As data migration projects have grown larger and more complex, many organizations are seeking ways to reduce manual work and associated risks. RPA is one approach to do exactly that. Companies in banking, insurance, and manufacturing are adopting robotic process automation to manage repetitive migration tasks, including data extraction, validation, and reconciliation across legacy and modern systems. Instead of relying on manual scripts and spreadsheets, RPA bots can work around the clock, follow predefined rules, and ensure data is moved consistently without disrupting business operations.
The adoption of automation is accelerating. Industry studies show organizations implementing RPA for migration initiatives can reduce manual labor by up to 50% and achieve significant cuts in migration timelines. RPA also helps improve accuracy, especially when migrating data from older systems that lack APIs or modern integration options. As hybrid and multi-cloud environments become more common, RPA is increasingly used to complement ETL and data integration tools and close automation gaps.
Continue reading this blog to explore how RPA for data migration works, where it delivers the most value, and the best practices to combine automation with modern migration tools for faster and more reliable results.
Key Takeaways
- RPA reduces manual effort by automating repetitive migration activities such as data extraction, validation, transformation, and loading across systems.
- Faster execution and consistent rule-based processing through RPA help shorten migration timelines while maintaining high data accuracy.
- Legacy-heavy and complex environments benefit from RPA because it works without requiring deep system integrations or architectural changes.
- When combined with traditional ETL and migration tools, RPA fills automation gaps and improves scalability and operational control.
- Kanerika applies RPA within a governed, secure framework to reduce migration risk, minimize disruption, and support enterprise-scale transformation.
- With structured planning, testing, and continuous monitoring, RPA becomes a long-term enabler for sustainable data modernization.
What Is RPA in Data Migration?
Robotic Process Automation in data migration uses software robots to handle the tedious, repetitive tasks involved in moving data between systems. These bots work through applications just like people do, clicking through screens, connecting to databases, and handling files, but they don’t need to change anything about your current setup. In data migration projects, RPA bots extract data from legacy systems, verify that everything looks right, fix formatting issues, and load it into new platforms such as cloud warehouses, ERP systems, or analytics tools.
RPA really helps when you’re dealing with data scattered across systems like ERP platforms, CRM databases, mainframes, spreadsheets, and custom applications. While traditional ETL tools usually want you to dig deep into system connections, RPA works on top of what you already have. This makes it perfect for complicated business environments where getting direct access to systems is either difficult or too risky to attempt.
Key aspects of RPA in data migration include:
- Automated data extraction from legacy systems, applications, and flat files
- Rule-based data validation to ensure accuracy, completeness, and consistency
- Data transformation to match target system schemas and business rules
- Automated data loading into target systems with minimal manual intervention
- End-to-end orchestration of migration workflows with audit logs and traceability
By automating these tasks, RPA reduces manual work, completes migration projects faster, and maintains high data quality even when handling large volumes.
RPA Security Best Practices: Enhancing Bot Defense Mechanism
Explore how to safeguard your automation with robust RPA security measures.
Why Use RPA for Data Migration?
Companies turn to robotic process automation for data migration because it saves significant money compared to manual processes or building custom software from scratch. RPA costs about 40-60% less than creating custom migration tools, and projects finish much faster, too.
1. Speed Makes All the Difference
Software robots operate continuously without interruptions. They process thousands of records every hour at speeds far beyond human capability. What manual teams take weeks or months to complete gets finished in just days. This speed helps companies meet tight digital transformation deadlines and reduces system downtime during cutover periods.
2. Accuracy Prevents Expensive Mistakes
People make mistakes when entering data, with error rates of 1-5%. That becomes a huge problem when you’re moving millions of records. But automated bots follow migration rules perfectly every time. They eliminate typing errors, duplicate entries, and formatting problems. Plus, built-in checks make sure data stays clean and accurate throughout the whole process.
3. Flexibility Handles Any Size Project
Here’s what makes RPA really powerful: it scales up or down based on your needs. The same bots that handle small datasets can process massive enterprise databases with equal efficiency. This flexibility works well for phased migrations, pilot programs, and keeping data in sync between cloud and on-premises systems.
