incident response manager. Essentially, RPA handles the “how,” while SOAR handles the “what to do and when.”
What is RPA in robot framework?
In Robot Framework, RPA (Robotic Process Automation) means using the framework to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks typically done by humans on a computer. It leverages keywords and libraries to interact with applications and systems, mimicking human actions. This boosts efficiency and accuracy by automating tedious processes. Essentially, it’s a powerful tool for building software robots within Robot Framework’s structured environment.