4. Lower Risk Through Better Control
RPA tools track every action, creating detailed audit trails that support compliance requirements. If something goes wrong during production migration, you can roll back changes quickly. This documentation also helps with testing and makes the whole process much safer for business-critical data.
5. Minimal Disruption to Existing Systems
RPA works at the user-interface level, which means it doesn’t require changes to source or target systems. This is especially useful when dealing with legacy applications, where APIs or direct database access may not be available. Bots can migrate data while systems remain live, reducing business disruption and avoiding the risks associated with deep system modifications.
RPA vs Traditional Data Migration Approaches
| Aspect | UI driven and rule-based automation | Traditional Data Migration Approach |
| UI driven and rule based automation | Using software bots | Requires deep system access, APIs, or schema-level integration |
| System dependency | Works on top of existing systems with minimal changes | Lower operational and long-term costs |
| Speed and efficiency | Faster execution with continuous bot operation | Slower due to manual steps and limited automation |
| Error rate | Low error rates due to consistent rule execution | Higher risk of human and scripting errors |
| Cost impact | Tool-based or manual coding-driven processes | Higher cost due to manual effort and rework |
| Scalability | Easily scalable across multiple systems and volumes | Scaling requires additional resources and time |
| Legacy system support | Highly effective for legacy and non API systems | Often limited support for older systems |
| Audit and compliance | Built in logs and traceability | Manual documentation and limited tracking |
| Flexibility | Quick adaptation to process or rule changes | Tool-based or manual coding driven processes |
Top 5 RPA Platforms for Data Migration
1. UiPath
UiPath is honestly one of the most popular and flexible RPA platforms out there right now. It has some powerful end-to-end automation capabilities that work really well for those complex data migration processes we all dread. The drag-and-drop workflow designer makes building automation pretty straightforward without having to write code from scratch. There is a huge library of pre-written automation parts, and it supports database and application integration really well. This makes UiPath a great choice for extracting, transforming, and loading data from legacy systems into modern environments.
What really sets UiPath apart is the AI and ML capabilities built right in. These help with decision-making during migrations, which honestly comes in super handy when dealing with unstructured or semi-structured data that needs intelligent handling.
2. Automation Anywhere
Automation Anywhere takes a cloud-native approach and has some really solid analytics through Bot Insight. The IQ Bot feature can actually process unstructured data, which is incredibly useful for migration projects that pull from a wide range of sources and require smart extraction and classification.
The platform handles large volumes of migration tasks really well, thanks to its scalability and secure architecture. Having real-time monitoring and control capabilities means you can keep track of everything as it happens, which honestly gives you peace of mind during those complex migration projects.
3. Blue Prism
Blue Prism focuses on enterprise-level automation and excels in large organizations with high security and compliance requirements. The strong governance controls, visual process design, and centralized management make it a solid choice for regulated industries that need to migrate sensitive data around.
Now, it does have a steeper learning curve than some other tools. But honestly, once your team gets comfortable with it, the scalability and integration features can safely and reliably handle really sophisticated migration pipelines.
4. Microsoft Power Automate
Microsoft Power Automate (formerly Microsoft Flow) is a low-code/no-code RPA platform that fits naturally into the Microsoft ecosystem. If your organization already uses Office 365, Dynamics 365, Azure services, or other Microsoft tools, this integration honestly makes it a powerful option for data migration.
The ready-made connectors and templates really speed things up when you are automating common extraction, transformation, and data entry tasks. This is especially valuable when you are migrating data within Microsoft environments or when your workflows overlap with Microsoft applications.
5. WorkFusion
WorkFusion is an AI-powered RPA platform that has built quite a reputation for combining traditional automation with intelligent features like OCR, NLP, and machine learning. It handles migration cases with tons of data really efficiently, especially when data needs to be validated, classified, or enriched before being moved to its new home.
What really sets WorkFusion apart is that its automation models can learn from human input. This works exceptionally well for enterprise migrations that involve adaptive decision-making, compliance verification, and high-accuracy data processing. That adaptive capability honestly makes it a standout choice for complex, long-running migration projects.
RPA for Enterprise: Streamlining Business Processes Automation
Discover how RPA simplifies and accelerates business process automation for enterprises.
Key Data Migration Tasks Automated by RPA
Robotic Process Automation streamlines numerous critical activities throughout the data migration lifecycle, transforming how organizations approach system modernization and digital transformation initiatives. These intelligent bots handle both simple and complex tasks that previously required extensive manual effort, dedicated IT resources, and significant project timelines.
1. Data Extraction and Collection
Software robots automatically gather information from multiple source systems, including legacy databases, mainframe applications, spreadsheets, CRM platforms, ERP systems, and flat files. Bots navigate various user interfaces, execute database queries, download reports, and compile data from multiple sources into centralized staging areas. This automated extraction eliminates the tedious manual process of accessing each system individually and copying information across platforms.
2. Data Cleansing and Standardization
RPA bots identify and remove duplicate records, correct formatting inconsistencies, validate email addresses and phone numbers, standardize date formats, normalize currency values, and fix common data quality issues. The automation applies predefined business rules to ensure consistency across datasets, identifies missing or incomplete fields, and flags exceptions requiring human review. This systematic approach improves overall data quality when entering target systems.
3. Data Transformation and Mapping
Bots execute complex transformation rules to convert data from source formats to target system requirements. This includes restructuring information hierarchies, splitting or merging data fields, applying calculation formulas, converting measurement units, and translating code values between systems. RPA handles field-level mapping automatically, ensuring source data aligns correctly with destination schema requirements.
4. Data Loading and Validation
Software robots transfer processed information into target applications, databases, or cloud platforms through automated loading procedures. Bots perform post-migration validation checks, comparing record counts, verifying data completeness, testing referential integrity, and confirming successful transfers. This verification ensures migration accuracy before system cutover.
5. Report Generation and Documentation
RPA automatically generates comprehensive migration status reports, error logs, exception summaries, and audit documentation. Bots track migration progress, document transformation rules applied, generate compliance records, and produce detailed analytics on data quality improvements achieved during the process.

Best Practices for Implementing RPA in Data Migration
Implementing RPA in data migration requires careful planning, structured execution, and continuous monitoring. By following a systematic approach, organizations can ensure accurate, secure, and efficient migration while minimizing risk and maintaining business continuity.
Step 1: Perform Detailed Migration Discovery and Readiness Assessment
The first step is to thoroughly analyze both source and target systems to understand data volumes, formats, dependencies, and access limitations. This assessment is critical for determining where automation can deliver the most value and for identifying potential risks early in the migration lifecycle.
Key considerations include:
- Identifying repetitive and rule-based tasks that can be automated, such as data extraction from legacy screens, manual data entry, or validation procedures
- Assessing data quality issues, including missing records, duplicates, inconsistent formats, or outdated information
- Evaluating technical readiness, including network bandwidth, infrastructure capacity, system compatibility, security measures, and compliance requirements
These activities ensure that the automation scope is well-defined, potential challenges are anticipated, and resources are allocated efficiently to prevent delays or errors during migration.
Step 2: Define Strong Data Governance and Quality Rules
Clear governance and well-defined quality rules are essential to maintain accuracy and consistency throughout the migration process. Without them, automated processes may spread errors, impacting business operations and compliance.
Key practices include:
- Establishing data ownership to account for the accuracy, completeness, and integrity of the data migrated
- Specifying validation checks to verify formats, ranges, referential integrity, and business rules prior to data being loaded to the target system
- Recording transformation logic, such as field mapping, calculation formulas, code translations, enrichment rules, so that they align with target system requirements
- Setting acceptance criteria to ensure data quality standards meet business and regulatory compliance, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX
By embedding these practices into the migration plan, organizations reduce the risk of errors, ensure accountability, and maintain audit trails for compliance.
Step 3: Design a Hybrid RPA-Driven Migration Architecture
RPA provides the greatest value when it is used in a hybrid migration architecture with conventional ETL and data integration tools. This ensures that each technology is used for the tasks for which it is best suited and that overall efficiency and reliability improve.
Typical elements include:
- Using RPA for UI based automation and legacy systems without APIs for the extraction and entry of data from applications, where direct integrations are not available
- Dealing with semi-structured data, such as spreadsheets, documents, and reports that need to be formatted or transformed before being loaded
- Using ETL Tools for Bulk Structured Data, Complex Transformations, and High Volume Migrations to Ensure Speed and Performance
- Balancing flexibility and performance so that the migration remains stable and scalable, including in enterprise-wide projects
A hybrid approach can enable organizations to migrate data efficiently between various systems and environments without causing excessive downtime and errors.
Step 4: Build Scalable, Reusable, and Resilient RPA Bots
Bots should be designed to be reusable, modular, and resilient, supporting multiple datasets, applications, and migration phases. This ensures the automation is sustainable and can adapt to future migration needs.
Important considerations are:
- Creating modular bot components reusable across multiple systems/migration projects to reduce development time and maintenance overhead
- Implementing solid error handling and retry logic to cope with temporary errors or system unavailability, without affecting the migration
- Maintaining detailed logs and monitoring to capture bot activities, system interactions, and performance metrics for troubleshooting and audit purposes
- Setting up alerts for critical errors so administrators can respond quickly without having to wait for a batch to complete
This way, reliability is high, and maintenance is easy to perform and can be automated at an enterprise scale.
Step 5: Execute Phased Testing and Controlled Rollouts
Phased Testing and Controlled Rollouts with Minimal Disruption and Ensuring Migration Success before moving to full production. This step serves as validation of the technical and business aspects of the migration.
Key actions include:
- Conducting pilot migrations with representative datasets to validate extraction, transformation, and loading logic
- Running parallel runs in which the source and target systems would be running at the same time to reconcile the results and find discrepancies early on
- Testing performance at different loads to ensure that bots can handle production data volumes efficiently
- Continuously improving workflows based on the results of the pilots for errors, performance optimization, and accuracy before full deployment
Phased execution enables organizations to identify and fix problems early, minimize downtime, and ensure business continuity.
Step 6: Monitor, Govern, and Optimize Continuously
Even after deployment, continuous monitoring, governance, and optimization are essential to maintain high performance, compliance, and reliability.
Key practices include:
- Tracking bot performance metrics, such as processing speed, error rates, and resource utilization, to detect inefficiencies
- Validating reconciliation results to ensure data completeness and consistency between source and target systems
- Maintaining audit logs and compliance records to support internal governance and external regulatory requirements
- Enforcing access controls and change management policies to prevent unauthorized changes to automated workflows
- Continuously optimizing automation by analyzing performance data, addressing recurring errors, and updating bots to handle evolving business or system requirements
This ongoing approach ensures that RPA-driven data migration remains efficient, reliable, and scalable for future enterprise modernization initiatives.
7 RPA Use Cases That Will Transform Your Supply Chain Management
Uncover how RPA enhances efficiency and transparency across supply chain operations.
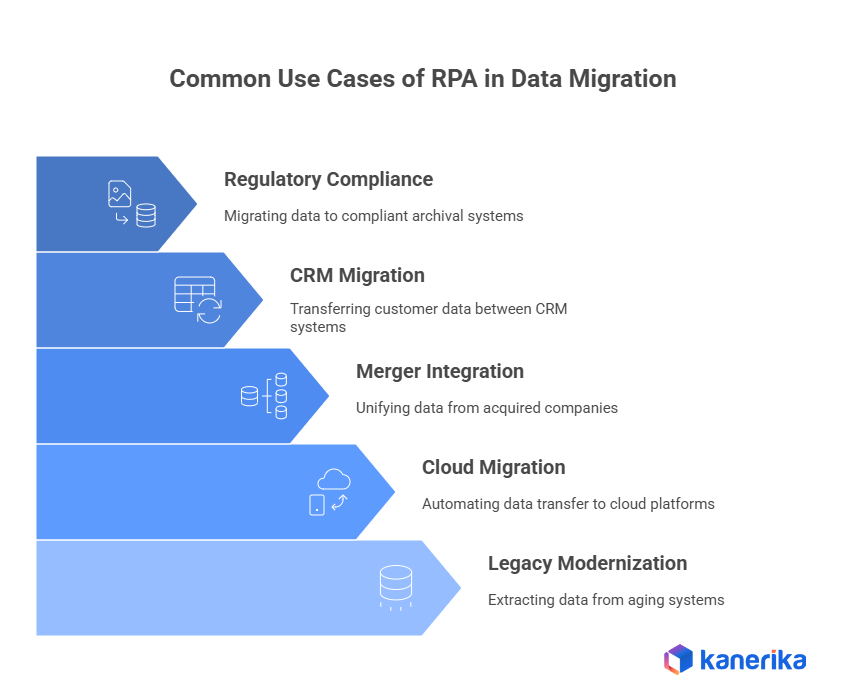
Common Use Cases of RPA in Data Migration
Organizations in various industries take advantage of RPA technology for various data migration scenarios and solve specific business challenges and operational requirements through intelligent automation solutions.
1. Legacy System Modernization
Companies that are replacing aging mainframe systems, AS/400 platforms, or legacy ERP applications with new cloud-based applications use RPA to extract decades of historical data. Bots interact with complex legacy interfaces that have no APIs, scrape data from terminal sessions, and transfer information to modern applications such as SAP S/4HANA, Oracle Cloud, or Microsoft Dynamics 365. This approach is especially useful when legacy system documentation is lacking or the original developers are unavailable.
2. Cloud Migration Projects
Enterprises migrating on-premises databases, applications, and file storage to cloud platforms such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform are deploying RPA to facilitate data migration. Bots automate data extraction from local servers, transform the data per the requirements of the cloud platform, and load it into cloud databases, data lakes, or SaaS applications. RPA handles hybrid cloud data sync between on-premises and cloud data during phased migration strategies.
3. Merger and Acquisition Integration
Organizations consolidating data from acquired firms use RPA to integrate different customer databases, financial records, employee data, and operational data into unified enterprise systems. Bots reconcile different data formats, resolve conflicts between overlapping records, merge customer profiles, and create single sources of truth across combined entities. This automation accelerates post-merger integration timelines while maintaining data accuracy throughout complex consolidation processes.
4. CRM and Customer Database Migrations
Businesses that are changing customer relationship management platforms from Salesforce to HubSpot, Microsoft Dynamics, or custom solutions are taking advantage of RPA for contact migration, deal pipeline transfers, and customer interaction history preservation. Bots extract customer information, such as contact details, purchase history, communication history, support tickets, and then map and load information in targeted CRM systems that keep relationships intact.
5. Regulatory Compliance and Data Archival
Financial institutions, healthcare providers, and regulated industries are using RPA to migrate data to regulatory-compliant archival systems to meet retention requirements. Bots are used to extract records nearing their retention deadlines, verify completeness against regulatory requirements, migrate information to secure archival platforms, and create audit documentation to demonstrate compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, or industry-specific requirements.
Case Study: Streamlining Order Processing Through RPA Automation
Client Challenge
The client managed order intake through a fully manual, email-based workflow. Staff had to read incoming messages, extract order details, validate fields, enter data into internal systems, and respond to customers. As order volumes increased, the process became slow, error-prone, and expensive, leading to delayed fulfillment and inconsistent customer communication.
Kanerika’s Solution
Kanerika deployed RPA bots using platforms like UiPath and Microsoft Power Automate to automate the entire intake cycle. Bots extracted data from emails, validated required fields, updated order management systems, and triggered acknowledgment messages. The workflow included exception handling and audit logs to ensure traceability and accuracy while minimizing human effort.
Impact Delivered
- 90% reduction in manual intervention
- 30% faster order-fulfillment capacity
- 55% faster email response times
These results improved process reliability and enabled the team to handle higher volumes without increasing operational load.
Why Kanerika’s RPA Approach Delivers Clear, Scalable Business Impact
Kanerika’s RPA services focus on removing repetitive, rules-based tasks that drain time and resources. By using platforms like Microsoft Power Automate and UiPath, we help enterprises streamline data handling, reduce errors, and improve workflow efficiency. This allows teams to make quicker, more accurate decisions while shifting effort from manual work to meaningful business activities. Kanerika supports organizations that want dependable automation without operational disruption.
A key strength in our approach is FLIP, our AI-enabled automation engine. FLIP automates complex backend tasks, including logic extraction, dependency mapping, configuration analysis, and validation. We originally built FLIP to accelerate large-scale data migrations, and it now elevates our RPA programs by improving consistency and reducing manual rework. This gives enterprises a smoother modernization path and helps them maintain stability through system transitions.
Our automation programs follow strong governance and compliance practices aligned with ISO 27001, ISO 27701, SOC 2, and GDPR. We design every workflow with secure data handling, clear audit trails, and controlled access in mind. As a result, organizations gain scalable automation that improves accuracy, accelerates processing, and supports long-term operational integrity — all delivered through Kanerika’s proven frameworks and automation expertise.
FAQs
Why is RPA suitable for data migration process?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels at data migration because it’s incredibly efficient at handling repetitive, rule-based tasks. It automates the tedious steps of extracting, transforming, and loading data, minimizing human error and drastically speeding up the process. RPA bots can seamlessly integrate with various systems, bridging the gap between legacy and modern platforms. Ultimately, this leads to quicker, cheaper, and more accurate data migration projects.
Can RPA be used for data entry?
Yes, RPA excels at structured data entry. It automates repetitive keyboard and mouse actions, drastically speeding up processes like filling forms or transferring data between systems. However, RPA struggles with unstructured data (e.g., handwritten notes) requiring human judgment. Think of it as a super-efficient digital clerk for well-organized information.
What are the three types of RPA?
RPA isn’t neatly divided into just three types, but we can categorize it based on capabilities. You have attended, where robots follow pre-programmed instructions; unattended, where they work autonomously; and hybrid, which blends both, leveraging the strengths of each for optimal efficiency. Think of it as a spectrum rather than rigid categories.
Can RPA be used for data analytics?
While RPA excels at automating repetitive tasks, it’s not a direct replacement for data analytics. RPA can support analytics by automating data gathering and preparation, feeding cleaner data into analytical tools. Think of it as a powerful prep cook, not the chef itself. Proper analysis requires statistical understanding and human interpretation, which RPA currently lacks.
What are three benefits of RPA?
RPA streamlines repetitive tasks, freeing up human employees for more strategic work. It significantly boosts efficiency and accuracy by eliminating human error in routine processes. This leads to cost savings through increased productivity and reduced operational overhead. Finally, RPA offers faster processing times, leading to quicker turnaround on various projects and improved customer service.
Can RPA extract data?
Yes, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels at data extraction. It essentially “reads” data from various sources like spreadsheets, databases, or even PDFs, mimicking human actions but much faster and more consistently. This extracted data can then be processed, analyzed, or moved to other systems, streamlining operations. Think of it as a highly efficient digital data clerk.
Which process is best suited for RPA?
The best process for RPA is one that’s highly repetitive, rule-based, and involves structured data. Think predictable, digital tasks with clearly defined inputs and outputs – less about judgment calls, more about consistent execution. Essentially, RPA excels at automating the “boring, but necessary” parts of your operations. Processes with lots of exceptions or human interaction are poor candidates.
Why do we need data migration?
Data migration is essential for keeping your data relevant and accessible. Outdated systems often lack scalability, security, or integration capabilities, hindering growth and efficiency. Moving to a new platform allows for improved performance, better data management, and the unlocking of valuable insights from your information. Essentially, it’s about modernizing your data infrastructure for a brighter future.
When should RPA be used?
RPA shines when you have repetitive, rule-based tasks that involve structured data. Think data entry, report generation, or invoice processing – anything a human does repeatedly, following the same steps. It’s best suited for tasks prone to human error and where freeing up human employees for more strategic work is a priority. Essentially, if a computer can easily follow clear instructions, RPA is a great fit.
Why is data migration important in ERP?
Data migration is crucial for a successful ERP implementation because your old system’s data is the lifeblood of your business. Moving this data cleanly and accurately ensures continuity, avoids disrupting operations, and allows your new ERP to deliver accurate insights from day one. Poor migration risks data loss, inaccuracies, and ultimately, a failed ERP project. It’s the foundation upon which a new ERP system is built.
Which of the following is a benefit of automating migration?
Automating database migrations speeds up the process dramatically, minimizing downtime and human error. It ensures consistency and repeatability, making updates reliable across different environments. This allows developers to focus on building features, not wrestling with manual migration tasks. Ultimately, automation significantly reduces the risk and cost associated with database changes.